What is VMware NSX? Definition, features and use cases
VMware NSX is a network virtualization feature that allows VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) subscribers to replicate their entire network infrastructure with software. NSX decouples network functions from hardware by creating a virtual network overlay that emulates physical network components. This allows network architects and engineers who are using VCF to provision and manage network functions programmatically and enforce global and local network policies automatically across distributed computing environments.
Until 2023, NSX was sold as a standalone software-defined networking (SDN) product that could be purchased with a perpetual VMware license. When Broadcom acquired VMware, however, they consolidated VMware's extensive product line into four core offerings and rolled NSX into VCF.
Since then, Broadcom has been marketing VCF as a subscription service for creating, deploying and managing private clouds. NSX is the network component that allows VCF subscribers to create, manage and scale software-defined networks across private cloud environments.
The history of NSX
NSX's origins can be traced back to Nicira, a company founded in 2007 by Stanford University professors and engineers. Nicira developed Network Virtualization Platform (NVP), an SDN platform that decouples virtual network functions from the underlying hardware.
In 2012, VMware acquired Nicira for approximately $1.26 billion. Following the acquisition, VMware began integrating Nicira's technology into its own product lines. This led to the development of VMware NSX, which was officially launched in 2013.
VMware NSX was originally a full stack layer-2 to layer-7 platform that combined the network virtualization capabilities of NVP with VMware's evolving network and security offerings. Early versions of NSX focused on providing a complete SDN and security platform for the software-defined data center (SDDC).
Broadcom and VMware NSX
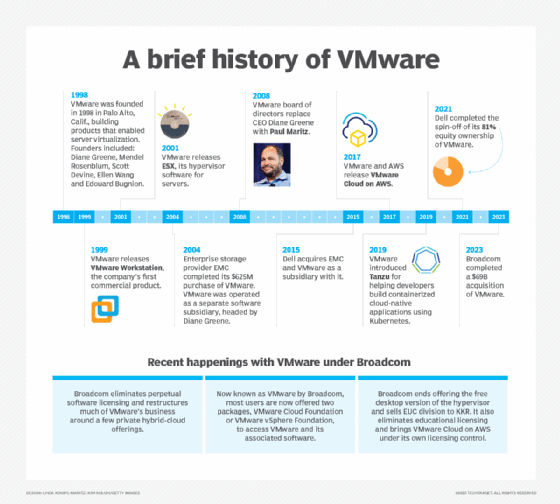
When Broadcom completed its acquisition of VMware in November 2023, it implemented sweeping changes to VMware's product line and business strategy. The changes significantly affected how NSX could be acquired and used.
Before the acquisition, VMware customers could purchase NSX as a standalone product that was available in four versions: NSX Professional, NSX Advanced, NSX Enterprise Plus and NSX ROBO. After the acquisition, Broadcom eliminated VMware's "a la carte" approach and bundled compute, storage, networking and infrastructure lifecycle automation functions into VCF. This removed the need for separate vSphere, vSAN, Aria (formerly vRealize) and NSX licensing tiers.
As part of its rebranding efforts, Broadcom's most recent technical spec for VCF clarifies the roles of individual components within VCF's full stack. NSX, for example, is being described strictly as VCF's networking component. The security capabilities that were once part of NSX offerings are now included as part of VMware vDefend.
VMware NSX vs. vDefend
VDefend is an optional security add-on for VCF. Essentially, vDefend consolidates and enhances the security functionalities that used to be part of NSX before Broadcom's acquisition.
Today, vDefend provides a distributed firewall (DFW) for managing east-west traffic and a gateway firewall for controlling north-south traffic. It also offers an advanced threat prevention (ATP) feature that can be enabled to facilitate the implementation of zero-trust architectures.
Zero trust is an important consideration in private cloud deployments because it enforces a "never trust, always verify" approach to accessing physical and virtual network resources. This helps protect sensitive workloads in private clouds from insider threats, as well as lateral movement attacks conducted by threat actors outside the organization.
How NSX works in VMware Cloud Foundation
NSX allows VCF subscribers to create overlay networks that have an encapsulation mechanism and a control plane. The encapsulation mechanism uses the Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation (Geneve) protocol to wrap network packets for transport across the overlay network. The control plane manages network configurations and distributes network topology definitions to data plane components in the VCF stack. This simplifies network provisioning and supports policy-driven network operations across private cloud environments.
