everythingpossible - Fotolia
Top 10 new vSphere 7.0 features
With vSphere 7.0, VMware introduced several new capabilities and tools. Explore the top 10 most innovative features in this latest vSphere release.
With vSphere 7.0, VMware takes an innovative approach to the vSphere suite, integrating it with the Kubernetes container management platform and adding several updates and features. Among the most useful new features are vCenter Server Profiles, Lifecycle Manager and Trust Authority.
Learn about the 10 most functional and innovative vSphere 7.0 features.
Integration with Kubernetes
Admins can now use vSphere with Kubernetes to manage VM workloads and container workloads with the same user interface. This approach enables application developers to use the tools and interfaces they're used to -- namely, Kubernetes -- and vSphere admins to manage both vSphere and the Kubernetes infrastructures via the tools and interfaces they're used to.
VMware only offers Kubernetes management with VMware Cloud Foundation. You must assign a VMware vSphere 7 Enterprise Plus license with an add-on license for Kubernetes to all ESXi hosts that you intend to use as part of a Supervisor Cluster.
VCenter Server Profiles
Server Profiles enables you to reuse vCenter server configuration in order to keep your large-scale deployments consistent. You can import and export configurations to replicate them between different vCenter server nodes.
This feature enables version control between vCenter servers and quick reversion to the last known configuration if needed. Server Profiles exports vCenter server configuration as a standard JSON file. You can find the API via the Developer center under the appliance API.

Multi-homing
Until now, vCenter server could not have two IP addresses. VCenter server 7.0 can now support two or more network interface cards (NICs) and multiple IP addresses. VMware support says vCenter server can support as many as four NICs. Having multiple IP addresses is handy in many situations -- for example, when you require a separate backup network and need another IP address to reach vCenter server.
However, when you add a second NIC to the vCenter server appliance, it reserves that NIC for a vCenter High Availability function. In order to use another network with your vCenter server, you must add a third NIC.
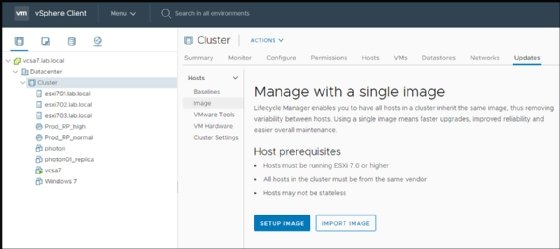
VCenter Lifecycle Manager
VMware previously used vSphere Update Manger to enable update management for ESXi hosts, clusters and vCenter servers. VMware has renamed this component vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM).
VLCM keeps server hardware consistent and up to date. It also supports the capabilities previously included in VMware Update Manager but adds a new desired state model that takes care of keeping server firmware that OEMs provide up to date as well.
Other new capabilities of vLCM include:
- cluster software management using desired state images;
- host hardware verification against the VMware Compatibility Guide and the vSAN Hardware Compatibility List; and
- the ability to perform automated firmware updates.
The new rebranded vLCM gives VMware admins more control over firmware and driver combination across large vSAN clusters. However, if your vSAN clusters aren't identical -- with the same storage cards running the same firmware and driver -- you might encounter performance or stability problems.
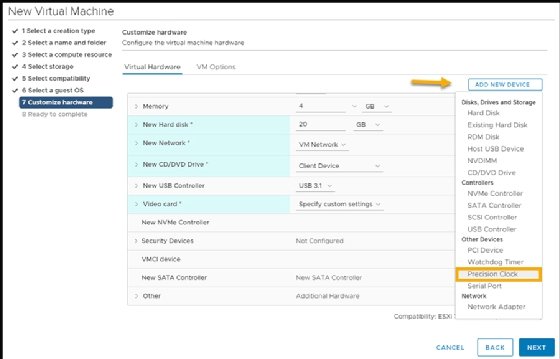
VMware Virtual Hardware 17
Virtual Hardware 17 adds some functionality to vSphere that was missing from previous versions. You can only configure the new virtual hardware on vSphere 7.0. Its two most important new features are:
- Virtual Watchdog Timer enables guest monitoring within clusters. This feature is particularly useful for Microsoft clustered applications, but it also benefits other cluster applications such as databases.
