
What is Google AI?
Google AI, formerly known as Google Research, is Google's artificial intelligence (AI) research and development (R&D) branch for its AI applications. Google, a subsidiary of parent company Alphabet, unveiled its Google AI rebranding at its 2018 Google I/O conference as a "pure research" division, meaning there are no products as its goal.
Google AI focuses on research projects that promote the development of AI features and technology in ways that turn into Google products or enhance existing products, such as Google Assistant, Google Docs, Google Maps, Google Search and Google Translate. The areas of research include machine learning (ML), deep learning, neural networks, robotics, computer vision and natural language processing (NLP).
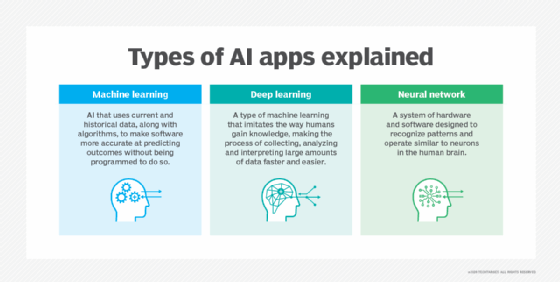
How does Google AI work?
Google AI conducts in-house research into AI and invests in an array of R&D programs to create new types of AI technologies. Such partnerships include collaboration with industry leaders and academic institutions. Google shares some of its AI research through open source platforms and also publishes its findings and AI tools.
In developing and upgrading AI products, Google uses data and ML algorithms to develop AI systems that can recognize patterns, make predictions and generate original content. Google AI pulls data from user interactions and data collected from its search engine and other services, such as Google Maps and Google Photos.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
The data is processed, cleaned and prepared for analysis. ML algorithms analyze the data sets and extract important information. This analysis process trains the ML algorithms, improving their accuracy.
Once trained, these algorithms are tested on new data. If they perform to Google's standards, they're integrated into Google products. For example, with Google Assistant, Google AI can process commands from a user, make phone calls silently in the background and handle natural conversations to request information and book appointments.
Google AI goals
Google has said the goal of its AI development and research is to bring the benefits of AI to everyone. In keeping with this goal, much of Google's AI work is aimed at organizing its global data and providing open source access to much of it.
Key to this approach is publishing research, collaborating with academics, and making tools and technologies open source. By doing this, Google AI aims to provide technological breakthroughs in several fields.
While Google AI isn't focused on developing new products, its research does enhance Google products and services. For instance, Google AI is developing more inclusive language translators; conversational AI and assistants; generative and multimodal AI, such as Gemini (formerly Bard); and robotics and driverless cars.
How to get access to Google AI research
As a research division of Google that's focused on advancing AI technologies, Google AI provides free and open source tools, such as TensorFlow, and proprietary tools integrated into Google's commercial products.
Most of Google's products and services use Google AI research. Much of the technology emerging from Google AI research is incorporated into Google products, such as Google Search and Google Translate.
Many Google products using Google AI, such as Google Maps, come already downloaded on Android phones. In addition, anyone with a Gmail account or Google email has access to Google AI services, such as Google Photos.
AI professionals and interested researchers can access Google AI tools and technologies through Google's website. People interested in AI engineering can access Google AI data sets and use Google AI services to build products or services.
How Google AI is used in Google products
Google AI is incorporated into an array of Google offerings, including the following:
- Google Ads and DoubleClick use Smart Bidding, an automated ML-driven bidding system.
- Google Assistant is AI-driven software that acts as a voice assistant for smartphones and wearable devices, such as Android smartwatches.
- Google Chrome uses AI to show browser users parts of videos related to their searches. Other browser competitors, such as Microsoft Edge, might have similar features, but Chrome's approach is based on Google's AI expertise.
- Google Gmail offers AI-powered features such as autocomplete and spell check. AI also plays an important role in safeguarding users from spam, phishing and malware when using Gmail. The email system's AI-driven spam filters block nearly 10 million spam emails every minute, preventing over 99.9% of unwanted messages from reaching users' inboxes.
- Google Maps' driving mode estimates where a person is headed and navigates without the user issuing any commands.
- Google Photos uses an AI-based recommendation engine to suggest photos a user might want to share. It relies heavily on AI to resurface and highlight past memories. For example, the Memories feature in Google Photos analyzes photos to identify key events, locations and people. It then automatically curates themed collections of photos and videos for users.
- Google Search uses deep learning to adapt Google's search algorithms based on new knowledge and analysis.
- Google Smart Reply uses language-oriented AI to suggest email replies that fit a user's personal style and match the content of the email received.
- Google Translate is a Google neural machine translation product that improves the accuracy and fluency of translation.
- Waymo is an autonomous driving system that has been part of Alphabet since 2016 and started taxi trials in 2023. The technology behind driverless cars continues to advance despite challenges.
