Virtual Machine Disk format (VMDK)
What is Virtual Machine Disk format (VMDK)?
VMware Virtual Machine Disk (VMDK) is a format specification for virtual machine (VM) disk image files. A file with a .VMDK file extension is essentially a complete and independent virtual machine. Originally, the format was developed specifically for VMware virtual appliances.
In virtual environments, a guest operating system (OS) is installed on a virtual disk. Doing this makes the virtual disk the equivalent of a traditional hard disk or solid-state drive (SSD) and makes the VM installed with a virtual disk (running the guest OS) ready for use. VMDK is one of the formats used for virtual disk drives.
VMDK allows the cloning of a physical drive for virtualization as well as the offsite backing up of VMs. The format was originally developed by VMware for use with a VMware virtual appliance (VA) such as VMware Workstation, VMware Player and VMware Fusion. But it is now an Open Source file format that can be used by different non-VMware virtualization platforms.
VMDK files can be dynamic (sparse) or fixed (flat or static). Fixed VMDKs are allocated a fixed, large size from the outset to account for size changes as the use of a VM increases. In contrast, dynamic disks expand with the size of the files in the guest OS.
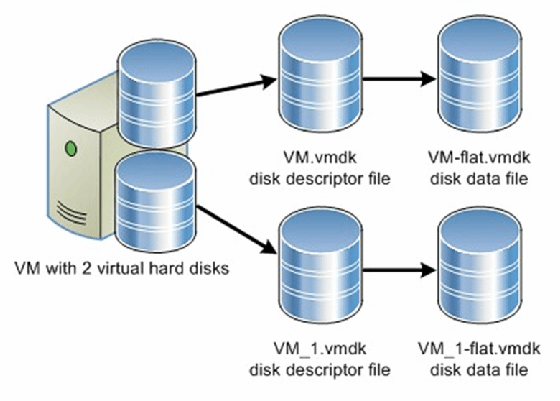
Virtual Machine Disk format vs. Virtual Disk Image
Virtual disks come in different formats, depending on the virtualization software used to create them. VMware's VMDK is one of the most popular formats, along with Oracle's Virtual Disk Image (VDI) and Microsoft's Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) and Hyper-V (VHDX).
VDI is the default disk format (.vdi extension) for the Oracle VM VirtualBox, an enterprise-class virtualization product that runs on macOS, Windows (including older Windows versions such as Windows 3.x and Windows NT 4.0), Linux and Solaris hosts. VirtualBox supports numerous guest OSes, including Windows, MS-DOS, Linux, Solaris, OS/2 and OpenBSD. VirtualBox and VDI are suitable for organizations that require backward-compatible support for software applications built for these operating systems and their predecessors. VirtualBox supports both VMDK and VDI formats.
Since VDI is portable, it can be run using other virtualization programs. Like VMDK, VDI allows both fixed-size and dynamically allocated storage.
Virtual Machine Disk format vs. Virtual Hard Disk
VHD is the standard virtual disk format for Microsoft's virtualization products. It has been superseded by the VHDX format, which is now the default format used in the Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor. Compared to the 2 TB capacity of VHD, VHDX has a significantly higher storage capacity of 64 TB.
VHD/VHDX hard disk images can be of four types:
- Fixed. It has a preset size and includes a raw disk image and a VHD footer.
- Expandable (or dynamic). Its size adjusts to accommodate the data it holds and includes a header and footer.
- Differencing. This image type allows VHD cloning. It saves all changes in the VHD to a child image. Changes can be undone or merged into the VHD.
- Pass-through. The disk image is linked to a physical hard disk (or to one of its partitions).
Regardless of the type, all VHD/VHDX images reside as files on the host OS. Both formats are widely supported by various virtualization platforms, including Oracle VM VirtualBox and VMware platforms.
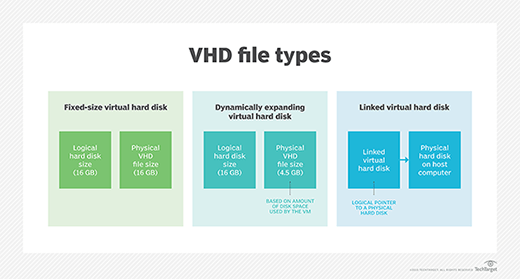
VMDK vs. VDI vs. VHD
VMDK competes with both Oracle VDI and Microsoft's VHD. VMDK is not directly compatible with VHD, but third-party tools such as the VMDK to VHD Converter aid with the conversion process. VDI is compatible with both VHD and VMDK, which means that Oracle VirtualBox can run images with both these extensions. It uses the Oracle Virtual Media Manager to create and copy VDI, VHD/VHDX and VMDK virtual hard disks. A number of free file image conversion tools are available.
VMDK allows incremental backups of data changes from the time of the last backup. This capability is not available with VDI and VHD. Because only changes and new data are backed up, the backup process for VMDK files is faster than the same process for VDI and VHD files.
Converting a physical drive to a virtual disk with VMware or Hyper-V
Both VMware and Hyper-V can be used to convert a physical hard disk or solid-state drive installed with Windows, Linux or another OS to a virtual disk -- a process often referred to as physical to virtual (P2V). The virtual disk can then be installed on a VM. The conversion process with Oracle VM VirtualBox can be somewhat complicated so care should be taken during the conversion process. Further, before converting a Windows PC, it's crucial to ensure that no Windows license terms are being violated.
With VMware, computers running Windows and Linux can be converted into VMs using the VMware vCenter Converter. The generated VMDK file can be used to install a VM with the operating system image on another PC. With Hyper-V, Windows virtual disks can be generated using the Disk2vhd tool. The resultant VHD file can be installed on another machine using Hyper-V.
Advantages of VMDK
VMDK is a significantly faster virtual disk format than both VDI and VHD (and VHDX). In addition, it includes live migration features to make it easier to move a VM to another server. It also provides snapshots, continuously protects data and uses high-performance SAN block storage. Finally, users can recreate and restart VMs with backup VMDK files.
Explore 3 VMware disk types you should know, see how to convert VMDK to VHDX using PowerShell commands and learn how to recreate a missing VMDK descriptor file.







