
Anna Khomulo - Fotolia
MAMR tech fuels mammoth 20 TB hard drives
Age-old hard disk drives get a new twist as energy-assisted technologies fuel Western Digital's upcoming new 20 TB HDDs and rivals Seagate and Toshiba work on product plans.
There's plenty of life in spinning disk technology, with innovative new 18 TB and 20 TB hard drive options on the horizon just months after 16 TB models started shipping.
Faster NAND flash and Optane solid-state drives may command more attention, but hyperscalers, cloud providers and enterprises in need of high-capacity storage at a lower cost still turn to hard disk drives (HDDs).
Western Digital recently pushed the HDD envelope with plans to begin sampling helium-based 16 TB, 18 TB and 20 TB hard drive models that use nine platters and its "energy-assisted" recording technology for the first time. The company expects to ramp up production in the first half of 2020, after sampling the drives with select enterprise OEM and hyperscale cloud customers late this year.
All three enterprise HDD manufacturers -- Seagate, Toshiba and Western Digital -- have been exploring the use of microwave-assisted magnetic recording (MAMR) and heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) technologies to overcome the challenges associated with recording data reliably at increasingly high HDD densities.
Not 'full MAMR'
Western Digital's new 18 TB Ultrastar DC HC550, with conventional magnetic recording (CMR), and 20 TB Ultrastar DC HC650, with shingled magnetic recording (SMR), will use "energy-assisted" recording heads, but they will not be "full MAMR" devices, according to Lenny Sharp, senior director of datacenter HDD product planning and management at WD.
Sharp said Western Digital would continue to develop and refine its MAMR technology, while also working in parallel on HAMR technologies. The company has yet to disclose its roadmap for HDDs that will fully use energy-assisted technologies.
Seagate claimed to be on track to grow its HAMR technology beyond the 20 TB hard drive mark in 2020 and achieve 40 TB or higher by 2023. A Seagate spokesperson also noted the company's ongoing efforts to improve performance with new MACH.2 Multi Actuator technology.
Toshiba declined to discuss its high-capacity HDD roadmap beyond saying that it "pioneered the nine-disk helium-sealed mechanical design." Toshiba introduced nine platters with its 14 TB HDD models.
"In hindsight, Toshiba's early move to nine platters foreshadowed the industry's difficulty to increase areal densities with non-energy assisted technologies," said Trendfocus vice president John Chen. "Nine disk drives will be utilized by all HDD suppliers in 2020."
In addition to more platters, HDD manufacturers have also used disks that are slightly larger in diameter to increase capacity and two-dimensional magnetic recording (TDMR) readers to resolve narrower tracks, Chen said.
Cost-per-GB savings
IDC Research VP John Rydning said the small additional cost for the extra disk and heads comes in exchange for a substantial capacity improvement as well as a reduction in the price per GB. He said the new wave of massive hard drives offer pricing approaching 1.7 cents per GB.
"This value proposition almost always puts the highest capacity point HDD in great demand," especially with hyperscale and cloud service provider customers, Rydning said.
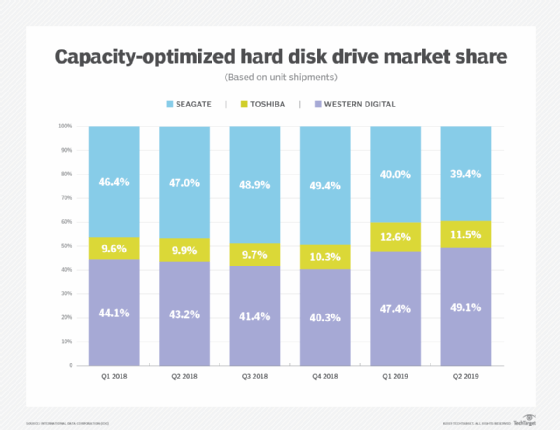
In the second quarter, 12 TB was the most popular capacity point, accounting for 27% of the unit shipments of 3.5-inch nearline drives that spin at 7,200 rpm, according to Trendfocus. Next in line at 16% were 4 TB HDDs that remain a sweet spot for OEMs, Chen said.
Trendfocus' second-quarter statistics show that 14 TB HDDs had the highest unit percentage growth and held 14% market share. The firm expects 14 TB will be the highest capacity point in unit shipments once third-quarter market statistics are in, according to Chen.
No significant volume of 16 TB HDDs shipped in the second quarter, but Chen thinks Seagate started to ramp up production in the second or third quarter. He said 18 TB CMR HDDs should emerge in volume by mid-2020.
SMR-based 20 TB hard drive
The new 20 TB hard drive that Western Digital recently unveiled uses SMR technology, in which tracks overlap like the shingles on a roof to increase the areal density. Host-managed enterprise SMR HDDs are best suited to workloads that write data sequentially, and they often require host-side adjustments to use them. Dropbox, one of the earliest adopters, noted that it had to make substantial changes to the software layer to prepare for running SMR.
Sharp said enterprise OEMs haven't shown much interest in SMR HDDs because they don't control the applications. But he said "virtually every hyperscale customer that we are engaged with" is working on SMR software because of the significant benefits in lowering cost per GB.
"They consume so much data, and the cost of that data deployed is such an intrinsic part of their business model that they cannot afford to miss out on any cost savings that might be possible," Sharp said. "SMR in the hyperscale data center is definitely a growing trend."






