
Getty Images/iStockphoto
Explore top AWS storage types for file, block, object
There are several AWS storage types, but these four offerings cover file, block and object storage needs. Explore how the cloud storage choices compare with each other.
Organizations just starting out with AWS are sometimes surprised to learn that Amazon offers several types of cloud storage. Amazon makes it possible for an organization to pick the best possible storage type based on costs and a workload's requirements.
AWS storage types across file, block and object -- including Simple Storage Service (S3), FSx, Elastic File System (EFS) and Elastic Block Store (EBS) -- vary sharply by features, management and performance. Make the right choice for each workload.
Amazon S3
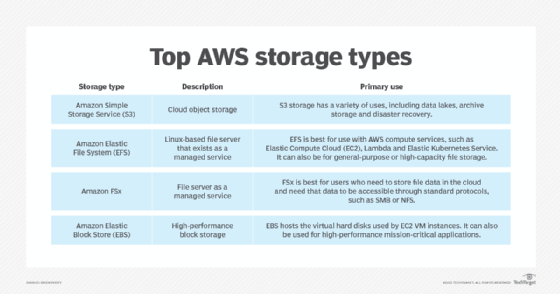
Amazon S3 is perhaps the most popular of all the AWS storage types. S3 is Amazon's cloud-based object storage.
S3 is versatile -- there are eight different storage classes. Each of these classes -- or tiers -- has its own unique characteristics and pricing. Some are better for creating data lakes (Standard), while others are suitable for data archiving (Glacier) or even deep archiving (Glacier Deep Archive). The S3 Intelligent-Tiering class can automatically move data to the cheapest tier based on how an organization uses the data.
S3 connectivity has become an industry standard. Numerous third-party products, in the cloud and on premises, support S3 connectivity. Similarly, smaller cloud providers, such as Backblaze, Cloudian and Wasabi, offer S3-compatible cloud storage.
Amazon FSx
Amazon FSx is essentially a fully managed, cloud-based file server. FSx enables users to choose the file system type. Deploy FSx on NetApp OnTap, OpenZFS, Lustre or Windows Server. Choose the platform that is most comfortable or the one that offers features that best align with the organization's requirements.
Don't worry about deploying or maintaining a cloud-based file server. Instead, Amazon manages all the back-end infrastructure.
The features and capabilities offered by FSx vary by platform, but each platform is configured for high availability. Users can access storage through industry standard protocols. For example, a file share that is hosted on FSx for Windows Server is accessible using the SMB protocol. Windows file servers also offer additional features, such as deduplication, compression, audit logging and automated backups.
Amazon EFS
Like Amazon FSx, EFS is a fully managed file server in the cloud. The main difference between these AWS storage types is that, while users can deploy FSx on their platform of choice, EFS is Linux-based and accessible through the NFS protocol.
There are several advantages to using EFS in addition to its managed service platform. First, storage scales automatically as users add or remove data and can accommodate multiple petabytes of storage. While EFS can be general-purpose storage, Amazon has specifically designed it to work with AWS compute services, such as Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Lambda, Elastic Kubernetes Service and others. Multiple services can simultaneously access an EFS share, making it a good choice for users who need to share data.
EFS consists of two separate storage tiers, and users can configure it to automatically move infrequently accessed data to a cheaper tier.
Amazon EBS
EBS is Amazon's high-performance block storage. EBS is the default AWS storage type for hosting EC2 virtual hard disks, but it can be for any high-performance workload in the cloud.
EBS supports throughput-optimized storage, as well as storage optimized for IOPS. When provisioning IOPS-optimized EBS, users can specify the number of IOPS required by workload.
Throughput-optimized EBS provides a base level of performance but can also accommodate potential bursts. Bursts are limited by a credit system in which credits automatically build up over time. Credits decrease when bursts occur. This method ensures that EBS can accommodate storage bursts when necessary but without consistently exceeding the baseline performance threshold.





