rvlsoft - Fotolia
Tips to increase ESXi host security
Harden your ESXi hosts against potential threats with AD integration and advanced settings modifications to keep your data center safer.
Most administrators are familiar with basic security setups on ESXi hosts, such as lockdown mode. However, you can take several more nuanced approaches to increase host security throughout your data center -- on a general and per-host basis.
You can use Active Directory (AD) integration to make vCenter host login easier and more secure. This configuration means you no longer have to share the root password with everyone who must directly log into the ESXi hosts.
You can also modify hosts' individual settings to increase security and then apply those settings to all hosts across your infrastructure. Both methods increase the security of vSphere in your data center and harden your hosts against specific attacks and vulnerabilities.
Configuring AD integration
To configure AD integration, you must first have an explicit, named AD group -- "ESX Admins," for example.
You can create the AD group "ESX Admins" with the AD Users and Groups tool on your AD server. Add the desired users to that group, such as the admins you choose to give host access to. Double-check that your DNS resolution and naming are correct before you configure your hosts and add them to your AD infrastructure.
Next, open the vCenter web GUI, navigate to the host you decide to add and select Configure > System > Authentication Services. The GUI should show an option to Join Domain.
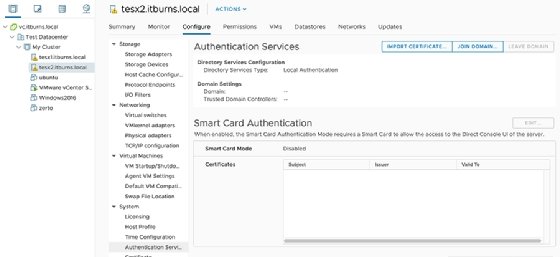
Provide the details for an account you want to have rights to the AD network. This should enable that account to use AD for ESXi host authentication.
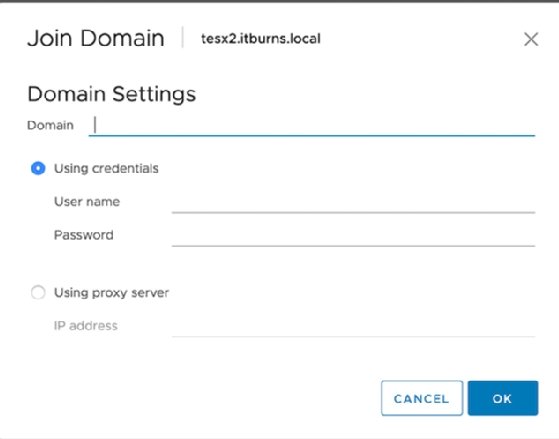
Then, directly log into the host to double-check everything works as desired.
Host configuration for host hardening
You can reconfigure your hosts to harden them against vulnerabilities. To increase security, you should adjust account lockout settings and Secure Socket Shell services.
To troubleshoot problems on a per-host basis, navigate on the host to Configure > Advanced System Settings > Edit and look for these three items:
- AccountLockFailures
- AccountUnlockTime
- PasswordQualityControl
Set security lock failures to a small, but reasonable, number of login attempts. Three attempts usually makes for a good middle ground.
Account unlock time is measured in seconds. VMware automatically sets this to 120 seconds. A more sensible option is 15 minutes or more -- roughly, 900 seconds.
Password quality control enforces password complexity. However, you must specify the requirements and options in the text box.
Each option modifies different variables, but the configuration should mirror that of the Linux implementation of the pluggable authentication module. VMware defaults to the following:
retry=3 min=disabled,disabled,disabled,7,7
The "retry" option is fairly intuitive -- an admin has three attempts to retry a password. The "min=disabled" option denies passwords of only one type, such as those of just alpha characters. The second "disabled" builds on the first and disallows passwords of just two-character classes. The third disables the use of passphrases.
The last two items, "7,7," determine minimum password length for the remaining allowed password types.
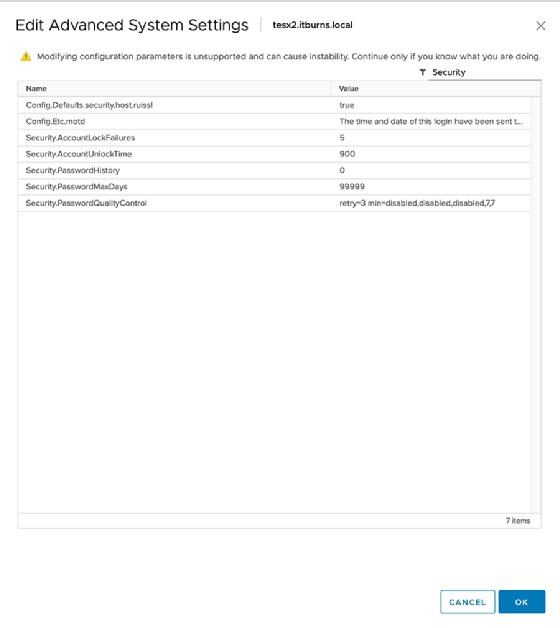
You can use a single line of code to represent these host security factors. These settings let you define many other password options, such as password history -- meaning whether someone can reuse an old password -- and password max days, which dictates the length of time before a password expires. VCenter defaults to 99,999 days, which, left unaltered, might pose a security vulnerability.
Ensure you leave no spaces between settings when entering a new configuration. This could create significant issues in the future.
You can do all of these configurations manually, but manual configuration always leaves room for error. If you use host profiles, you can easily apply the same profile consistently across all of your ESXi hosts to ensure consistent configuration.
Finally, make sure you test these features before you put them into production.