
Getty Images/iStockphoto
Understanding CPaaS market growth, trends and providers
The CPaaS market is maturing as increased demand for digital communications drives new use cases. Learn about the trends and providers fueling CPaaS market growth.
Communications platform as a service, or CPaaS, continues to mature as demand for cloud communications over the last year expanded use cases and prompted new vendors to enter the market. Market revenue reached $5.9 billion in 2020, according to an IDC report. Global CPaaS revenue in 2019 was $4.26 billion and is expected to reach $17.71 billion by 2024, according to IDC.
The CPaaS market has evolved beyond basic APIs for messaging and voice capabilities to address more sophisticated use cases that can be tailored to vertical markets. Organizations looking to buy CPaaS APIs should examine the various use cases that APIs can address and how to choose a CPaaS provider.
How did the pandemic affect CPaaS market growth?
The pandemic drove demand for embedded and digital communications as organizations looked to replace in-person communication. New CPaaS use cases emerged around telehealth, e-commerce and retail. For example, in addition to the typical use case of text message appointment reminders, healthcare groups can use CPaaS to enable virtual waiting rooms and remote patient monitoring.
Programmable video is another growth area as organizations look to replicate in-person communication with video. Programmable video use cases include video banking, video-assisted sales and customer support.
The pandemic also drove contact centers to adopt CPaaS to enable agents to work remotely. Organizations with on-premises contact centers had to shift to the cloud quickly to support remote work. Many cloud-based contact center platforms have CPaaS APIs under the hood, so the rapid adoption of cloud-based contact centers also boosted CPaaS adoption.
What are other use cases driving the market?
Customer communications are also driving new use cases as people look to communicate with businesses through multiple channels and IP-based messaging applications, such as WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger. Omnichannel CPaaS enables a business to communicate with customers through any channel without disrupting or restarting the conversation.
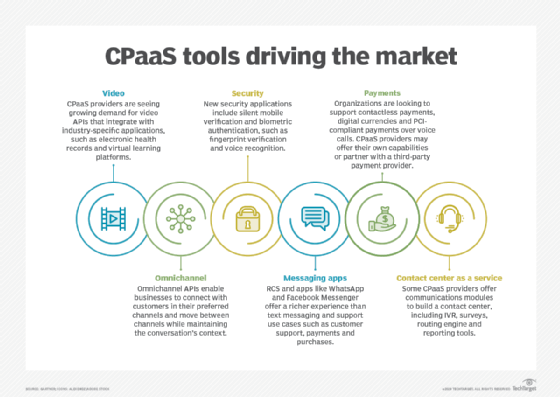
Organizations that use CPaaS for text messaging can find a more customizable and interactive experience with rich communication services. RCS is considered the next generation of text messaging and can provide a similar experience to IP-based messaging applications. RCS supports capabilities such as group chat and high-resolution video that are delivered over a cellular network, regardless of mobile carrier.
Organizations that adopt RCS can take their CPaaS-based text messaging beyond appointment reminders and notifications. For example, a company advertising a new product could use multimedia, like product gifs or images, in promotional messages to customers.
Additional use cases driving CPaaS market growth include enhanced security capabilities and payments.
What does the CPaaS provider landscape look like?
CPaaS providers come in two flavors. First are standalone providers that focus mainly on offering CPaaS APIs. Second are communications providers that offer CPaaS as either a standalone offering or as part of their portfolio.
Standalone CPaaS providers include Infobip, MessageBird, Plivo and Twilio. Communications providers that offer CPaaS as part of their larger portfolios include Amazon, Avaya, RingCentral and Vonage.
Twilio has long been the market leader and shaped much of the CPaaS landscape. The provider is a major revenue driver for CPaaS market growth, according to IDC. But Twilio is expanding its focus beyond communications APIs. For example, Twilio acquired customer data platform Segment in late 2020 to compete in the customer engagement technology market.
This has opened the door for new entrants to the market that could challenge Twilio. Amazon, Cisco and Microsoft, for example, have made moves into the CPaaS space in the last few years.
In 2020, Microsoft announced Azure Communication Services, which offers capabilities like messaging and video calling using the same infrastructure as Microsoft Teams.
Amazon introduced an SDK for its Chime communications platform in 2019. The Chime SDK enables developers to build and embed capabilities, including video and screen sharing, into business applications using Chime infrastructure.
Cisco acquired CPaaS provider IMImobile in early 2021. Cisco plans to integrate IMImobile's cloud-based messaging APIs with its cloud contact center, which will enable customers to build contact center workflows without extensive coding.
How do you choose a CPaaS provider?
When selecting a CPaaS provider, organizations need to weigh the benefits and trade-offs of the two types of providers. For example, organizations that add CPaaS capabilities from their unified communications provider can consolidate communications to a single provider, often at no additional cost. But the API capabilities may not be as extensive as those from a standalone provider.
Standalone CPaaS providers tend to offer rich communications functionality and low-code/no-code development tools for deployment flexibility. However, deploying CPaaS from a standalone provider can incur additional subscription costs.
According to the IDC report, organizations should also use four criteria to evaluate CPaaS providers:
- interconnections with tier 1 telecom operators and multiple mobile and wireline operators;
- a wide range of use cases that support a variety of verticals and service types;
- integrations with major CRM, contact center as a service and UC platforms; and
- additional services, such as visual building tools, serverless computing and omnichannel messaging.








