A quick guide to Server Manager for Windows Server 2008
New to Windows Server 2008, the Server Manager feature can be a huge benefit to admins – once they figure out where to find everything. This article gives you a crash course on everything Server Manager has to offer.
If you've installed Windows Server 2008, than you've already been forcibly introduced to Microsoft's new feature called Server Manager. With a full screen. After every boot. While Server Manager does take a little getting used, it can be a valuable tool once you figure out where to find everything.
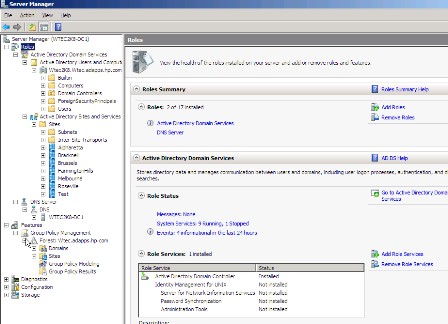
The following is a list of common administrative tasks and where to find them in Windows Server Manager. Figure 1 shows the primary features of Server Manager. Note that all of the applications and components formerly found under Add/Remove Programs in the Control Panel are now in Server Manager as either a role or feature. Also note that the standard snaps for the roles installed on this machine -- domain services and DNS -- are included in the Windows Server Manager Console.
Roles
| Task | In Windows Server 2008 |
| Active Directory Certificate Services Active Directory Domain Services (needed to promote a DC) Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (ADLDS) Active Directory Rights Management Services Application Server (provides features to enhance a server hosting applications) DHCP Server DNS Server Fax Server File Services Network Policy and Access Services Print Services Terminal Services UDDI Services Web Server (IIS) Windows Deployment Services Windows Server Update Services |
Install as a role in Windows Server Manager. |
Features
| Task | In Windows Server 2008 |
| Failover Clustering Group Policy Management Console Message Queuing Multipath I/O Network Load Balancing Remote Differential Compression |
Install as a feature in Windows Server Manager. |
| Remote Server Administration Tools Many tools here: AD Certificate Services tools AD LDS Tools AD Domain Services Tools DHCP Server Tools File Services Tools: File Service Resource manager Distributed File Services Tools Services for NFS Tools Print Services Tools Terminal Services Tools Web Server (IIS) Tools Windows Deployment Services Tools Hyper-V Tools |
Install Remote Server Administration Tools as a feature. Expand Remote Server Administration Tools and select the tools you want. Note that not all tools are listed here -- just the most common ones. |
| Feature Administration Tools BitLocker Drive Encryption Tools Failover Clustering Tools Network Load Balancing Tools SMTP Server Tools WINS Server Tools |
Install Feature Administration Tools (under Features) then check the individual tools you want installed. |
| Removable Storage Manager RPC over HTTP Proxy Simple TCP/IP Services SMTP Services Storage Manager for SANs Subsystem for Unix-Based Applications Telnet Client Telnet Server TFTP Client Windows PowerShell Windows Process Activation Service Windows Server Backup Features Windows System Resource Manager WINS Server Wireless LAN Service |
Install each of these as a feature under the Features node in the left-hand pane of Server Manager. |
Diagnostics
Under Diagnostics, there are three items: Event Viewer, Reliability and Performance (which used to be Performance Monitor) and Device Manager.
Event Viewer
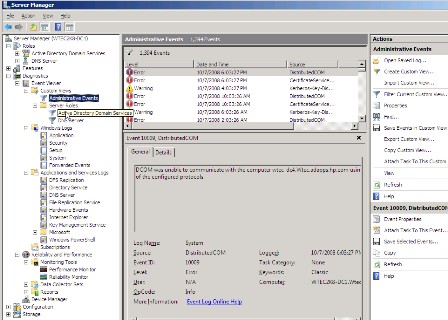
There are a lot of event logs now with Windows Server 2008, and you can even customize your own. Note in Figure 2 under Event Viewer that we see Custom Views, Windows Logs, Applications and Services Logs and Subscriptions.
