Understand your storage infrastructure management
Emerging technology, such as AI and software-based storage management systems, have simplified how IT manages its infrastructure. Explore the many components of modern management.
Storage infrastructure typically covers all storage devices, servers and network elements that intersect with the rest of the overall IT infrastructure and its associated technology. Administrators must keep storage infrastructure under control using proactive management techniques.
The storage infrastructure includes the physical space, physical security, power and HVAC systems the storage equipment uses. Storage infrastructure management ensures the safe, secure and uninterrupted operation of storage services, workload processing and related assets.
In addition to a primary on-premises data center, storage infrastructure can include secondary data centers, equipment rooms in buildings and storage equipment closets.
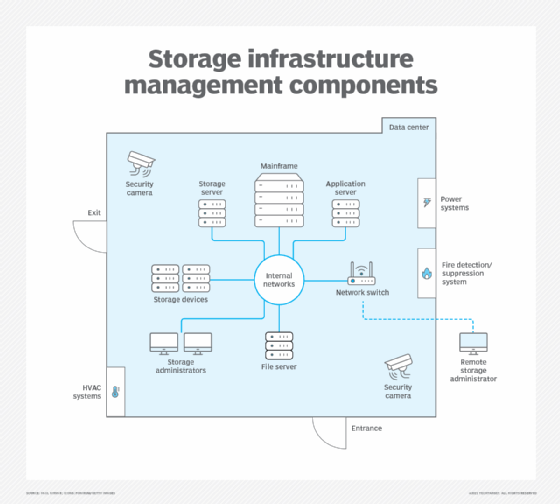
Data storage physical infrastructure
Within a data center or other storage facility, admins must manage and maintain several key components to achieve optimum storage system performance.
They must secure the physical data center with access control to the area. The data center could include the following security features:
- Closed-circuit television for intruder identification.
- Doorways to the data center with at least one means of authentication, such as a proximity card or a fingerprint scanner.
- Primary power supplies from the local utility, plus power distribution units to route power to each device.
- Backup power systems to minimize system downtime.
- HVAC systems to keep the temperature and humidity at prescribed levels.
- Underfloor water detection equipment if a raised floor is used.
- Emergency lighting.
- Fire detection and suppression systems.
Have at least two access/egress points in the facility, each protected by security systems.
In addition, to help ensure environmentally friendly infrastructure, use energy efficient equipment and comply with existing standards and regulations for green data centers.
Data storage technology infrastructure
Storage servers connect storage devices to users and help plan, organize and manage resources. Storage can be on fixed HDDs, SSDs, RAID arrays, NAS and remote cloud-based storage.
Storage infrastructure management tools must ensure high-performance storage resources are available to users and are secure with sufficient capacity and data speed.
Strong connectivity within a storage infrastructure is essential to ensure admins can securely transport data, once created, to where they can safely store, archive and retrieve it. SANs and internal networks, such as those using Ethernet, are key assets for storage connectivity.
As the amount of data increases, scalability of storage resources is necessary to accommodate the changes. This can involve scaling up or scaling out physical storage devices or using NAS to establish a hybrid arrangement of on-site and cloud storage.
Capacity management
Capacity management ensures that the storage infrastructure has ample capacity for applications, files, databases, utilities and other resources.
Capacity management applications, especially those using AI, monitor a variety of storage parameters -- such as active and static storage, numbers of storage transactions and changes in storage activity -- to provide data that administrators use to scale resources up or down. That data identifies when an organization needs additional storage so administrators can order and install equipment in time to use in production.
Data management
Data management policies and standards directly impact storage infrastructures. Data protection and privacy are increasingly important based on several standards and regulations, especially GDPR. Storage infrastructures must protect data, ensure its accessibility and privacy, and minimize the likelihood of data loss, data corruption and data theft.
Performance management
If users must wait excessive periods of time to access or back up files, it could compromise storage performance. Performance management activities examine processes associated with moving data between users and storage devices. They present various metrics that identify when performance does not meet expectations. AI can enhance storage performance by analyzing data from various sensors and data collection tools. The systems then recommend steps to enhance performance and identify potential issues before they occur.
It might be necessary to examine the internal networks that employees use to connect into the IT environment. Also examine the SANs that connect storage devices with servers and other storage infrastructure devices. Storage administrators can adjust various devices to provide greater bandwidth. They also attempt to identify and remove roadblocks to storage performance, such as problems with storage devices and cyberattacks that sabotage resources.
Storage availability management
It can spell disaster for an organization if storage resources suddenly become unavailable or insufficient. Storage administrators must prepare for such events by ensuring that backup plans are available to address unplanned storage changes and proactively communicating with key users to keep abreast of their short- and long-term requirements. By taking a proactive approach to storage, administrators can prepare for unplanned requirements. AI technology is an important resource for proactive storage management.
Be on top of changes to the business -- perhaps a merger or acquisition, for instance -- that could alter storage requirements. From that point, it is a matter of analyzing the likely storage capacity requirements and arranging with the primary storage supplier to have resources readily available. When cloud storage is part of the mix, the administrators must also be in regular touch with the cloud vendors to ensure that resources can be available quickly.
Storage access management
Access management ensures that employees who need storage resources can access them on demand. This is often part of the overall access security approach taken by the organization. It can include the use of multifactor authentication for access verification, among other resources.
A user's profile can specify the storage resources available to that particular user. Regularly monitor user access activity for storage capacity planning and to identify possible security breaches.
Operations management
Storage operations management today is far more automated than in previous decades, which makes storage administrators' jobs easier but no less important. The advent of AI helps administrators better anticipate storage capacity changes based on an analysis of historical trends and current intelligence. And with so many storage options available -- both on-site and cloud-based -- automated storage capacity management has become an essential tool for storage administrators.
Software-based storage technology makes it possible to see the entire storage infrastructure -- from all corners -- which helps administrators manage the entire storage portfolio. And considering that storage today is typically added as an automated service, admins can parcel out storage resources to where they are needed most. If service-level agreements are part of storage infrastructure management, automation makes it easier to meet the performance requirements.
Storage management for disaster recovery
Storage management is a key attribute of a strong technology disaster recovery (DR) program. Storage administrators can designate specific storage arrays for DR activities, in addition to devices for general data backup.
Availability of cloud-based storage has become an important tool for disaster recovery, as it can serve as primary as well as backup storage for critical systems, files, databases and other mission-critical assets. Software-based storage capacity management tools typically include disaster recovery components so that administrators and the technology DR team can make emergency storage available if the primary resources are suddenly unavailable.
The impact of AI on storage infrastructure management
Many tools include AI capabilities to improve storage infrastructure management. Features include the following:
- Storing data in appropriate tiers based on specific metrics.
- Data based on predictive analytics that identifies potential storage issues.
- Faster identification and triage of potential security risks.
- Enhancing HVAC system performance by evaluating data from various sensors.
Paul Kirvan, FBCI, CISA, is an independent consultant and technical writer with more than 35 years of experience in business continuity, disaster recovery, resilience, cybersecurity, GRC, telecom and technical writing.








