What is BCDR? Business continuity and disaster recovery guide
Business continuity and disaster recovery, also known as BCDR, is a set of closely related practices that support an organization's ability to remain operational after an adverse event.
Resiliency has become the watchword for organizations facing a varied array of threats including natural disasters, pandemics and the latest round of cyberattacks. In this climate, business continuity and disaster recovery has a higher profile than ever before. Every organization, from small operations to the largest enterprises, is increasingly dependent on digital technologies to generate revenue, provide services and support customers who always expect applications and data to be available.
"Mission-critical data has no time for downtime," said Christophe Bertrand, practice director of data management and analytics at Enterprise Strategy Group (ESG), a division of TechTarget. "Even for noncritical data, people have very little tolerance."
Fifty-five percent of respondents to Uptime Institute's 2023 "Global Data Center Survey" had some sort of outage in the past three years. The annual survey, which polled more than 850 data center operators, reflected a downward trend in the percentage of organizations experiencing outages. In the 2020 survey, for example, 78% of the respondents reported an outage, according to Uptime Institute, a New York-based data center standards, professional services and training organization. The 2023 figure was the lowest recorded in the 13 years the survey has been conducted.
The report on the survey credited an increased focus on BCDR practices for the ongoing improvements, but also indicated that more needs to be done. "Uptime data shows that data center owners/operators have been investing in resiliency, adding more redundancy," the report stated. "In spite of this, outages remain an issue."
This comprehensive guide to BCDR further explains what it is, why it's important to organizations, who's typically involved in BCDR efforts and how to build a BCDR plan, among other topics. It also includes an overview of common BCDR scenarios as well as standards, templates, software and services that can be used in the planning process. Throughout the guide, hyperlinks point to related articles that cover the topics in more depth.
Why is BCDR important?
The role of BCDR is to minimize the effects of outages and disruptions on business operations. BCDR practices enable an organization to get back on its feet after problems occur, reduce the risk of data loss and reputational harm, and improve operations while decreasing the chance of emergencies.
Some businesses might have a head start on BCDR. DR is an established function in many IT departments with respect to individual systems. However, BCDR is broader than IT, encompassing a range of considerations -- including crisis management, employee safety and alternative work locations.
BCDR professionals can help an organization create a strategy for achieving resiliency. Developing such a strategy is a complex process that involves conducting a business impact analysis (BIA) and risk analysis as well as developing BCDR plans, tests, exercises and training.
Planning documents -- the cornerstone of an effective BCDR strategy -- also help with resource management, providing information such as employee contact lists, emergency contact lists, vendor lists, instructions for performing tests, equipment lists and technical diagrams of systems and networks. BCDR planning documents should be reviewed annually and whenever a business experiences a major change such as a merger or acquisition.
What is business continuity and disaster recovery?
An organization's ability to remain operational after an incident relies on both BC and DR procedures. The goal of BCDR is to limit risk and get an organization running as close to normal as possible after an unexpected interruption. These practices also reduce the risk of data loss and decrease the chance of emergencies, which helps maintain and even improve the organization's reputation.
Combining business continuity and disaster recovery into a single concept is the result of a growing recognition that business and technology executives need to collaborate closely when planning for incident responses instead of developing schemes in isolation.
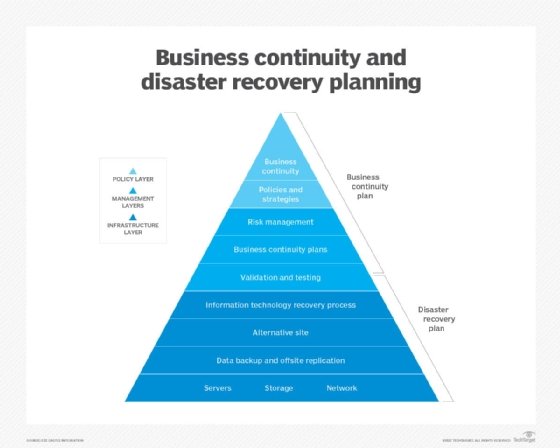
What's the difference between business continuity and disaster recovery?
