VMware vSphere Client
The VMware vSphere Client is a web-based application that connects to the vCenter Server so IT administrators can manage installations and handle inventory objects in a vSphere deployment. vSphere Client is a part of VMware’s comprehensive product line.
As an application, VMware vSphere Client enables the management of a vSphere installation so IT administrators can access key functions of vSphere without needing access to a vSphere server directly. The vSphere Client presents a graphical user interface (GUI) with an object navigator, the main workspace, as well as the tasks and alarms panel. Through this GUI, vSphere administrators can manage and supervise the objects listed in a virtualized data center.
VMware introduced vSphere Client with the vSphere 5.1 release in 2012. At that time, the product was known as vSphere Web Client.
The final version of vSphere Client to be released was version 6.0 update 3, which was released in February 2017. Since that time, VMware has moved to an HTML5-based web client. The web client is installed as a part of vCenter Server. It’s included with both the appliance and the Windows version.
Why vSphere Client matters for vSphere users
Administrators can use vSphere Client to manage ESXi hosts in organizations that don’t have a vCenter Server. This way, IT administrators can access key functions of ESXi without needing access to a vSphere server directly.
However, because VMware has stopped updating vSphere Client, it doesn’t support functions that were introduced in vSphere 6.5 and subsequent versions.
What vSphere Client is used on
It’s still possible to download and use the stand-alone vSphere Client. VMware provides download links to various versions of the client.
The vSphere Client is comprised of a Java server and an application based on Adobe Flex that runs in a browser. Because vSphere Client is based on the Adobe Flex platform, the operating system (OS) must have Flash installed. For vSphere 6, the vSphere Client requires Adobe Flash Player 16 or later. VMware recommends using the Google Chrome browser for the best performance.
The vSphere Client acts as an administrative interface to access VMware hosts. These hosts, which run VMware ESXi, are the servers that run individual virtual machines (VMs). The vSphere Client attaches to the host servers. By using this interface, admins can create and manage VMs, as well as host resources.
How to install vSphere Client
When IT administrators install VMware ESXi, the server is automatically assigned an IP address by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server. A message on the server console states that admins can manage the server by opening a web browser on a client computer and navigating to the host’s IP address. Doing so will bring up a screen similar to the one shown in Figure A.

This screen contains a link to download vSphere Client for Windows. Simply click on this link, click Run and then follow a few simple prompts to complete the installation process. Alternatively, you can download the client from VMware.
Once downloaded, the client is installed using a very simple installation Wizard. Administrators can complete the setup process in just a few clicks.
For organizations that might prefer to use the HTML5 client, no installation is necessary. The web client is installed with vCenter Server.
Important features
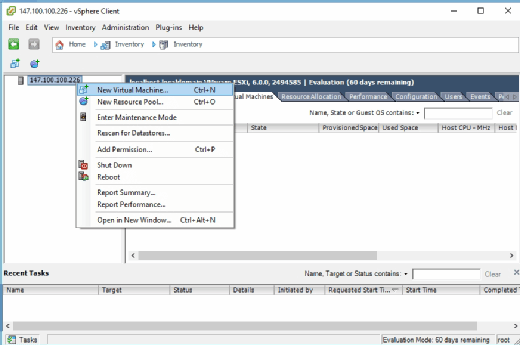
IT administrators can use vSphere Client to fully manage a VMware deployment. Among its most important features is the ability to create and manage VMs, as shown in Figure B. Admins can also use vSphere Client to monitor performance, allocate resources and manage user permissions.
Configuration
It’s possible to use vSphere Client without performing any client-level configuration tasks. Admins can log into a vSphere environment by entering the host’s IP address and a username and password at the client’s login prompt.
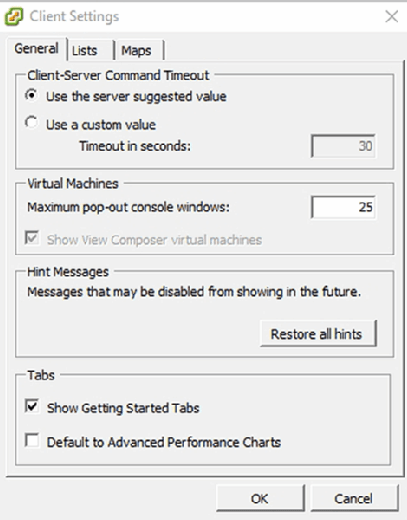
To customize the client’s configuration after logging in, choose the Client Settings option from the Edit menu. The resulting Client Settings screen, as shown in Figure C, displays options to configure connection timeouts, limit console pop-out window usage and perform other basic configuration tasks.
What’s new in vSphere Client
Although the VMware vSphere Client is no longer being updated, VMware regularly makes updates to the HTML5 client. For example, some of the new features found in version 6.5 update 1 of the web client include:
- the ability to use the web client to create a distributed switch;
- the ability to create raw device mapping (RDM) disks or to add existing hard disks to VMs;
- the ability to perform VM drag-and-drop operations -- such as moving a VM to a folder or migrating to a different cluster -- which were previously only possible using vSphere Web Client;
- smart card authentication for vSphere hosts;
- numerous storage and vSAN-related functions, such as the ability to view storage policy rules or to erase a partition; and
- the ability to customize guest OSes during cloning operations.
To see any available updates in the vSphere Web Client, users will need to access the Update Manager administration view. To do this, select the vSphere Web Client Home menu, then Update Manager. Select the Objects tab here, then click the IP Address of the Update Manager instance.






