petabyte
What is a petabyte?
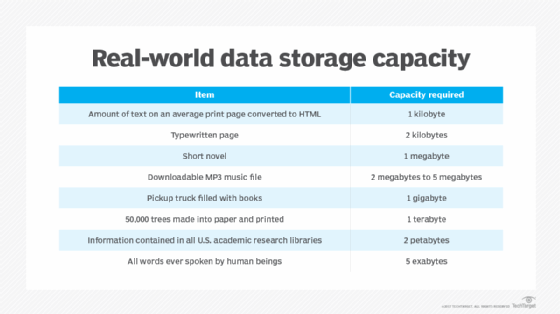
A petabyte is a measure of memory or data storage capacity that is equal to 2 to the 50th power of bytes. There are 1,024 terabytes (TB) in a petabyte and approximately 1,024 PB make up one exabyte.
Traditional network-attached storage (NAS) is scalable and capable of handling petabytes of data, but it can take too much time and use too many resources when going through the system's organized storage index.
In terms of memory, a typical laptop or desktop computer contains 16 GB of random access memory (RAM). A top-end server can contain as much as 6 TB of RAM. That means it would take 170 top-end servers -- or roughly 61,000 desktops -- to add up to a single petabyte of RAM.
For another example of how large a petabyte is, a typical DVD holds 4.7 GB of data. That means a single terabyte of storage could hold 217.8 DVD-quality movies, while a single petabyte of storage could hold 223,101 DVD-quality movies.

Petabyte storage vendors
Barely a decade ago, data storage vendors would boast of selling an aggregate of a petabyte or two in all of their storage systems sold. Due to the continued rapid increase in data storage capacity requirements, it's now common to see individual companies and even single storage systems with more than a petabyte of storage capacity.
Storage vendors that offer petabyte-level storage include the following:
- Fujitsu
- Qnap
- Spectra Logic
- StoneFly
- Vast Data
Petabyte backups and storage
Other data storage technologies can back up and archive at a petabyte scale.
- Snapshots and other disk-based backup technologies provide a local copy of the data, enabling a rapid restore.
- Tape and the cloud provide relatively low-cost backup options for petabytes of data, but they are more often used as off-site archival storage rather than primary storage.
- Solid-state storage can scan petabytes of data at a much higher speed without sacrificing data integrity.
- Object storage assigns each object a unique identifier, enabling the system to search large amounts of data in a flat space as opposed to examining a complete storage index to find a specific file.
Petabytes and big data
There is no specific quantity of data that qualifies as big data, but the term often refers to information in the petabyte, or even exabyte, range. Mining for information across petabytes of data is a time-consuming task. Organizations working with big data often use the Hadoop Distributed File System because it facilitates rapid data transfer and enables a system to operate uninterrupted while working with petabytes of data.
To get a sense of how big some data warehouse stores have become, in July 2017, the European research center CERN announced that its data center had 200 PB archived in its tape library.
With the increased use of 4K video and the advent of the internet of things, IDC predicted that by 2025 there will be 175 zettabytes -- or approximately 175,000,000 PB -- of data that needs storage.
Editor's note: This article was revised in 2022 by TechTarget editors to improve the reader experience.







