What is electronic data processing (EDP)?
Electronic data processing (EDP) refers to the gathering of data using electronic devices, such as computers, servers and internet of things (IoT) technologies. It's another term for automatic information processing. It also involves analyzing data and summarizing and recording the output in a human-usable form.
The concept of EDP has evolved from data processing. The term emerged in an era when most computing input was physically provided to a computing device, usually in the form of punch cards. With those applications, the output was presented either on punch cards or as a paper report.
Why is electronic data processing important?
The volume of data generated daily is growing at an unprecedented pace. Some estimates suggest the size of the global datasphere will be several hundred zettabytes within the next few years. One zettabyte equals 1 trillion gigabytes. Increasing digitization and the emergence of new technologies, such as IoT and artificial intelligence (AI), are contributing to this data explosion.
Data is considered the "new oil" since it creates opportunities for learning, improvement and advancement. However, companies need a way to efficiently gather and glean insights from their massive data stacks. Manual data processing methods aren't able to handle large volumes of data, but EDP can.
EDP provides rapid and accurate data processing and data analytics capabilities. It also provides clear presentation of results. Using technology and automation, EDP systems help business users capture and interpret information and insights about their industry, market, customers and competitors.
Electronic data processing advantages
EDP systems offer organizations multiple advantages when dealing with large data sets, including the following:
- Rapid processing. The main advantage of EDP systems is that they enable the rapid processing and analysis of large volumes of data.
- Reduced management costs. EDP tools eliminate the need for physical storage locations, as well as the printing and courier services paper documents need. As a result, EDP reduces the costs of managing and storing physical documents.
- Simpler processing tasks. EDP tools support user-friendly document search and streamline business workflows. Users can collaborate on projects and track the status of data. They gain useful insights for their specific requirements in a format that makes the most sense to them. EDP tools also reduce the need for manual effort and minimize the presence of redundant or bad data, which enables better enterprise decision-making.
- Data availability. EDP systems can store vast quantities of data and make it readily available for further analysis and presentation.
Electronic data processing challenges
Despite these advantages, there are also a few disadvantages for businesses to be aware of:
- Malfunctions and reliability issues. EDP equipment encompasses hardware and software components that are susceptible to downtime or malfunctions, especially in the event of power outages and natural disasters. There's even a segment of the insurance industry that offers EDP coverage for these types of issues.
- Data security breaches. EDP systems manage vast quantities of data, making them susceptible to various types of cyberattacks and data breaches. Data containing confidential or sensitive information must be safeguarded with appropriate security measures, which requires increased efforts and resources.
- Data privacy issues. Both external and internal misuse of private data could occur if EDP systems aren't protected and employees aren't trained properly.
Elements of electronic data processing
EDP systems are composed of four key elements.
1. Hardware
Hardware refers to all physical parts of the EDP system, including devices and peripherals. Some common digital devices used in EDP are the following:
- End-user computing devices and computer systems, such as laptop computers, desktop PCs and smartphones, that can capture data and enable data entry.
- A central server that supports data processing and analysis.
- Audio and video devices that are used when data is to be captured in multimedia format.
- Scanners that convert paper-based data into digital format.
- Barcode readers and point-of-sale systems that capture product pricing data for billing.
- Medical devices and sensors that collect patient data for diagnosis and treatment.
2. Software
EDP software makes the hardware work and ensures the expected output is produced. Different types of EDP applications are available for various business needs, including data entry, accounting, bookkeeping, analytics, scheduling, time management and inventory management.
3. Procedures
In addition to hardware and software, EDP involves procedures or steps for data collection, aggregation, conversion, sorting, analysis and reporting.
4. Personnel
The final element of EDP is personnel. Although EDP tools are designed to replace manual labor with automation to minimize human intervention, people are still required. They use the systems and generated insights for business decision-making.
Steps or procedures in electronic data processing
The EDP process includes multiple steps or procedures:
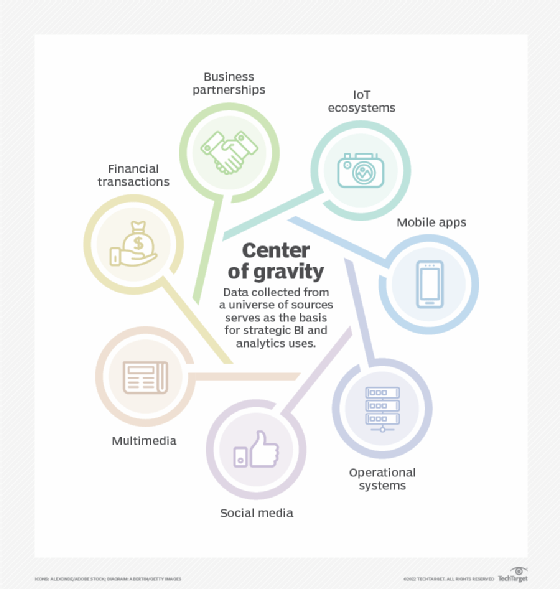
- Data collection. Data is collected from multiple sources, which must be trustworthy and yield high-quality data to maximize the system's usefulness and value. Advanced EDP tools can pull massive amounts of data from large data lakes and data warehouses.
