
Getty Images/iStockphoto
Explore Google Cloud Storage classes
For organizations that use Google Cloud Storage, it's crucial to store data in the optimal class. Understand top uses, benefits and drawbacks of Google Cloud's assorted services.
Like other hyperscale clouds, Google Cloud offers several different storage options. Though organizations have the most choices in object storage, Google Cloud also provides file and block.
All of Google Cloud's storage types are designed for low-latency access and high durability and can be redundant across regions. Additionally, there are no storage limits or minimum object sizes associated with any of the storage types. However, rather than treating storage as one size fits all, Google Cloud Storage classes are each designed for a specific use.
Google Cloud Standard Storage
As its name suggests, Google Cloud Standard Storage acts as multipurpose data storage. Standard is best for use with hot data, or data that users frequently access. It's also a good choice for transitory data that only exists for a short period. Some of the more common uses for Google Cloud Standard Storage include hosting websites or VM instances.
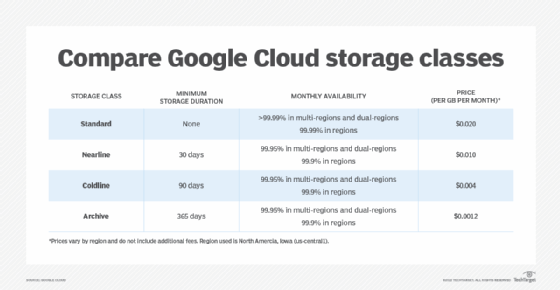
Standard Storage does not have a minimum duration, nor is it subject to data retrieval fees.
Most of the other Google Cloud Storage classes have a minimum duration. For example, users who create a file might not be able to delete it for 30 days or more. Storage types with these types of minimum durations are not suitable for transitory data.
Similarly, most of Google Cloud's storage types are subject to data retrieval fees. Users would not want to have to pay a data access fee -- which Google refers to as a "retrieval fee" -- for data they frequently access.
Google Cloud Nearline Storage
Google Cloud Nearline Storage is for data that organizations use actively but not daily. It's a good fit for data that users need to access between once a month and once per quarter. It can also store backups and archival data.
Nearline Storage costs less than Standard Storage but comes with a minimum storage duration of 30 days. There is also a retrieval fee to access Nearline Storage data.
Google Cloud Coldline Storage
Coldline Storage, as the name suggests, is for organizations to store the coldest data that they still occasionally need to access. In other words, data that needs access a few times a year at most may be a good fit for Coldline Storage.
Like with Nearline, Google charges a retrieval fee for Coldline Storage access. Coldline has a minimum storage duration of 90 days. The tradeoff, however, is that the at-rest storage cost is significantly lower for Coldline than Nearline.
Google Cloud Archive Storage
Google Cloud's coldest storage offering is Archive Storage. It's Google's cheapest storage and only suitable for data that users need to keep but hardly ever plan to access. Items in Archive Storage have a 365-day minimum duration.
Google charges a retrieval fee to access data in Archive Storage. However, Google's Archive Storage is different from the archival options offered by other major cloud providers. While competing clouds often require hours or days to retrieve data from archival storage, Google can retrieve it in milliseconds.
Google Cloud file and block storage
Standard, Nearline, Coldline and Archive are all types of object storage. However, not all Google Cloud storage is object storage. Google also offers file and block storage.
Google Cloud's block storage options consist of Persistent Disk and Local SSD. Persistent Disk storage is primarily for VMs but has other purposes, such as database hosting. Local SSD is best for stateless workloads but can also be for caching, scratch disks or other applications in which organizations don't require persistent storage.
Google's file storage is Filestore. It's essentially a cloud-based, managed file system. Organizations can scale Filestore based on capacity and performance requirements. It can handle demanding workloads.






