public cloud storage
What is public cloud storage?
Public cloud storage, also called online storage, is a service model that provides data storage on a pay-per-use basis.
The public cloud storage model is similar to the way a public utility like electric or gas provides and charges for services.
Public cloud storage costs
Public cloud storage usage is generally charged on a per-gigabyte-per-month basis. In many cases, there are also charges for moving data in or out of the cloud storage facility, so data transfer and access charges are likely to increase the cost of cloud storage services.
Pricing for public cloud storage is typically tiered in a similar manner to the way storage is often tiered by service level in corporate data centers. For example, Microsoft Azure offers several cloud storage services, including file storage, object storage and data lake storage. Similarly, among Google's cloud storage products are block storage for virtual machines, high-performance file storage and object storage. Pricing for these services vary, generally based on the performance of the storage systems and access speed.
Some services have exceptionally low capacity-based rates, such as Amazon S3 Glacier's minuscule $0.0036 per-GB-per-month charge for archival storage. The tradeoff is the time it takes to access and download data from Glacier -- plans provide retrieval ranging from a few minutes to 12 hours. The cost of retrieving data will depend on data access speed.
Benefits of public cloud vs. locally installed storage
Cloud storage service's pay-per-use model enables companies to only pay for the actual storage capacity that they consume, as contrasted with purchasing and installing a storage system and paying for a set amount of capacity whether it's used or not. Most installed storage systems are rarely fully used because as the amount of drive capacity on a system rises, performance typically decreases.
In addition to being able to increase or decrease the amount of data storage capacity with the corresponding adjustments to costs, the on-demand nature of cloud storage makes it readily available to easily handle the peak conditions that may occur as expected or without notice for some businesses.
Another important advantage of using a public cloud for storage is that the provider is responsible for building and maintaining the storage infrastructure and its associated costs, including power, cooling, and technical support and maintenance. Those ongoing costs are often the most onerous operational expenses for data centers, so being able to avoid those charges could be very compelling for some companies -- particularly mid-sized or smaller organizations.
Disadvantages to public cloud storage
There are some drawbacks to using public cloud storage. For example, a company may be averse to turning over control of its data to a service provider, particularly if the company is subject to regulatory restrictions related to how they handle their customers' data. Some cloud storage service providers endeavor to address these data custody concerns by seeking and attaining certain compliance certification for regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
The public storage provider is responsible for maintaining and protecting its customers' data on its multi-tenancy infrastructure and assuring it remains secure during transfer to and from its facilities. However, if the provider suffers an outage, data may not be accessible for the duration. If the provider suffers a catastrophic failure, there is always the risk that the data may be lost. However, most cloud storage service providers store data in several locations, so while access to one's data may be impaired for a while, it will usually be recoverable.
How a company connects with its public cloud storage service may also be an issue. Most public cloud storage services support a variety of access methods with the internet generally the least expensive. But if a company requires faster or more secure access, the alternatives range from VPNs to several classes of leased lines or private lines. The cost of leased line access may be considerable.
Uses of public cloud storage
The earliest uses of public cloud storage were generally for data protection -- routine daily data backups for operational recoveries and disaster recovery. Using public cloud storage for data protection can yield substantial savings over having to maintain a remote facility for use as a secondary data repository. This represents a very economical use of public cloud storage for data protection as well as archiving email and static non-core application data.
Another early application of public cloud storage was for archival data. Companies tend to retain large amounts of data that is rarely accessed. Keeping this data in the data center can require maintaining high-capacity storage systems, which can be very expensive, especially for data that is not being actively used. Cloud storage can be ideal as it affords ample capacity at a relatively reasonable cost.
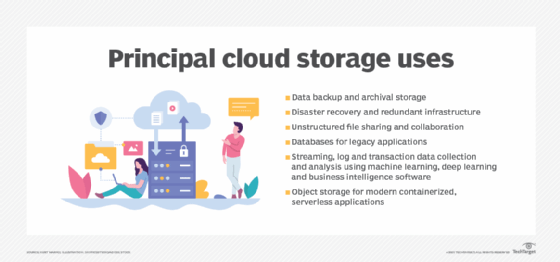
Initially, public cloud storage was not seen as a viable alternative to in-house storage for companies' critical business applications, but now all the major cloud storage service providers -- and many of the regional or smaller services -- offer an extensive array of application development and hosting products. That means that an application can sit beside its data hosted by a cloud service and because both data and app are local, performance is generally acceptable.
Most companies still maintain storage systems in their data centers and use public cloud storage. These hybrid environments often offer the best of both worlds -- local storage that can be internally secured and can provide required performance levels paired with cloud storage that offers limitless capacity and lower costs.
Editor's note: TechTarget editors revised this definition in 2023 to improve the reader experience.







