IP SLA (Cisco)
What is Cisco IP SLA?
Internet protocol service level agreement (IP SLA) is a network performance monitoring (NPM) feature of the Cisco Internetwork Operating System (Cisco IOS) that enables an IT professional to collect information about network performance in real time.
Cisco IOS IP SLA provides a way to monitor network performance and report on it with the help of statistics. IP SLA generates and monitors traffic continuously across the network, which is why it's considered an active method of network monitoring.
A Cisco IOS IP SLA router can continuously collect data about various aspects of the network, including:
- Response times.
- Latency.
- Jitter.
- Packet loss.
- Voice scoring quality
- Connectivity
All of this information provides the network administrator with baseline information about network performance. It also enables them to verify the network's quality of service (QoS) levels and quickly identify the root of a problem if performance levels drop.
How Cisco IP SLA works
For the IP SLA feature to work, certain components must first be determined and configured:
- Select the type of IP SLA operation to be configured: Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) jitter, HTTP GET request, Domain Name System (DNS) server request, voice over IP, etc.
- Specify the IP SLA operation number, which is between 1 and 2147483647.
- Configure the IP SLA schedule so the IP SLA router knows when to run and stop the IP SLA operation.
A Cisco IP SLA router can monitor a network and provide useful network statistics even if there is no router or device at the other end. However, adding a router or device -- which is known as an SLA Responder -- can facilitate more detailed information reporting about the network. The SLA Responder can be another Cisco device -- such as a router -- or a non-Cisco device such as a computer or a remote network application server.
Configuring an SLA Responder enables IP SLA to perform more complex operations, such as sending Real-Time Transport Protocol packets, setting up Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connections or checking File Transfer Protocol (FTP) servers. If a certain IP SLA operation could benefit from an SLA Responder, configure it before the SLA operation begins.
An admin must configure the ICMP jitter operation to send an ICMP timestamp request. This Type 13 request goes to the configured destination host and retrieves an ICMP timestamp reply response from the destination.
The IP SLA Responder receives a packet and inserts timestamps of both its reception and transmission. These two timestamps enable the IP SLA packet to measure the packet round-trip time (RTT) from the source to the destination, as well as how long it takes the destination to process the packet. If the IP SLA's probe response time is longer than expected, it could be a sign that the receiving device has too high a load. Network engineers can investigate the issue to find the root cause and improve network performance.
Using IP SLA in conjunction with other features
Cisco IP SLA can be used in conjunction with other monitoring features, including Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP ) and NetFlow, to determine the root cause of network issues. Using an SNMP agent to poll the IP SLA router helps to retrieve IP SLA reports and make them more readable and understandable for human users. Agents also make it easier to record, graph and view historical data about IP SLA results. Popular SNMP agents include Cacti, SolarWinds and PRTG.
When organizations integrate IP SLA with a network management system (NMS), they can capture visual alerts of threshold violations in real-time. IP SLA can also be integrated with static routes, predetermined pathways that data packets must travel to reach a destination network or host. IP SLA can also be combined with routing protocols like Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) or Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP).
What are the benefits of IP SLA?
IP SLA on Cisco IOS devices provides a useful way to monitor and ensure network performance. The feature also enables network engineers and administrators to investigate network issues and discover their root causes with the help of tangible statistics.
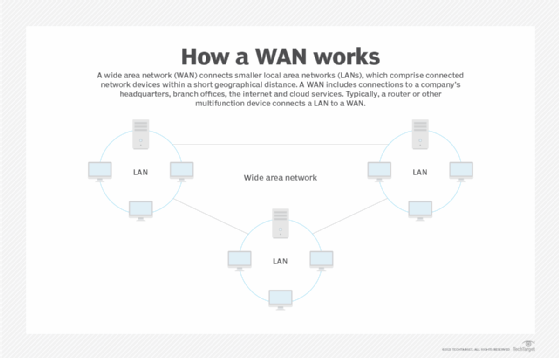
Engineers can use IP SLA to monitor traffic paths to a destination to confirm that a particular web server is accepting connections. Wide area networks (WANs) that connect multiple geographies and require monitoring from one central location can benefit from IP SLA.
IP SLA is also useful for policy-based routing, a technique for forwarding data packets based on certain policies or filters. The policies can be applied based on specific parameters such as packet size, source address, destination address or traffic type to improve the network's traffic-handling capabilities and its overall agility.
What is IP SLA used for?
The IP SLA feature enables Cisco routers to simulate specific types of traffic, such as User Datagram Protocol (UDP) jitter, HTTP, TCP connect, ICMP echo, DNS, FTP and DHCP, and report statistics such as path jitter. This helps network engineers to analyze network performance and identify performance issues.
IP SLA can also measure application performance. Network engineers can use one of many available application configuration options such as TCP/UDP port numbers and TOS byte.
Other useful applications of Cisco IP SLA include:
- Track reachability and decrement Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)/ Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)priority values.
- Measurement of network availability and reliability.
- Generation of SNMP traps from various events, such as one-way packet loss, connection loss and timeout.
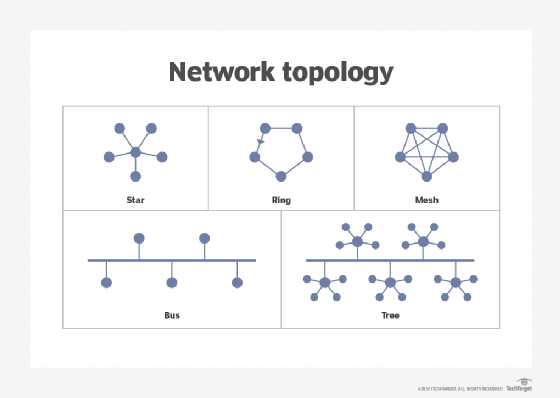
- Design and optimization of network topologies.
Check out seven top open source network monitoring tools and read about 12 common network protocols and their functions. Learn about four network resiliency factors and what steps organizations can take to build redundancy into their networks. Computer networks come in all shapes and sizes. Explore the seven common types of networks, along with their pros and cons.