Custom Views allow you to build your own event log. The figure above displays the Administrative Events log. This identifies several standard Windows logs from which we can cull important events, such as warnings and errors, but not informational events. Also under Custom Views is the Server Roles folder, where we have the Active Directory Domain Services (the old Directory Services log) and DNS server logs. You can also add more as you install more roles.
Note: Windows logs are basically the standard logs most administrators are familiar with from Windows 2000 Server and Windows Server 2003.
The Applications and Services logs contain a variety of logs by default as seen in Figure 2, such as Distributed File Service Replication (DFSR), Directory Service, File Replication Service (FRS), Internet Explorer, Windows PowerShell and others.
The Subscriptions node lets you set up event forwarding to collect events from a number of servers on this machine.
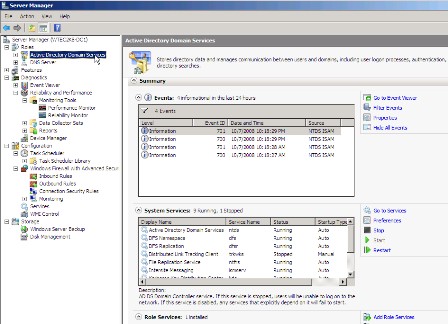
For Event Viewer, It is important to note that in addition to the options here (including the customizable event logs), each role -- as viewed in the Roles section of Windows Server Manager -- will contain its own specific event logs. Figure 3 shows the result of clicking in the Active Directory Domain Services role icon in the left-side pane. It displays the Directory Services-related events from the last 24 hours and all related system services. Further down the screen (though not visible in the figure) is a section of links to Active Directory-related tools. Note in the right-hand pane that you can "Go to Event Viewer", and take advantage of other options such as filtering and hiding events and changing properties.
Reliability and performance
This section contains Windows Server 2008's new iteration of Performance Monitor, as well as the new Reliability Monitor. You can customize your own data collector sets, which works as sort of a library of counters you can use to collect PerfMon data, as well as custom reports that can be created. This is a very interesting and powerful feature in Windows Server 2008. Check out this article for more information on the Reliability and Performance Monitor.
Configuration
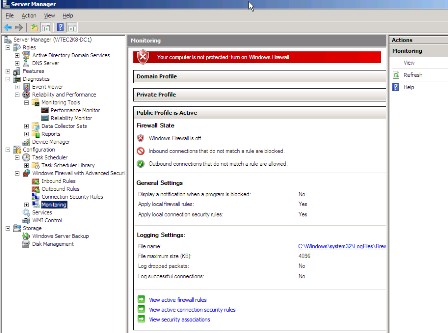
Under the Configuration icon are the Task Scheduler, Windows Firewall, Services and Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) control options, as shown in Figure 4. There are some nifty features in the Task Scheduler, including the ability to create a library for and monitor tasks. The Windows Firewall, if you use it, is easily configurable here along with the common Services listing, which looks like the old Services snap-in.
Storage
This section contains Windows Server Backup and the Disk Management utility. There is no NT Server backup anymore with Windows Server 2008. It was replaced by Windows Server Backup, which must be installed as a feature, as it's not installed by default. Windows Server Backup uses the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to take volume snapshots and stores them in virtual disk files.
Well, that's the whirlwind tour of Server Manager for Windows 2008. It really has some great features, and Microsoft has done a good job of collecting them in one tool. You are no longer forced to deal with a million different snap-ins in order to manage various parts of your environment. Just remember that if you need a tool, component or standard Windows application installed, do it through Server Manager's Roles and Features wizards.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Gary Olsen is a systems software engineer for Hewlett-Packard in Global Solutions Engineering. He authored Windows 2000: Active Directory Design and Deployment and co-authored Windows Server 2003 on HP ProLiant Servers. Gary is a Microsoft MVP for Directory Services and formerly for Windows File Systems.