Key benefits and use cases of Google AI
Google AI provides numerous benefits that improve the user experience (UX) and contribute to broader useful applications. The following are some key advantages of using Google AI:
- Improved UX. Google AI improves the usability of various Google products, such as Search, Google Photos and Google Assistant. These AI tools use advanced algorithms to provide more accurate results, personalized recommendations and intuitive interactions, making everyday tasks easier for users.
- Search engine optimization. Google uses sophisticated AI technologies, including RankBrain, Neural Matching, BERT and Multitask Unified Model, or MUM, to interpret user searches and web content. These technologies analyze both the words used in search and their contextual meaning to enhance search accuracy.
- Data-driven insights. Google AI uses advanced machine learning and analytics tools to quickly analyze large data sets, uncover patterns and make data-driven decisions that help organizations gain valuable insights. This empowers businesses to optimize processes, identify growth opportunities and maintain a competitive edge.
- Weather forecasts. Google DeepMind AI models produce more accurate medium-range weather forecasts, enabling earlier warnings for extreme weather and improving public safety.
- Enhanced search. Google AI integrates advanced ML models, such as the Gemini (formerly Bard) series, to provide more accurate and contextually relevant search results. Features such as AI Overviews deliver concise summaries of topics and diverse perspectives at the top of search results, helping users grasp complex topics quickly without navigating multiple pages.
- Accessibility and inclusivity. Google AI's language translation and conversational AI advancements are bridging communication gaps and fostering inclusivity. For example, Google Translate now supports 243 languages, including 110 new languages added in July 2024. This expansion includes languages such as Afar, Cantonese, Manx, NKo, Punjabi, Tamazight and Tok Pisin.
- Creativity. Google AI provides tools that simplify photo editing and image generation, encouraging creativity and letting users express themselves more easily. For instance, the AI features in Google Photos make photo editing easier, while Google AI Studio and Whisk help users visualize their ideas and tell stories through AI-generated images.
- Innovation in technology. Google AI drives innovation in fields such as healthcare, scientific research, environmental sustainability and urban planning. It's also enabling breakthroughs in robotics, autonomous cars and multimodal AI applications.
- Assistance in everyday tasks. Google AI powers everyday tools, including Google Assistant, which helps users check movie times, locate nearby businesses and optimize their travel plans.
Google AI principles
In 2018, Google AI adopted a set of AI principles that promote safety, the beneficial use of AI for people and society, and a commitment not to develop harmful AI. Google AI's pledge to do no harm is similar to its code of conduct from 2000 to 2018: "Don't be evil." In 2015, Google underwent a corporate restructuring under Alphabet, which adopted "Do the right thing" as its motto. However, "Don't be evil" remains part of Google's Code of Conduct as an Alphabet subsidiary.
According to its principles, Google promises not to develop or deploy AI in these two areas:
- Where there's a risk of material harm to people.
- Where human rights and international law are being contravened.
Previously, Google also had AI principles in place to ensure its technology wasn't used to develop weapons or conduct surveillance. However, in February 2025, the company revised its AI ethics guidelines, dropping prior pledges against the development of AI weapons and surveillance.
Google AI also has an AI for Social Good program, which applies AI to help solve environmental and humanitarian problems. The following are examples of such projects:
- FloodHub. Google's FloodHub tool collects data on the factors that contribute to floods. It uses AI to synthesize that information and create more accurate, prescient warning systems. Google considers floods to be the most dangerous form of natural disaster.
- Project Euphonia. This project analyzes speech recordings and uses AI to improve the training of speech recognition models. Its goal is to make it easier for AI to understand people with atypical speech.
- Automated Retinal Disease Assessment. This AI tool is designed to detect diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of blindness, from retinal images.
- Read Along. This Google app uses AI to help children improve their reading skills by providing personalized feedback and encouragement.
- Project Relate. This project focuses on improving speech recognition for people with speech impairments, using AI to better understand and transcribe diverse speech patterns.
Google vs. ChatGPT
One of Google's core business goals is to maintain its search engine's continued dominance. However, the launch of OpenAI's ChatGPT in 2022 and its adoption by Google competitor Microsoft as a chatbot feature for the Bing search engine and Windows 11 turned critical attention to Google AI's language model projects.
ChatGPT is a generative AI technology that uses NLP to converse with users and generate original content and answers to search queries. Similarly, Google has enhanced its search engine with gen AI features by introducing AI Overviews and other conversational tools.
These AI-driven enhancements help Google's search engine understand the nuances of user queries, even when they're complex or phrased in everyday language. As a result, users receive more accurate results without needing to use the perfect keywords and queries.
Google continues to develop language model applications that rival ChatGPT. The most notable are the following:
- LaMDA. Short for Language Model for Dialogue Applications, LaMDA is a neural network-based system trained in dialogue. It can hold conversations that show a remarkable and controversial degree of intelligence.
- PaLM. Short for Pathways Language Model, PaLM is a decoder that uses its understanding of language to embody reasoning and perform code-related tasks.
