Speeds of storage networking technologies rise as flash use spikes
Thunderbolt is a high-speed interface designed to facilitate the transfer of all types of data, including audio and video, over a single cable between a host computer and a peripheral device. Thunderbolt technology supports the USB Power Delivery specification to enable either the host or the peripheral device to supply power to the other.
A Thunderbolt port on a computer enables the connection of up to six devices, including storage drives, video cameras, Ethernet network adapters, displays and docking stations. Thunderbolt storage networking technologies can be beneficial for backup, restore and archival storage operations due to its high speed and low latency.
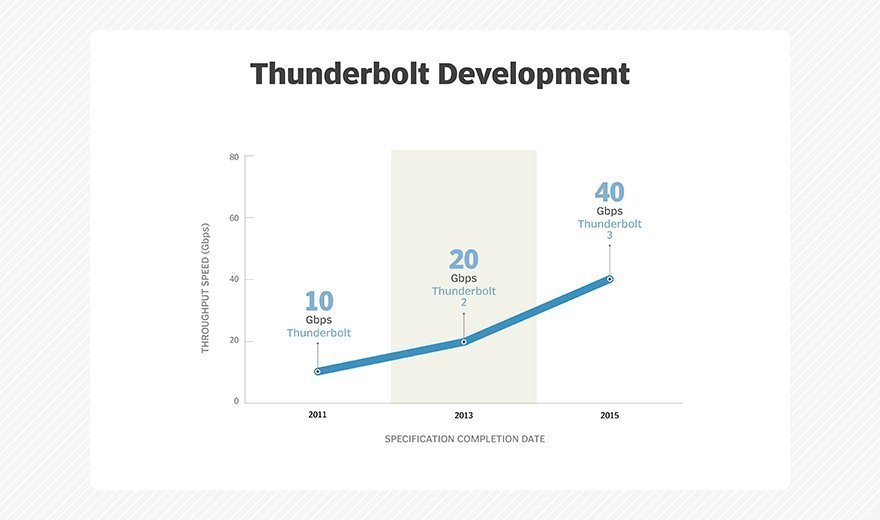
Intel developed Thunderbolt technology under the code name Light Peak and released the first version in 2011 at a speed of 10 Gbps, or a total of 20 Gbps running across two independent 10 Gbps channels. Apple was the first personal computer maker to offer products that supported Thunderbolt.
Thunderbolt 2 emerged in 2013 and combined the two previously separate 10 Gbps channels into a single 20 Gbps bidirectional channel. Intel said the updated Thunderbolt technology would enable the simultaneous transfer and display of high-resolution 4K video files. As with the initial version of Thunderbolt, Apple was the first vendor to ship products that supported Thunderbolt 2.
In 2015, Intel released Thunderbolt 3 to double the speed to 40 Gbps, through two channels of 10 Gbps flowing bidirectionally at the same time. Thunderbolt 3 connects to a computer bus via PCIe 3.0 for faster data transfer than the prior Thunderbolt versions offered with PCIe 2.0. An additional benefit with the third version of the Thunderbolt technology is reduced power consumption.
A Thunderbolt 3 port uses the newer USB Type-C connector to allow any data device, display or dock to connect. Thunderbolt and Thunderbolt 2 ports supported DisplayPort, developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association, and Mini DisplayPort, designed by Apple. Intel moved to the USB Type-C connector to enable Thunderbolt 3 to deliver 40 Gbps and fit into smaller form factor devices.
The third version of the Thunderbolt technology is backward compatible with prior Thunderbolt versions. Products built to the Thunderbolt and Thunderbolt 2 specifications require an adapter to work with Thunderbolt 3 devices.