nearline storage
What is nearline storage?
Nearline storage is the on-site storage of data on removable media. The removable storage concept dates to the IBM mainframe computer and remains a popular option for individuals, small businesses and large enterprises. The term nearline is a combination of the words near and online.
Nearline storage products include magnetic disk, magnetic tape and high-density optical disk formats.
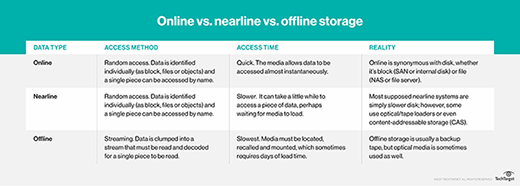
Compare nearline storage, always-on storage and archival storage
Data housed on nearline storage does not require the high availability or redundancy of primary storage. As such, it straddles online storage and long-term archiving. Although users access it only occasionally, the data needs to be available on demand. Nearline storage thus relies primarily on inexpensive disk storage.
Online storage -- or always-on storage -- provides rapid access to frequently used data, often to a large number of users simultaneously. Archival storage is often offline on tape cartridges or on an infrequently accessed tier of cloud storage.
By definition, online storage refers to electromechanical magnetic disks that need to remain continuously available to support ongoing business operations, while access to an archived copy typically requires some human intervention.
As solid-state storage remains popular, some industry experts believe that nearline storage represents one of the last significant growth areas for legacy HDD vendors.
Examples of removable nearline storage media
As the term implies, nearline storage is a midpoint between fast storage and archiving. The data in nearline storage is kept on a secondary or tertiary tier. In that respect, nearline storage works in a similar manner as an active archive. Nearline drives are not attached to a computer, but may be made available quickly to handle I/O tasks, without direct intervention of IT staff.
High-capacity nearline HDDs have emerged as a staple for bulk storage in enterprise data centers. These are Serial Advanced Technology Attachment drives that work with storage devices equipped for the serial-attached SCSI (SAS) protocol. Nearline SAS drives also are widely used for high-performance secondary storage.
Several hundred or more nearline SAS drives grouped together is known as a massive array of idle disks (MAID). This configuration offers the potential to reduce the cost per terabyte of storage to a level on par with magnetic tape.
In a MAID, the only drives that rotate are those performing reads or writes. For the most part, the drives in a MAID remain idle, which helps extend their overall life and helps to reduce power consumption. A drive will spin into action only when an application calls for data to be read or written.
A nearline storage system can request data from a specific cartridge in a physical tape library. A robotic autoloader handles the request and automatically loads the correct cartridge in a tape drive, either sequentially or in another specified order. The time between requesting the data and the insertion of the cartridge takes a few seconds.
Although it has given way to other backup storage media, many organizations continue to use tape for archiving due to its high capacities, relatively low cost and durability. Tape performs read and write operations faster than disk, although spooling is required to enable reads and writes in a sequential format.
Cloud nearline storage
The emergence of cloud platforms provides an additional option for parking data off site for rapid retrieval when needed. Many customers choose to buy some, if not all, of their storage as a service from providers. Using this model, a company leases space as a tenant on a service provider's physical IT infrastructure. This can help reduce costs associated with managing backups.
Google Cloud Nearline Storage is one of four services in the public Google Cloud Storage platform. The other classes are Google Cloud Standard Storage, Google Cloud Archive Storage and Google Cloud Coldline Storage.
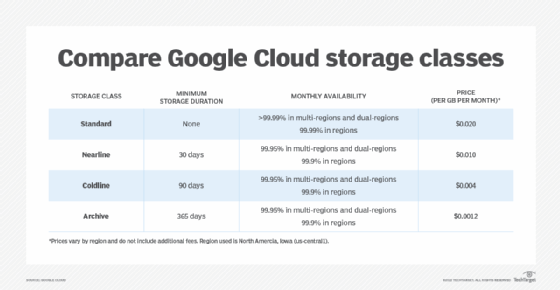
Google Cloud Storage was launched to compete with market leader Amazon Glacier cloud storage, which is designed for data users retrieve in three to five hours. Amazon Glacier is less expensive than Amazon Simple Storage Service, which retrieves data in real time.
Nearline storage media, when on the shelf, are immune to infection by online viruses, Trojan horses and worms because the media are physically disconnected from networks, computers, servers and the internet.
Editor's note: This article was revised in 2022 by TechTarget editors to improve the reader experience.






