computer system
What is a computer system?
A computer system consists of hardware components that have been carefully chosen so that they work well together and software components or programs that run in the computer.
The main software component is itself an operating system (OS) that manages and provides services to other programs that can be run in the computer.
In its most basic form, a computer system is a programmable electronic device that can accept input; store data; and retrieve, process and output information.
Evolution of computer systems
Computers are programmable electronic devices that can process data. To comprehend what a computer system is, it's important to analyze the history and evolution of computer system development over the years.
Early models
The history of computer systems goes way back to Charles Babbage's differential machines. Despite never being completed, this machine is considered the first example of a computing system. It came before the early 20th-century mainframes and large computers. The Von Neumann machine and others of its kind were later used as the first massive, monolithic computers in the human world.
The personal computer
The microprocessor revolution of the 1970s and 1980s saw the introduction of personal computers, also known as desktop computers. The first true home computer that came with a monitor display was released to the public in 1977. At the time, many large organizations used expensive and massive computers. The personal computer employed a computer box as its main piece of hardware, together with peripheral devices such as a mouse and keyboard and computer software that was downloaded into floppy disks.
Operating system
The operating system was initially created to support a complete computer system in a box and to provide users with a common interface for using the software that operated on that hardware. Additionally, the actual software components to execute on a specific operating system, such as files, apps and executables, were also introduced. The first IBM PC, officially known as the IBM Model 5150, ran Microsoft's MS-DOS operating system and had an Intel 8088 processor running at 4.77 MHz.
Laptops
The laptops emerged as hardware became smaller and more portable over time. The Portal, the first authorized portable microcomputer, debuted in 1980. It was built using an 8-bit, 2 MHz Intel 8085 processor and was equipped with a 64K byte random access memory (RAM).
The Cloud
The introduction of the modern cloud in the early 2000s revolutionized software distribution and data storage. The out-of-the-box software strategy was rendered obsolete in the enterprise IT sector as software was provided digitally through the internet in place of physical media, such as floppy disks and compact disks.
Virtualization
The concept of hardware and software configurations has recently undergone a radical change thanks to virtualization. Instead of using physical hardware, the majority of current computing systems use virtualized computer systems. Through the use of virtualization, a single computer's hardware resources can be split up into several virtual machines.
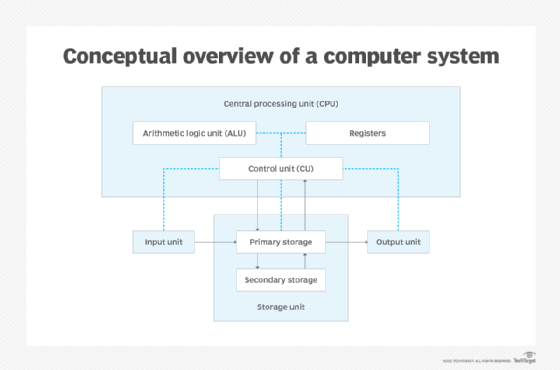
Components of a computer system
The components of a computer system are typically divided into hardware and software parts, which are both essential in making a computer system functional.
Hardware components
The hardware components include the computer itself; the physical parts inside the computer, such as a circuit board and storage devices; and any peripherals attached to the computer. These components can be either classified as input devices, such as a mouse or keyboard, or output devices, such as a monitor or a printer. While output devices reflect or display user data, input devices are designed to accept user data.
The following are common hardware components of a computer system:
- Keyboard.
- Monitor.
- Mouse.
- Printer.
- Computer case.
- Graphics card.
- Motherboard.
- Power supply unit.
- Central processing unit (CPU).
- RAM.
- Hard disk drive.
- Solid state drive.
- DVD-ROM.
Software components
Software components are the set of instructions that are stored and run on the computer hardware. The software controls how a computer system works. It can be grouped into the following two categories:
- System software. Programs that are needed for the computer to function, including the OS, utilities software, programming language translators and library routines.
- Application Software. Programs that let a user perform particular tasks, including word processing, database management, spreadsheet calculations, web browsing, gaming, programming and graphic design. Additionally, it may also include specific programs such as accounts, payroll and air traffic control.
Types of computer systems
Depending on the applications and performance requirements, numerous computer system types are utilized in various fields. Computers are typically divided into two groups based on their size and their capacity for handling data.
The following are computer system types based on their size:
- Microcomputers. These are commonly used for personal computing purposes. They carry a single processor for their CPU and a microprocessor that controls it. Examples of microcomputers include laptops, tablets, mobile phones and personal digital assistants.
- Minicomputers. These computers were created in the middle of the 1960s and the early minicomputers replaced vacuum tubes with transistors. They have a larger storage capacity and faster computing power than microcomputers and are capable of supporting hundreds of users simultaneously. Devices such as the Apple iPad, iPod and Samsung Tab are examples of minicomputers.
- Medium-sized computers. Compared to both microcomputers and minicomputers, these computer systems offer faster speeds and a larger storage space. These computers have numerous disk drives that can be utilized to process online access requests as well as a sizable number of high-speed input-output devices. Common example of a medium-sized computer includes IBM's Power Systems.
- Mainframe computers. Large, multi-user mainframe computers can access billions of pieces of data and are capable of processing millions of instructions each second. With little operator input, mainframes can support multiple computer programs and hundreds of thousands of users at the same time. The banking and telecom sectors are a good candidate for mainframe computers as they process data in large quantities.
- Supercomputers. These computers are enormous in size and extremely powerful. They're specifically designed to handle huge amounts of data. They're capable of executing hundreds of millions of instructions every second. Supercomputers are typically used for calculation-intensive tasks such as molecular modeling, climate research, weather forecasting, quantum physics and physical stimulations.
The following are computer system types based on their data handling capacity:
- Analog computer. This type of computer system continuously processes varying data. Without translating it first into numbers and codes, it can simply accept the data from the equipment of measurement. It gauges the constant variations in physical quantities, and a reading on a dial or scale serves as the output. A speedometer or a mercury thermometer are examples of analog computers.
- Digital computer. Digital computers effortlessly calculate algorithms and logical processes at rapid speeds. They use stored programs in their memory to process raw data as an input and then output the result. Since they can only understand binary inputs, these computers convert the raw input data to 0 and 1, after which the data is processed to create the result. Digital computers include all current models of desktops, laptops, and cellphones.
- Hybrid computer. This computer is a combination of both analog and digital computers. Hybrid computers combine the speed of an analog computer with the accuracy and memory of a digital computer. As a result, they can handle both continuous and discrete data. Hybrid computers convert analog signals into digital signals for use when processing input data after accepting analog signals as input.
Desktop management, a part of systems management, is an all-inclusive strategy for controlling every computer in an organization. Learn how desktop management works and the various desktop management tools that are available.