BC is more proactive and generally refers to the processes and procedures an organization must implement to ensure that mission-critical functions can continue during and after a disaster. This area involves more comprehensive planning geared toward long-term challenges to an organization's success.
DR is more reactive and comprises specific steps an organization must take to resume operations following an incident. Disaster recovery actions take place after the incident, and response times can range from seconds to days.
BC typically focuses on the organization as a whole, whereas DR emphasizes the technology infrastructure. Disaster recovery is a piece of business continuity planning that concentrates on accessing data easily following a disaster. But BC also considers risk management and any other planning an organization needs to continue operations during an event.
There are similarities between business continuity and disaster recovery. They both consider various unplanned events, from human error to a natural disaster. They also have the goal of getting the business running as close to normal again as possible, especially concerning mission-critical applications. In many cases, the same team is involved with both BC and DR.
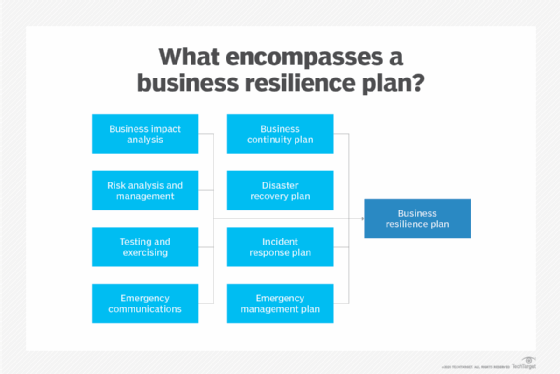
What's the difference between business resilience and business continuity?
Business resilience and resiliency began appearing in the BCDR vocabulary in the early 2000s. Resilience, at times, has been used interchangeably with business continuity, but the terms have different shades of meaning.
BC, for its part, aims to help organizations maintain business-critical functions during a disaster and in its aftermath. This approach revolves around guidelines detailing what a business must do to preserve essential functions.
Business resilience, sometimes termed organizational resilience, takes a somewhat wider view. This approach emphasizes adaptability in an era of sudden and unpredictable change. An International Organization for Standardization standard, ISO 22316:2017, defines organizational resilience as "the ability of an organization to absorb and adapt in a changing environment to enable it to deliver its objectives and to survive and prosper."
What’s the difference between organizational resilience and operational resilience
Operational resilience is related to business or organizational resilience but tends to focus on specific lines of business, business processes or systems.
For example, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines operational resilience as the "ability of systems to resist, absorb, and recover from or adapt to an adverse occurrence during operation that may cause harm, destruction, or loss of ability to perform mission-related functions."
BCDR scenario examples
BCDR managers must prepare for a wide range of disruptive events or, in some cases, combinations of events. The COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, led to supply chain disruptions and influenced the "great resignation," in which the number of people leaving their jobs increased. Similarly, ransomware and other cyberattacks often follow natural disasters, as threat actors attempt to exploit businesses preoccupied with a physical calamity.
Here are a few BCDR scenarios to consider:
Natural disasters
The potential list of emergencies includes severe weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes and floods, and other natural disasters such as earthquakes and wildfires. Business leaders should assess their organization's exposure to such disasters, considering the geographic locations of its operations and the historical frequency of a given event. They can then invest in BCDR strategies commensurate with the level of risk involved.
Power outages
Natural disasters, equipment failure and grid overload can all lead to power outages. Risk mitigation approaches run the gamut from diesel generators and uninterruptible power supplies for data centers to power banks and power stations for home-based employees.
Cyberattacks
Security incidents can affect business operations as well as IT systems. A ransomware attack, for example, could cut off access to business-critical files. A serious incident might compel an organization to activate its BCDR plan to resume operations.