- Precision Time Protocol enables you to configure VMs with sub-millisecond accuracy. With this protocol, you can achieve very low latency for applications that require it -- for example, financial or scientific applications. In order to add a precision clock device to a VM, you must add and activate the in-guest device and ensure that you activate the ESXi service on the host.
VSphere Trust Authority
VSphere Trust Authority is a set of security features that can reinforce your organization's security with a trusted platform module that integrates directly into your hardware.
The main piece of the feature relies on a hardware module called Trusted Platform Module -- a cryptographically signed chip that you can order from your hardware manufacturer attach to the host when you first plug it in.
VSphere 7.0 scalable shares
With vSphere 6.7 and earlier releases, admins could only adjust resource pool settings based on the number of VMs running in each resource pool. VSphere 7.0's scalable shares feature adjusts resource pool settings automatically.
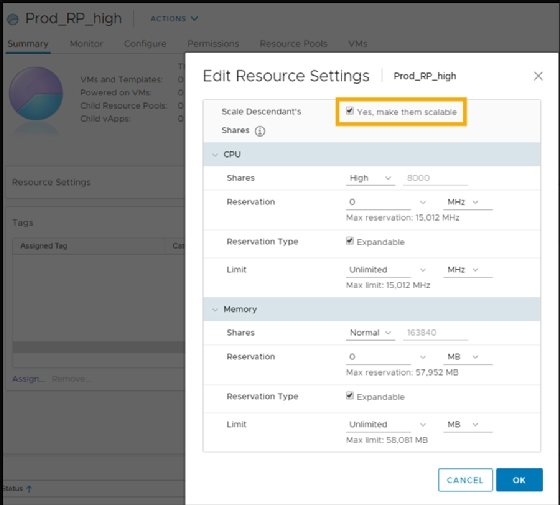
If you enable scalable shares, the Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) looks into each resource pool, takes into consideration the number of VMs inside and also looks into the priority of each resource pool. Based on those elements, scalable shares then assigns the resources in each pool based on priorities and the number of VMs in each pool.
Improvements to DRS
DRS features a new logic built in that computes a DRS score for VMs in your environment and automatically moves VMs to the host with the highest VM DRS score. The DRS score is calculated based on the host's data, such as how many VMs run on it, its memory and its CPU consumption. It calculates this score every minute -- compared to the last version, which calculated the score every five minutes --and can help you optimize your resources more granularly.
The improved DRS focuses less on the ESXi host use and more on the workloads running on the VMs.
Identity Federation
You can choose to add Identity Federation or you can keep your existing Active Directory authentication through single sign-on (SSO). Identity Federation presents a new method for authentication in a vSphere environment.
If you configure this optional feature, your vSphere Client must use external authentication. Version 1.0 of Identity Federation supports only Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services. However, VMware SSO still exists and vSphere uses it as the default authentication service upon installation.
VM template check-in and check-out
With check-in and check-out templates, you can maintain single template copies with different versions. After creating a traditional VM template and copying it to the library, you can check-out the VM from that template for edits and then check that template back into the content library to save the changes.
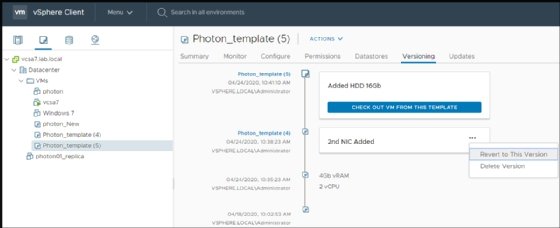
After processing at least one change to the VM's virtual hardware or content, you can see that template's versioning. You must annotate the different changes to the template VM to know what each version contains. You can revert to old versions or delete the versions you don't need anymore.