Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
What is Active Directory Domain Services?
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is a server role in Active Directory that allows admins to manage and store information about resources from a network, as well as application data, in a distributed database.
AD DS helps admins manage network elements -- both computing devices and users -- and reorder them into a custom hierarchical structure. AD DS also integrates security by authenticating logons and controlling access to directory resources.

How is Active Directory Domain Services used?
Active Directory is a directory service that runs on Microsoft Windows Server. It is used for identity and access management. AD DS stores and organizes information about the people, devices and services connected to a network. AD DS serves as a locator service for those objects and as a way for organizations to have a central point of administration for all activity on the corporate network.
AD DS is used in on-premises Windows environments, and Microsoft Azure AD DS is used in cloud-based Windows environments. They can be used together in hybrid cloud environments.
How does AD DS work?
AD DS is the core component of Active Directory that enables users to authenticate and access resources on the network. Active Directory organizes objects into a hierarchy, which lets various Domain Services connect with them and users access or manage them. The hierarchical structure includes the following:
- Domains. A group of objects, such as users or groups of devices, that share the same AD database makes up a domain.
- Organizational units. Within a domain, organizational units are used to organize objects within the domains.
- Active Directory trees. Multiple domains grouped together in a logical hierarchy make up an AD tree. The bonds between domains in a tree are known as "trusts."
- Active Directory forests. This AD functional level is made up of multiple trees grouped together. Trees in an AD forest share trusts, just like domains in a tree share trusts. Trusts enable constituent parts of a tree or forest to share things like directory schemas and configuration specifications.
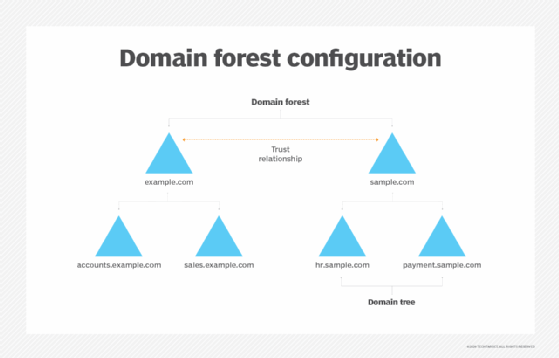
What services does AD DS provide?
Active Directory covers a range of services. AD Domain Services is the main service that encompasses these five services.
Domain Services
Domain Services stores centralized directory information and lets users and domains communicate. When a user attempts to connect to a device or resource on a network, this service provides login authentication, verifying the user's login credentials and access permissions.
Lightweight Directory Services (LDS)
AD LDS is similar to Domain Services, but it uses Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), which has fewer restrictions. AD LDS enables cross-platform capabilities that, for instance, let Linux-based computers function on the network.
Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS)
AD FS provides single sign-on authentication, enabling users to sign in once to access multiple applications in the same session.
Rights Management
This service controls data access policies and provides access rights management. For example, Rights Management determines which folders users can access.
Certificate Services
Certificate Services allows the domain controller to create and manage digital certificates, signatures and public key cryptography.
What are the benefits of Active Directory Domain Services?
The four key benefits of AD DS include the following:
- Hierarchical structure. This is the main benefit of AD DS, providing the organizational structure for the information contained in Active Directory.
- Flexibility. AD DS gives users flexibility in determining how data is organized on the network. It simplifies administrative tasks by centralizing services like user and rights management and provides some security. Users can access Active Directory from any computer on the network.
- Single point of access. Domain Services creates a single point of access to network resources. This lets IT teams collaborate more efficiently and limit the access points to sensitive resources.
- Redundancy. AD DS has built in replication and redundancy If one domain controller fails, another automatically takes over its responsibilities.
What are Active Directory Domain Services terms to know?
Some common AD DS related terms and concepts include the following:
- Global catalog. The Global catalog holds all AD DS objects. Administrators can find directory information -- such as a username -- across any domain.
- LDAP. This protocol provides the language that servers and clients within the directory use to communicate with each other.
- Multi-master replication. A function that ensures all domain controllers on a network are updated with any changes made to Active Directory.
- Objects. These are the pieces of information that Active Directory organizes. There are two types of objects: Container objects are organizational units, such as forests and trees, that hold other objects inside of them. Leaf objects represent things like users, computers and other devices on the network.
- Query and index mechanism. This mechanism enables users to search the global catalog for directory information.
- Schema. The schema is a set of rules a user establishes to define classes of objects and attributes in the directory. These rules also dictate the characteristics of object instances and naming formats.
- Sites. The physical groupings of IP subnets. They enable the easy replication of information among the domain controllers and the deployment of group policies.
What role do domain controllers play in AD DS?
Domain controllers are physical servers that host AD DS and newer Windows services like Kerberos Key Distribution Center, Netlogon, Intersite Messaging and Windows Time. Active Directory requires at least one domain controller to respond to authentication requests and verify users on the network.
Domain controllers also replicate the AD DS database inside an AD forest. Changes made in a directory on one domain controller -- such as a password change or account deletion -- replicate to other domain controllers on the network.
Learn more about Active Directory and how to troubleshoot common issues and find out how to handle replication problems.