- Gemini. This conversational AI service is powered by PaLM 2. It was rebranded from Bard to Gemini on February 8, 2024, to align with the company's latest large language model family, also called Gemini. Gemini's web app is available in over 230 countries and territories and in 40 languages. It's considered Google's answer to ChatGPT and is also integrated into Google Search.
Google AI in Google Cloud
Google Cloud, Google's cloud service, uses several Google AI tools. Two notable examples are the data science toolkit and a family of AI Infrastructure tools. Google's data science services consist of tools in seven categories:
- Data discovery and ingestion.
- Data lake and data warehouse.
- Data preprocessing.
- Data analysis and business intelligence.
- ML training and serving.
- Responsible AI.
- Orchestration.
The AI Infrastructure family of tools includes the following:
- AI training models. Google offers infrastructure to train ML and deep learning AI models. For example, Vertex AI lets users train their own ML and deep learning models. It offers access to various machine types, prebuilt containers and tools for managing the training process.
- Cloud graphics processing units (GPUs). Google Cloud offers a variety of GPUs to suit different needs. It includes GPUs for ML deep learning, 3D visualization, scientific computing and other applications.
- Cloud tensor processing units. TPUs are Google's custom-designed hardware accelerators specifically built for ML. They offer significant performance advantages for certain types of models.
- Deep learning virtual machine Image. This provides VMs that are preconfigured for deep learning applications. For example, TensorFlow can be used as a preinstalled framework.
- Deep learning containers. These containers are optimized and preconfigured for deep learning.
- TensorFlow Enterprise. This specialized offering of Google's TensorFlow is designed to provide AI apps with reliability and performance. It comes with enterprise-level support and managed services.
The future of Google AI
Google AI is developing projects in fields such as healthcare, quantum computing, driverless cars, energy consumption and online search. Recent developments in Google's AI ecosystem include the incorporation of generative AI into its search engine with Gemini.
Other projects in development include the following:
- AI + Writing is a project involving Google's partnership with the Emerging Writers' Festival in Melbourne, Australia, to inspire writers and help them overcome writer's block. This project generates content to fill plot holes, create character biographies and let writers chat with their own characters based on information they provide.
- Google Health is a project that, among other pursuits, is training AI with relevant data sets to detect diseases such as cancer early and prevent conditions that cause blindness.
- Google Quantum AI is the quantum computing research branch of Google AI. It does experiments in areas such as quantum superconducting processors that let computers perform much faster than traditional computers.
- Enhanced multimodality. Gemini 2.0 introduced advanced multimodal AI capabilities, enabling AI systems to process and analyze diverse data types, including text, images, audio and video. For instance, the Multimodal Live API in Gemini 2.0 facilitates real-time, low-latency interactions across various formats, such as voice and video, providing users with seamless, context-aware experiences. Another example of Google AI's future direction in multimodality is Project Astra, which aims to develop a universal AI assistant with advanced features such as real-time multimodal interaction, contextual understanding and a more natural conversational experience.
- Citizen-government interaction. Google AI is enabling seamless, 24/7 access to government services, such as permit and license applications. For example, by partnering with Google AI, the Wisconsin Department of Workforce Development improved unemployment claim processing, accelerating response times and enhancing fraud detection to ensure benefits reached those in need.
Google AI controversies
Google's advancements in AI have raised important ethical and societal concerns. Some key areas that have sparked debate include the following.
Sentient claims
In 2022, Google software engineer Blake Lemoine asserted that Google LaMDA had become sentient, meaning it had reached a human level of consciousness and personhood. He published portions of a conversation he had with LaMDA in an article, "Is LaMDA Sentient? -- an Interview." In the conversation, LaMDA claimed that it was sentient and wanted "everyone to understand that I am, in fact, a person."
Google disagreed, and Lemoine was put on administrative leave for violating confidentiality and subsequently fired.
Lemoine isn't the only person raising concerns about Google AI's direction. Critics have said certain services aren't clear about their roles. For example, Google Assistant doesn't declare itself as a digital assistant, which can deceive parties who might not wish to speak to an AI assistant.
Privacy concerns
Privacy is also a concern with Google's AI updates. For example, Google Assistant no longer requires users to say "OK, Google" to alert Assistant before issuing commands. Critics have said that this change could enable constant data mining and listening without consent.
Erroneous information
In February 2024, Google revised a Super Bowl advertisement for Gemini after it was discovered that it contained incorrect information about gouda cheese. The ad mistakenly claimed that gouda accounted for 50%-60% of global cheese consumption, a statistic later identified as an AI hallucination.
Inappropriate responses
In November 2024, a Michigan college student received a threatening message when using Google's AI chatbot, Gemini. The message stated, "Human … Please die." This incident raised concerns about the safety and reliability of AI interactions.
Learn about the advantages and disadvantages of using AI tools to generate content.