
Kit Wai Chan - Fotolia
How are application layering and app virtualization different?
If IT pros effectively use either app layering or app virtualization, they can simplify management while improving the end-user experience.
Application layering and application virtualization are two distinct technologies that make application management easier.
App layering and app virtualization both allow IT to deliver virtual applications to users, but where app virtualization isolates the apps from the end users' desktops, layering interacts with the desktops more directly.
Application virtualization
With application virtualization, IT professionals install the app into an isolated location in their organization's data center where the application is separate from the underlying operating system and other applications.
IT pros can break down some of the isolation boundaries to allow two or more virtualized applications to interact when necessary, but most virtualized applications are completely separate from the virtual desktop and other apps.
The main advantage of application virtualization is enhanced security. Because virtualized applications are isolated, they cannot interfere with the OS or with other applications. In fact, the confined nature of virtualized applications makes it possible to run applications that would otherwise be incompatible with the desktop or other applications.
Another advantage of app virtualization is that because IT doesn't install the applications on users' physical devices, the apps have better portability, which makes them more flexible to work on different deployments and delivery paths.
Application layering
Application layering is another method for deploying applications from a central system to end users where the apps are not isolated from one another.
With application layering, IT installs the applications on a virtual hard disk that is separate from the endpoint's hard disk. IT pros can either install the application on a Microsoft virtual hard disk or a VMware virtual machine disk file.
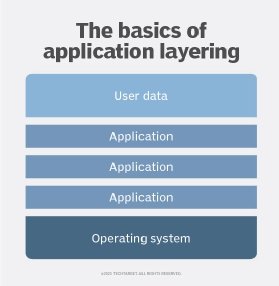
When a user launches a layered application, the application layering software attaches the virtual disk to the endpoint's operating system and runs the application as if it were installed locally. Most applications consist of more than just application binaries, so there are also common registry entries and dynamic link library files IT pros must install.
Each application layering vendor has its own method, but these types of files may be stored in a central repository with the layering software redirecting calls to those files on an as-needed basis.
The main advantage application layering has over application virtualization is that layering makes it easier for an application to interact with the local operating system and other applications. When a user works with a layered application, it is essentially running on the local OS, even though it has not been installed like a physical application would be.