- Data preparation and conversion. Raw data must be cleaned up and organized. An EDP system checks and removes human errors in the data and redundant or incorrect data that affects the output quality. If the data isn't in an acceptable format for processing, the system converts it into the right format before sending it on to the next stage.
- Data input. The clean, organized and properly formatted data is fed into a destination application, such as a customer relationship management or enterprise resource planning platform, in terms the application can understand. The data is then ready for processing and transformation into usable information.
- Data processing. AI and machine learning capabilities have become useful for enterprise data management in general, but advanced EDP systems also include these capabilities to process and interpret data. Data processing methodologies vary depending on the types of data, sources and intended uses.
- Data output. The processed data is translated and converted into a human-readable form, such as graphs, text and images. The conversion lets users draw conclusions from the data without requiring any specialized technical expertise.
- Data storage. Data storage is the final step in EDP. The processed and converted data is stored on media for future use. In many industries, compliance regulations mandate the proper storage and, in some cases, encryption of data.
EDP methods
EDP is a broad term that encompasses many different methods, depending on how the data is processed and presented. The following are some of the most common EDP methods:
- Time sharing. In this method, many nodes or user terminals are connected to a central computer. In theory, each user can access the central processing unit (CPU), along with all other users, at the same time. In practice, they're allocated a "time slice" of the CPU in a round-robin sequence. The EDP system's multiuser operating system controls how much time each user gets.
- Real-time processing. This method provides accurate and up-to-date information since the data is processed as soon as it's available. The computer processes all incoming data in real time and generates instantaneous or near-instantaneous output.
- Multiprocessing. EDP multiprocessing involves the undertaking of multiple tasks at the same time using different processors on the same computer. Since there can be more than one independent CPU, processing is fast.
- Multitasking. Multitasking, also known as multiprogramming, involves different processors working at the same time. Various tasks share the same processing resource to enable parallel processing to produce results in less time.
- Batch processing. Data is collected over a specified time period, and then all of it is processed at the same time.
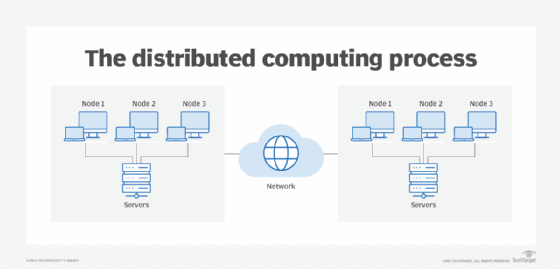
- Distributed processing. This method involves distributing processing tasks to multiple computing devices that are physically distinct but linked electronically for data transmission and exchange. ATMs are an example of distributed processing EDP.
Electronic data processing applications
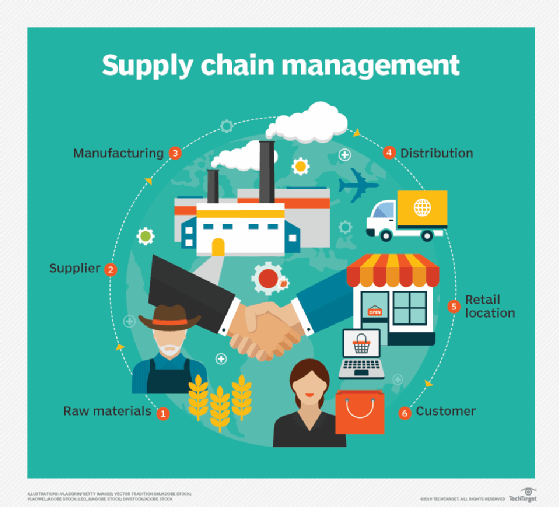
Two of the most common EDP applications are inventory stock monitoring and supply chain logistics systems. Modern-day retail and e-commerce supply chains are extremely long and complex because of the number of elements involved and the quantities of data generated.
With these systems, data must be efficiently captured to ensure orders are fulfilled on time and the sales pipeline keeps moving. EDP systems enable the seamless flow of data to streamline supply chain operations and smooth the interactions among the various moving parts of the chain.
Other industries and sectors where EDP has many applications include telecommunications, electronics, education, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, clinical research, hospitality, tourism, financial services, law enforcement and natural sciences, such as paleontology and geology.
The evolution of data processing
Companies used manual data processing throughout much of the 20th century. People entered data into books and paper-based spreadsheets and managed calculations with adding machines and other rudimentary devices. Such manual data processing was error-prone and time-consuming.
The advent of mainframe computers in the latter half of the 20th century brought some degree of automation, where programmers could provide instructions for computers to process and store data. Data was delivered to these machines via physical punch cards and were processed using batch processing. Early EDP applications were for payroll and billing processes. However, this meant buying and maintaining expensive data processing equipment, which was mainly accessible to large businesses, not small and midsize ones.
As new technologies, such as spreadsheet software and structured databases, were developed and became cheaper and accessible in the 1980s and 1990s, EDP use became more widespread and practical. This simplified the steps involved in EDP, whether it be data entry, calculation, conversion or storage, yet human oversight is still needed.
The advent of AI and machine learning have brought about fully automated data processing, but this technology has yet to be made fully available to businesses of all sizes.
Data processing is just one step in an overall data management strategy. Learn how companies can also create a data quality management process.