IT outages
Hardware failures, software flaws and human error -- as well as the previously mentioned power failures and cyberattacks -- can all lead to IT downtime. An organization's BCDR plan may be called upon when outages result in significant data loss or the unavailability of critical services.
Public health crises
COVID-19 underscored the need for BCDR plans to encompass public health emergencies. The pandemic forced businesses into unfamiliar territory as they deployed social-distancing protocols and arranged for remote work on a massive scale. The potential scope of health crises includes pandemics, regional infectious disease outbreaks and bioterrorism.
Physical security threats
Here, the concerns range from workplace violence to civil unrest. A BCDR plan can bring together cybersecurity and physical security, traditionally the responsibility of a company's facilities management function.
Supply chain disruptions
Geopolitical events, pandemics and transportation disruptions can all result in supply chain bottlenecks. A BCDR plan can make provisions for alternative sourcing and supply routes when the usual suppliers and transportation networks are unavailable.
Why should you use BCDR, and when should it be activated?
Motivations for an organization developing a BCDR strategy might include protecting the lives and safety of employees, ensuring the availability of services to customers and protecting revenue streams. Competitive positioning and reputational management are factors that often underlie other motivators: A business perceived as unable to protect employees or deliver services will struggle to attract workers and customers.
The regulatory and compliance environment also influences organizations in their pursuit of BCDR. The HIPAA Security Rule, for example, requires covered entities such as hospitals to provide an emergency mode operation plan, which includes "procedures to enable continuation of critical business processes for protection of the security of electronic protected health information."
Similarly, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), an organization that oversees securities broker-dealers, requires such firms to "create and maintain written business continuity plans" that address emergencies or disruptions to the business. FINRA spells out its required business continuity measures in its emergency preparedness rule.
U.S. federal agencies are also required to develop BCDR strategies, which in government terminology are called continuity of operations plans. The aim is to "ensure that essential government services are available in emergencies -- such as terrorist attacks, severe weather, or building-level emergencies," according to the Government Accountability Office.
Customers might also put pressure on businesses to develop adequate BCDR plans. An assessment of an organization's BCDR stance might be part of a prospective client's vetting process. Federal regulators, such as the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), encourage banks to include resilience as part of the vendor due diligence process. Specifically, OCC Bulletin 2023-17, "Third-Party Relationships: Interagency Guidance on Risk Management," states that banks should "determine whether the third party maintains appropriate operational resilience and cybersecurity practices, including disaster recovery and business continuity plans that specify the time frame to resume activities and recover data."
The "why" of BCDR potentially has many answers, and the "when" of business continuity and disaster recovery is similarly nuanced. Organizations must weigh several factors before declaring a disaster and triggering the BCDR plan. Chief among those is the expected duration of an outage, its effects on the organization, the financial cost of activating the BCDR plan and the plan's potential to cause disruption itself. Paradoxically, the process of failing over from an organization's primary place of business to a backup facility -- and then failing back after an event -- might significantly interrupt operations, noted Paul Thomann, regional principal for cloud and data center transformation at Insight Enterprises, a solutions integrator based in Chandler, Ariz.
Accordingly, an organization's leadership must carefully size up when to enact the BCDR plan. Migrating to a backup facility, Thomann said, "comes with an impact to the budget." An organization, for instance, might deem a six-hour outage not significant enough to make the disaster recovery call.
That decision, particularly in larger enterprises, is typically made by a committee rather than an individual executive, Thomann said. The committee might consist of the CEO, CFO, CIO and other C-suite executives, he added.
BCDR management teams
The team that builds, manages and -- in the event of a disaster -- executes a BCDR plan should be cross-functional, drawing upon multiple stakeholders and pockets of expertise across the organization.
The team's leadership varies somewhat by organization. In a large enterprise, for example, the risk management officer might chair the BCDR team, with a representative from the IT department as a vice chair, said Jeff Ton, an author and speaker on IT topics.
