Fotolia
VMware enhances NSX-T 3.0 to ease networking
Version 3 of NSX-T gets new alarms, security features and admin tools, as well as new and improved integrations to provide VMware admins with better networking capabilities.
VMware released version 3 of NSX-T this year. Major new features in this release include new administrator tools, alarms and security features and two new features called VRF Lite and Federation. The NSX-T 3.0 enhancements make networking more efficient and network management easier for VMware admins.
Virtual Distributed Switch 7
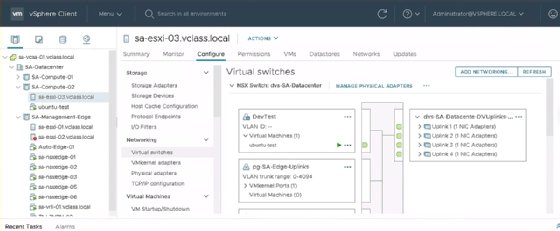
VSphere 7 Virtual Distributed Switch (VDS) now integrates with NSX-T. This means admins no longer must add an additional N-VDS switch to a vSphere host. Previously, an ESXi host required a standard or distributed switch to contain the management port, vMotion port and IP storage. It was possible, though difficult, to migrate these services to an NSX-T N-VDS, and not all vSphere features were compatible with this setup. Now admins can combine all these services with the help of the NSX-T Geneve overlay networking on the same distributed switch.
When assigning a cluster to a transport node profile that uses VDS as the format, NSX-T 3.0 maintains all existing services while an admin converts the switch. Administrators can then use all uplinks under these services, as opposed to previously, where a VDS and N-VDS each required their own dedicated uplinks.
Administrator tools
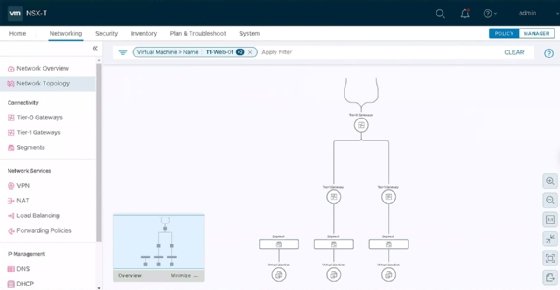
The toolkit for administrators includes several familiar tools -- either the same tools as previous versions or tools that have only undergone cosmetic changes. For example, Traceflow still works the same way to inject and inspect packets and analyze traffic flow between network entities, but its appearance and user-friendliness have improved.
VMware has replaced Port Connection with another tool named Network Topology, which shows administrators how all system components -- including VMs, segments and routers -- connect. Applying a Network Topology filter can show admins the connections from a chosen VM to other machines.
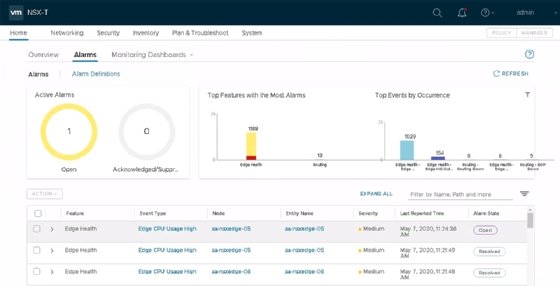
Alarms and security features
A new alarms feature helps administrators manage their environment. NSX-T now reports issues from the larger NSX infrastructure when they arise.
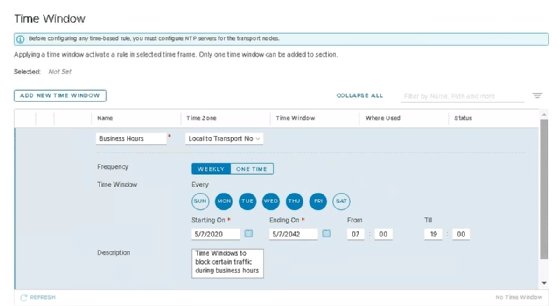
VMware has also improved several security features in NSX-T 3.0. Admins can establish a time window for firewall rules, which lets them choose to have rules enforced based on the day of the week or time of the day.
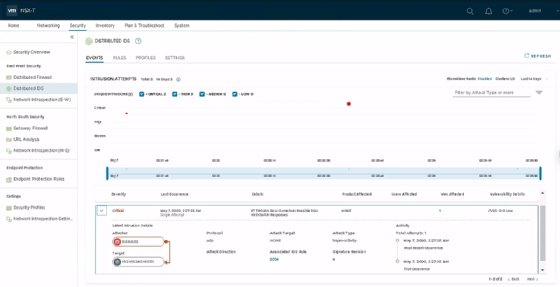
A new security dashboard displays statistics about rule enforcement and intrusion attempts. This enables administrators to easily diagnose security issues in the environment.
NSX-T 3.0 also introduces Distributed Intrusion Detection. Admins can use it in conjunction with the third-party service Trustwave for increased intrusion detection capabilities. Trustwave maintains a database of threats that the NSX Manager Appliance can download to check traffic against the signatures of those common attackers.
VRF Lite
NSX-T offers two types of routers: the tier 0 gateway with a main use case for north-south connections -- i.e. those leaving the hypervisor -- and the tier 1 gateway, which NSX-T uses for east-west traffic between workloads on hypervisors. Each tier 0 gateway requires an edge cluster, which makes scalability difficult. If an organization requires a separate router for a large number of tenants, then deploying many edge devices reduces efficiency.
Virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) Lite enables admins to create virtual routers inside of a tier 0 gateway. These are isolated routers with their own routing tables that live inside the same Edge Transport Node as the parent tier 0 gateway. These routers connect to the same internal segments as the tier 0 gateway and share configuration with the parent tier 0 gateway.
VRF routers have their own subinterfaces and connect into individual VLANs on the network, so networks can overlap and connect via the same tier 0 gateway as long as they each have their own virtual router. This new feature makes NSX-T much more scalable, with a maximum of 100 VRFs per edge node.
Federation
Federation enables admins to place the NSX-T Managers of up to three sites under the management of a Global Manager. From that Global Manager, an administrator can create global and stretched gateways and segments. This enables them to extend networks across sites and have workloads communicate on those stretched networks. Admins can also create firewall rules for global groups that span more than one site.
Federation isn't a feature that customers can implement on their own in a production environment. Organizations must work with VMware for this, but admins could potentially set up proof of concept for the feature.