
vali_111 - Fotolia
Evaluate the top hybrid cloud providers
There are a few different ways you can go with hybrid cloud platforms. Take a look at the top offerings and overall strategy from IaaS vendors and other large infrastructure providers.
While the Big Three dominate the IaaS market, the hybrid cloud market is open to cloud hyperscalers and on-premises infrastructure providers alike because it combines public cloud, private cloud and traditional on-premises computing.
Hybrid cloud is popular among enterprises, with 87% saying they have a hybrid cloud strategy, according to the Flexera "2020 State of the Cloud Report." It can be a good way for organizations to start cloud computing -- it keeps users compliant and cloud costs in check.
However, picking the right hybrid cloud vendor is different than choosing a public cloud vendor. The Big Three public cloud platforms -- AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) -- have their differences, but for the most part it's still an apples-to-apples comparison.
Hybrid cloud platform comparisons are more apples-to-oranges. When choosing a hybrid environment, an organization's approach can be based upon a few different situations. A more traditional enterprise may opt for hybrid cloud because it wants greater scalability but doesn't want to rearchitect its legacy software for the public cloud. On the other hand, a cloud-first enterprise may opt for a hybrid model to run and house expensive machine learning data and analytics on private hardware.
Get to know some popular hybrid cloud options -- including those from IaaS vendors and traditional infrastructure providers -- as well as their services and capabilities.
IBM and Red Hat
IBM and Red Hat focus their hybrid cloud capabilities around IBM Cloud and the Red Hat Cloud Suite. IBM still has a public cloud, though it doesn't have the same reach as the Big Three's offerings. Instead, it and Red Hat, which IBM acquired in 2019, focus higher up the stack on platforms, applications and tools that facilitate hybrid cloud, even offering services that work directly with AWS, Azure and GCP.
IBM Cloud includes a suite of services, including IBM Cloud Pak and IBM Cloud Satellite, that enables you to run workloads on private and public clouds and edge locations, as well as in Kubernetes and VMware vSphere environments. And with recent investments in Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud, there are more options for enterprises to develop and deploy modern applications with IBM Cloud.
The Red Hat Cloud Suite offers multiple services you can use to build and manage a hybrid cloud. With the Linux-based RedHat OpenStack Platform, you can build your own public and private clouds, and manage them with Red Hat CloudForms. The previously mentioned Red Hat OpenShift is a flexible Kubernetes container platform you can use to manage hybrid cloud deployments. You can build applications and run workloads on Red Hat OpenShift and then host those OpenShift clusters on premises, or on IBM Cloud, AWS, Microsoft Azure or GCP.
VMware and Dell EMC
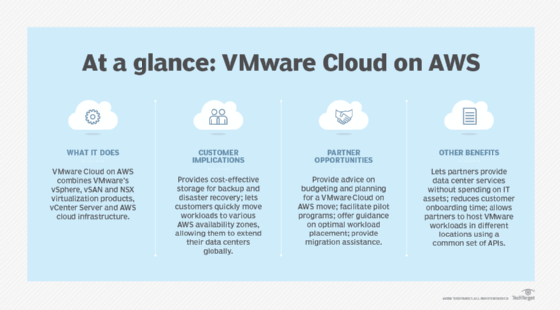
Like IBM and Red Hat, VMware and Dell EMC don't have a popular cloud IaaS as a foundation to build a hybrid cloud offering. However, VMware did partner with AWS to offer VMware Cloud on AWS, a hybrid service that organizations can use to run VMware workloads on AWS' public cloud.
It took a few years for AWS to even acknowledge the hybrid cloud model, let alone create services specifically for this type of architecture. VMware Cloud on AWS was the first major hybrid cloud offering available on Amazon's cloud, as it was co-developed by the two companies. This service is a good fit for enterprises with investments in VMware workloads that also need cloud scalability.
VMware also offers its own hybrid cloud platform with VMware Cloud Foundation. Built on VMware compute, storage and networking, Cloud Foundation brings Kubernetes and VMs together to automate builds to private and public clouds. Cloud Foundation is designed to give developers and administrators some of the flexibility and agility of the cloud, with the same VMware technologies they're used to.
Dell EMC tackles hybrid cloud in a few different ways, many of which tap into Cloud Foundation and VxRail. It offers the Dell EMC Hybrid Cloud Platform, which essentially provides hybrid and multi-cloud as a service. Its main benefit is its single vendor experience. It runs AWS, Azure, GCP and other cloud platforms from one central hub.
There's also the Dell Technologies Cloud Platform, also called Cloud Foundation on VxRail. This is a data center device that integrates Cloud Foundation with on-premises infrastructure to link workloads together in one platform. With this service, you can port workloads between on premises, private clouds and public clouds, and it includes automated lifecycle management to launch applications.
AWS
AWS Outposts is an on-premises device installed and operated by AWS. IT teams use it to host and provision AWS resources -- like EC2 instances and Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes -- on premises the same way they do in the cloud. This is good for AWS-invested organizations that need to move workloads in house or want to sync their on-premises and cloud infrastructure.
Outposts must connect to AWS' public cloud to work. When provisioned, it links with the nearest Region through AWS Direct Connect or an internet gateway. Outposts supports some basic AWS services like EC2, EBS and some container-based services, but it does not yet support S3, SageMaker, or Lambda, among others.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure offers a few different ways to build a hybrid cloud. Azure Stack, similar to AWS Outposts, is a on-premises device with which users can extend an Azure public cloud environment into a local data center or other privately owned locations. This suits organizations that may need to move applications between on premises and the cloud, for latency or compliance reasons.
There are three variants to Azure Stack.
- Azure Stack Edge. Use this Azure-managed device for workloads that need to process data close to its source, such as machine learning and IoT data.
- Azure Stack HCI. This is a hyperconverged Windows Server 2019 cluster that can run virtualized workloads on premises and connect to Azure cloud services for backup, recovery and monitoring. It works on hardware from several Microsoft partners.
- Azure Stack Hub. This service, run on industry standard hardware, offers an extension of Azure cloud services on premises. You can run Azure VMs, Key Vault, Functions, Resource Manager and more in your data center.
Like AWS Outposts, Azure Stack has some limitations in terms of what cloud offerings are available on premises, but it offers more cloud-native services than its AWS counterpart.
Azure Arc is a hybrid cloud management platform, which is in public preview at time of publication. It's a collection of services and management portals that bring Azure Resource Manager capabilities to Linux and Windows Server VMs, as well as Kubernetes clusters. Enterprises can then manage all their resources -- on premises or in the cloud, containers or VMs -- from Azure Arc.
The Azure Hybrid Benefit allows on-premises Windows Server customers to run Azure VMs at a reduced rate.
Google Cloud
GCP runs a container-forward hybrid cloud strategy. Google Anthos is a hybrid cloud platform that runs versions of Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) in Google's cloud and in an enterprise's on-premise vSphere environment. It also relies on service mesh technology, as well as configuration and security management tools. This enables enterprises to have a centralized view of their applications across unified environments.
Anthos is a way traditional enterprises can begin to modernize their applications and processes with containers. Cloud-forward organizations can also use it to move workloads on premises for compliance and security.
Google Cloud also offers hybrid cloud integrations with Cisco, VMware Cloud Foundation and CloudSimple, a VMware-to-cloud migration service Google acquired in late 2019.







