kentoh - Fotolia
Unlock storage savings with Windows Server deduplication
Windows Server comes with a data deduplication feature to reduce the organization's storage crunch, but it's important to plan around some potential drawbacks.
Even though Microsoft introduced data deduplication in Windows Server 2008 R2, it's one of those hidden features that few administrators know.
Data deduplication finds identical blocks of data and keeps one copy as the central source to reduce the data footprint. Deduplication typically works on a file or block level, the latter offering a more efficient technology to save space. But block-level deduplication often requires specialized and expensive hardware because of the intense processing needed. The file or chunk level is not as efficient as block level, but does not require specialized hardware requirements, which is where Windows Server deduplication steps into the picture.
Microsoft introduced data deduplication with Windows Server 2008 R2 and refined it in succeeding versions. It can help cut down on storage needs on shared disk space -- potentially up to a 70% space savings -- which can help extend the life of the file server, but it's important to plan and follow a few simple guidelines.
Situations for using Windows Server deduplication
Because Windows Server deduplication works on the file level, it operates at a higher level than block level to find matching data chunks. While not as granular as block level, this form of deduplication can make a noticeable difference in the right role.
Because this is an operating system-level deduplication, administrators can use it on Hyper-V data stores to cut down on hard drive files. Administrators can enable deduplication inside virtual guests when using other hypervisors.
Why a file server is made for deduplication
A prime target for Windows Server deduplication is a file server. Even in this era of online storage and SharePoint, users continue to put massive amounts of data into these repositories. Some users will not let go of older technologies and outdated workflows, while others will make multiple copies of the same files just to be safe. File servers turn into data bricks that administrators have to back up and manage, which makes for a good opportunity to use Windows dedupe.
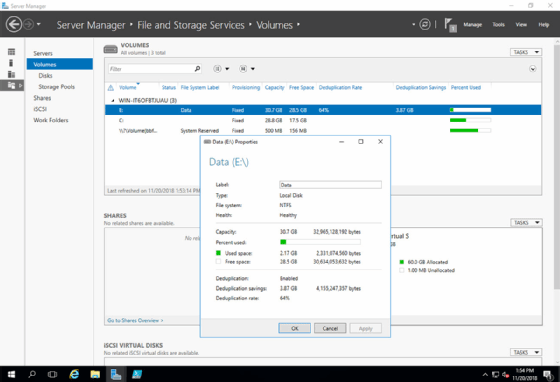
Windows data deduplication is simple to install and only takes a few minutes to execute. It's a role the administrator adds onto Windows Server, and, in most cases, it doesn't even require a reboot. While it's not complicated to deploy, there is some additional work needed to complete the process properly.
How to prepare for Windows Server deduplication
How to implement Windows Server 2019 data
deduplication
To start, run the data deduplication tool DDPEval.exe against the selected volume, which will analyze the potential space savings.
To enable data deduplication, right-click on the volume in Server Manager to launch the wizard that walks the administrator through proper type of deduplication for a file server, VDI or Hyper-V scenario. Each option is tuned for the specific role, so select the right one.
Set up a proper time for Windows Server deduplication
Deduplication does not run on dedicated hardware, and the optimization process does not occur on the fly, but rather during a scheduled time. Storage savings will decrease during the day and then increase the next morning after deduplication process runs.
Deduplication is not a lightweight process; it requires a lot of the CPU's resources. The dedupe process involves several jobs, including optimization, garbage collection and integrity scrubbing. Administrators should avoid running deduplication during peak hours -- or even during production hours -- unless they can allocate enough resources to avoid system slowdowns that could affect users.
Storage savings will vary, but Microsoft documents estimate deduplication will reduce the storage footprint by an average of 50% to 60% based on general files, ISOs, virtual disks and Office documents. Even if an organization doesn't reach those numbers, even a 40% space reduction can result in significant savings both on the infrastructure and on the bottom line for what is essentially a free deduplication service.






