Gartner
What is Gartner?
Gartner is an IT research firm and consultancy, formerly known as Gartner Group. Gartner was founded in 1979 by Gideon Gartner and is headquartered in Stamford, Conn.
The company has additional offices in North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific and other regions of the world and is publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the stock symbol IT.
What does Gartner do?
Gartner uses data visualization and analysis tools to help IT professionals around the world make decisions regarding technology investments for their organizations.
Gartner provides insights and solutions across many areas of IT, offering clients actionable advice on developing strategies, selecting technologies and implementing them in their businesses.
Their mission is to help customers use technology to improve their performance and create value for their stakeholders. Gartner's global network of research analysts provides analysis to support those decisions.
Gartner's clients range from large enterprises and government agencies to educational institutions. Gartner works with these organizations as a trusted advisor, helping them understand the latest trends in technology; developing technology strategies, plans and budgets; and identifying, selecting and deploying the right technologies in their organizations.
What services does Gartner provide?
Gartner offers a variety of services ranging from Gartner Summits -- global events featuring innovative discussions on industry trends, technology challenges and emerging solutions -- to Gartner Peer Insights, an online platform providing verified customer reviews of products and services.
Gartner also has research reports, premium advisory services, professional services, Gartner Consulting and Gartner Ventures, which invests in early-stage startups with disruptive technologies. These provide clients with a variety of options to help them make informed decisions in their IT investments.
One research tool is Gartner Magic Quadrants -- a research method and visualization tool for monitoring and evaluating the progress and positions of companies in a specific, technology-based market.
Magic Quadrants use a two-dimensional matrix to illustrate the strengths and differences between companies. Research reports help investors find companies that fit their needs and help businesses compare competitors in their market.
Gartner also offers Gartner Executive Programs, which help C-level executives analyze technology trends, develop strategies and innovate faster with Gartner's proprietary intelligence, insights and research. Gartner Executive Programs provide an exclusive community of peers to help executives stay ahead in their fields.
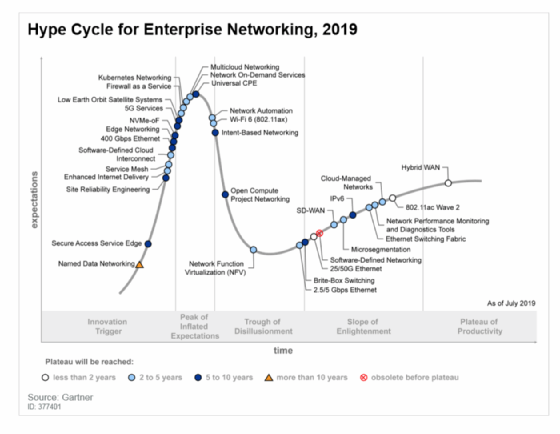
For example, Hype Cycle is a graphical representation of the lifecycle stages a technology goes through from conception to maturity and widespread adoption. Hype Cycle stages are often used as reference points in marketing and technology reporting; businesses can use Hype Cycle to guide technology decisions in line with their level of comfort with risk.
Gartner use cases
The following are three examples of potential Gartner use cases, which show how Gartner could work with clients to develop strategies, select technologies and implement them in their businesses:
- A media company might use Gartner to improve its customer experience by employing business analytics to create a unified data repository and machine learning to optimize performance across multiple channels.
- An insurance company might work with Gartner to develop a technology roadmap, or a business plan, for digital transformation.
- A logistics company might use Gartner to identify an optimal technology stack for its operations. Gartner would work with the company to develop a comprehensive strategy that includes selecting the right tools, defining key performance indicators and developing processes to ensure successful implementation.
In summary, Gartner is a provider of research and consulting services for businesses in the IT sector, working with organizations to develop technology strategies, plans and budgets, as well as select the right technologies for their operations.
With this, companies can identify opportunities to innovate and optimize performance, as well as develop technology roadmaps for digital transformation.