Microsoft Remote Desktop Web Access (Microsoft RD Web Access)
What is Microsoft Remote Desktop Web Access (Microsoft RD Web Access)?
Microsoft Remote Desktop Web Access (Microsoft RD Web Access) is a Remote Desktop Services role in some versions of the Windows Server operating system (OS), including Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. It enables users to access RemoteApp and Desktop Connections on these OSes via a web browser.
Microsoft RD Web Access was earlier known as Terminal Services Web Access (TS Web Access).
To start a RemoteApp program, the user visits a website to access a list of available programs and then clicks on the required program's icon. This starts the TS session on the terminal server that hosts the program. The other option to access these services is through the computer's Start menu.
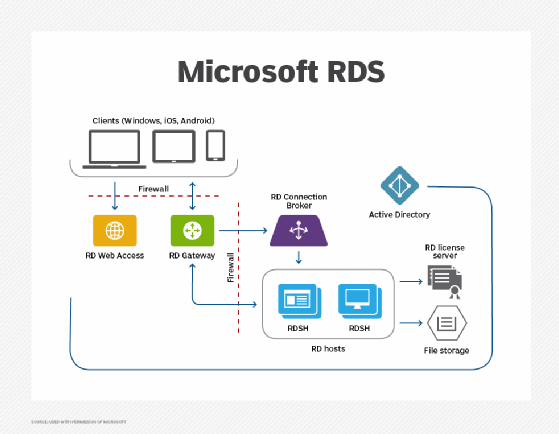
RD Web Access includes RD Web Connection, which enables users to connect remotely to the desktop of any computer with RD Web Access. RD Web Access must be configured to specify the source that provides the virtual desktops and RemoteApp programs that are displayed to users. It can be configured using either a RemoteApp source or RD Connection Broker server, which provides users access to virtual desktops hosted on RD Virtualization Host servers and RemoteApp programs hosted on RD Session Host servers.
Deploying Microsoft RD Web Access
The server where the RD Web Access role is installed acts as the web server. It does not have to be an RD Session Host server. The role works with minimal configuration. The default RD Web Access webpage includes a customizable frame plus a web part that can be incorporated into a customized webpage.
The role service must be installed on the server that users connect to over the web to access RemoteApp programs. Once the role is installed, admins can specify the terminal server they want to populate the web part. All the RemoteApp programs on the specified terminal server that are configured to show in RD Web Access appear in the web part. The list can be populated from an external data source by the web server, which is why the RD Web Access server does not have to be a terminal server.
When the RD Web Access role is installed, Microsoft Internet Information Services 7.0 is also installed. IIS is a Microsoft web server role that's included with all versions of Microsoft's OSes. The web server in IIS 7.0 enables server customizations by adding or removing modules to meet the organization's or user's specific needs.
Here's how the RD Web Access role service is installed on Windows Server:
- Open Server Manager (Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager) on the computer where the role is to be installed.
- If the role is not already installed, click Add Roles under Roles Summary. Select the Remote Desktop Services checkbox on the Select Server Roles page, review the Remote Desktop Services page and select Remote Desktop Web Access.
- If the role is already installed, click Remote Desktop Services under Roles Summary, click Add Role Services under Role Services and select the Remote Desktop Web Access checkbox on the Select Role Services page.
- Review the information about the required role services.
- Click Add Required Role Services, and then click Next.
- Review the IIS page.
- Select the role services that are to be installed for IIS on the Select Role Services page.
- Click Install on the Confirm Installation Selections page.
- Confirm successful installation on the Installation Results page, and click Close.
To provide users access to RemoteApp and Desktop Connections, RD Web Access must be configured to specify the source -- either RD Connection Broker or RemoteApp source -- to provide the RemoteApp programs and virtual desktops displayed to users. To specify the source, a connection to the RD Web Access website is required using a local Administrator account on the RD Web Access server.
The RD Connection Broker server can be configured with the Remote Desktop Connection Manager tool. RemoteApp programs can be configured on a RemoteApp source -- an individual RD Session Host server -- with the RemoteApp Manager tool.
Microsoft RD Web Access: Role in publishing and updating the RD web client
Before setting up the RD web client, it's important to ensure that RD Web Access is running on Windows Server, e.g., Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2019. In addition, public trusted certificates must be configured for the RD Web Access role.
The role is also required to publish and update the Remote Desktop web client.
To publish the RD web client, users must obtain the certificate used for RD connections on the RD Connection Broker server, export it as a CER file and copy the file from RD Connection Broker to the server running the RD Web Access role. Next, an elevated PowerShell prompt must be opened on the RD Web Access server, followed by updating the PowerShellGet module. This is followed by installing the RD web client management PowerShell module from the PowerShell gallery, downloading the latest version of the RD web client and, finally, publishing the RD web client. The name of the server where the web client is accessed -- at the web client URL -- must match the RD Web Access public certificate in the URL. This is typically the server fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
The RD Web Access server enables installation of the RD web client without an internet connection. This can be done either by importing the RD web client management PowerShell module or by copying the downloaded RDWebClientManagement folder to a local PowerShell module folder listed under $env:psmodulePath.
The RD web client can also be updated using the RD Web Access server and an elevated PowerShell prompt. Once the client is updated, it gets replaced for all users when they relaunch the web client webpage.
RD Web Access role and trusted certificates
If a user gets a security warning in their web browser when trying to access the web client, it may mean that the RD Web Access role is not using a trusted certificate. This issue can be prevented by ensuring that the role is configured with a publicly trusted certificate. If this step doesn't work, there may be a mismatch between the server's name in the web client URL and the name provided by the RD Web Access certificate. This issue may be resolved by checking that the URL uses the FQDN of the server hosting the RD Web Access role.
It's also important to check that the certificate has not expired. It must be copied in CER format to the RD Web Access server. Without these precautions, a user may not be able to connect to a resource with the web client even if they can see the items under All Resources. They may also get an "unexpected server authentication certificate was received" error message when trying to connect to the web client.
When the connection between a desktop and its host fails, it's time to do some remote desktop troubleshooting. See how to fix common remote desktop connection problems. Also, compare the features in the Windows Server 2022 editions, and learn how to set up a Windows Server 2022 domain controller.







