Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
What is Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)?
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) is a feature of Windows-based OSes -- included since Windows 98 and Windows ME -- that enables a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol client to automatically assign an IP address to itself when there's no DHCP server available to perform that function. APIPA serves as a DHCP server failover mechanism and makes it easier to configure and support small LANs.
DHCP is a network management protocol that organizations can use to dynamically assign IP addresses and other network parameters to devices or nodes on their networks. A DHCP-based service automatically manages client network configurations from a central server, eliminating the need to manually assign IP addresses to the managed devices. DHCP supports networks of all sizes, from those in small organizations to enterprise-scale networks.
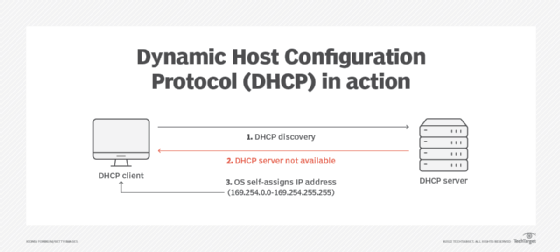
When a DHCP client computer connects to the network, it attempts to communicate with a DHCP server. If a server is available, it will assign an IP address and other network parameters to the DHCP client. In some cases, a DHCP server may not be available. For example, the server may be down temporarily or there's no DHCP server on the network.
If this occurs and APIPA is enabled, the client computer selects an IP address from a range of predefined addresses -- 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 -- and automatically assigns that address to itself. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) reserves these addresses specifically for APIPA use cases to ensure they don't conflict with DHCP routable addresses.
As part of the APIPA assignment process, the DHCP client uses the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to ensure the chosen address isn't being used by another network computer. Once the client has assigned itself an IP address, it can communicate over TCP/IP with other computers on the LAN that are either configured for APIPA or manually set to the correct address range and using a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
The APIPA service can be beneficial even if the DCHP client has received a previous IP address from the DHCP server. This is true even if the lease for that address has expired. The user is typically notified when a DHCP client switches between DHCP and APIPA addressing.
APIPA is enabled by default, but it can be disabled in some cases, depending on the OS and how the DHCP client is configured.
See also: 12 common network protocols and their functions explained