Benefits of NSX in VMware Cloud Foundation
Broadcom's bundling NSX into VCF helps improve operational efficiency by providing network engineers with a single management interface (UI) that can be used to configure logical network switches, network gateways and routing policies. Additional benefits of using NSX in VCF private cloud deployments include the following:
- Automation. NSX allows VCF subscribers to automate the provisioning and management of network services. Automation not only enables the rapid deployment of network resources, it reduces the potential for human errors.
- Multi-cloud support. NSX allows VCF subscribers to enforce network policies for multi-cloud deployments consistently. This capability can simplify management tasks for private cloud deployments that combine on-premises private clouds with hosted private cloud services.
- Network visibility. VCF allows subscribers to visualize network connectivity and performance through a centralized management console. Having a single pane of glass can simplify troubleshooting and decrease the average time it takes to rectify network issues.
- Declarative APIs. NSX uses declarative application programming interfaces and an intent-based approach to simplify network service delivery and network consumption. Declarative APIs allow users to define the desired state of the network. In contrast, imperative APIs require users to specify the exact steps required to achieve the desired network configurations.
NSX use cases
NSX provides the networking layer that enables VCF to support private cloud deployments. Key use cases for NSX within VCF include the following:
- Network virtualization. NSX abstracts traditional network functions such as switching, routing and load balancing into software. This allows network architects to define and manage network topologies logically and quickly deploy isolated or multi-tier virtual networks for different applications or tenants without touching physical network.
- Multi-tenant and isolated network environments. VCF supports multi-tenancy, and NSX enables each VCF workload domain or tenant to have its own logically isolated network. When vDefend is enabled in VCF, traffic can be segmented, and both networking and security policies can be consistently applied to ensure strict isolation between tenants.
- Application mobility and data center extension. In VCF deployments, NSX overlays make it possible to move applications and workloads across clusters, racks and geographically separated VCF instances without needing to reconfigure physical network settings or change edge node IP addresses. This is useful for disaster recovery, optimizing cloud capacity and ensuring that planned maintenance won't disrupt private cloud operations.
- Consistent multi-cloud networking. Organizations using multi-cloud architectures can rely on the networking capabilities of NSX within VCF to enforce consistent routing policies across distributed computing environments. NSX abstracts the complexity of different underlying infrastructures, and this makes it easier to maintain policy compliance for private cloud deployments that are hosted in more than one cloud computing environment.
- Centralized lifecycle management. Because NSX is fully integrated into VCF, network services are deployed, updated and managed alongside compute and storage resources. This reduces operational silos and helps ensure the network stack evolves consistently across all environments.
- Integration with vDefend for security policy enforcement. Although NSX doesn't enforce security policies anymore, the virtual network fabric it provides is essential for enforcing security policies delivered through the vDefend Security Suite.
Certification and training
VMware by Broadcom currently offers two certifications for IT professionals who are working with VCF. The focus of the certifications reflects the importance of VCF's role in private cloud deployments.
- VMware Certified Professional – VCF Administrator (VCP-VCF). This VCP-VCF certification validates the holder's ability to install, configure, manage and troubleshoot VCF. The exam for this certification covers the basic components of VCF: NSX, vSAN, vSphere and the VMware Aria Suite.
- VMware Certified Specialist – VCF Deployment 2024. This is an advanced certification designed for VCP-VCF certified professionals. The exam for this certification validates the candidate's expertise in using VCF to deploy private clouds. Broadcom recommends this certification for private cloud solution architects and deployment engineers.
VMware for Broadcom also provides three online courses to help IT professionals learn more about VCF.
- VMware Cloud Foundation: Deploy, Configure, Manage is a comprehensive online course that covers VCF architecture, deployment and management. This course, which includes videos and hands-on labs, is recommended for candidates preparing for the VCP-VCF certification exam.
- VMware Cloud Foundation: Troubleshooting is an online course intended for candidates who have already earned their VCP-VCF certification. It focuses on the skills required to identify VCF infrastructure issues and fix them.
- Migrating to VMware Cloud Foundation is an online workshop that provides attendees with practical insights into transitioning workloads to VCF. This accelerated course of study is designed for VMware vSphere administrators who want to gain hands-on experience managing VCF.
At this time, Broadcom is also providing additional continuous learning resources for VCF through a paid offering called VMware's Enterprise Learning Subscription. An ELS subscription provides IT pros with a wide range of digital learning resources, along with complimentary VCP exam vouchers (per year), exam prep materials and access to community forums. The variety of learning resources that ELS provides allows subscribers to customize their own learning paths and manage specific types of projects that use VCF to create, deploy and manage private clouds.
Explore the top private cloud providers today and learn more about how to select the right private cloud platform for your organization's immediate and long-term needs.