A chief resilience officer, an emerging C-level role, might also lead BCDR and crisis management activities at larger companies.
Smaller organizations lacking a risk management department might appoint the CFO to lead the BCDR team, Ton noted. And, in some cases, the IT department head might direct the team.
Other members of the team typically include representatives from the organization's key business functions: for example, finance and accounting, facilities, marketing, public relations and legal, including both in-house and outside counsel.
The task of pulling multiple stakeholders together to develop a BCDR plan -- and conducting the necessary impact and risk analyses -- can prove challenging. Project management thus becomes an important consideration. Organizations should think about appointing a project manager to shepherd the process of building a BCDR plan, Ton noted.
The BCDR team should also take on the task of ongoing business continuity management, making sure plans are up to date. Business initiatives and data center technologies change frequently, so BCDR plans will need regular maintenance to stay on point.
A BCDR team might also want to consider a business continuity plan audit, which assesses the effectiveness of a plan. The audit should detail the risks that could threaten the plan's success and test the controls currently in place to determine whether those risks are acceptable to the organization. An IT general controls audit can also be used to assess risks to the infrastructure and identify areas for improvement.

The various roles and responsibilities of BCDR team members, from planning to testing, can be detailed in an organization's business continuity policy. Such a policy might also encompass external personnel, such as vendors and customers.
BCDR training and certifications
Another aspect of BCDR team building is getting individuals up to speed on BCDR best practices. To that end, BCDR team members can avail themselves of business continuity training and certification programs.
The Business Continuity Institute, a global professional organization based in the U.K., offers its Certificate of the Business Continuity Institute, which covers business continuity management process and practices. It also offers online courses, including introductory ones on business continuity and organizational resilience.
BCM Institute, a Singapore-based education and training organization that focuses on business continuity management, offers several certifications, including Business Continuity Certified Expert, Business Continuity Certified Planner and Business Continuity Certified Specialist. In addition, it offers courses in business continuity management and crisis communication, among other topics.
Other organizations that grant professional business continuity certifications include Certified Information Security, DRI International, the International Consortium for Organizational Resilience and the National Institute for Business Continuity Management.
Conferences also provide an opportunity to educate BCDR team members. Ton said DRI and Disaster Recovery Journal are among the organizations that host events on business continuity and resilience.
How to conduct BIA and risk assessments for BCDR
BIA and risk assessments are critical tools for organizations building a BCDR strategy and plan.
The initial step in launching this process is gathering BCDR management team members to conduct the BIA. This group gathers information from business stakeholders, using automated surveys and in-person interviews. The responses are then compiled for the subsequent analysis step. The analysis helps the team identify information that will inform BCDR planning. That information includes the following:
- The critical business processes that must be recovered in the event of a disaster.
- The resources required to support those critical processes -- communication/collaboration tools, databases, end-user devices, etc.
- Internal and external relationships and dependencies.
With the analysis completed, the BIA group creates a report to document its findings.
The BCDR management team then shifts its focus to the risk assessment, which complements the BIA. This phase involves determining the potential hazards a business faces and the likelihood of their occurrence. Team members must also consider the potential damage and financial effects of a given threat should it occur. Based on those findings, the team might create a risk assessment matrix, which summarizes the threats, the probability of events happening and their potential consequences.
The matrix and other risk assessment documentation can now be coordinated with the BIA report. For example, the team can map the threats profiled in the risk assessment to the critical processes identified during the BIA process.
How to build a BCDR plan
Organizations can break down a BCDR plan into separate BC and DR components.
Specifically, a business continuity plan (BCP) contains contact information, change management procedures, guidelines on how and when to use the plan, step-by-step procedures and a schedule for reviewing, testing and updating the plan. A disaster recovery plan (DRP) features the following items:
- A summary of key action steps and contact information.
- The defined responsibilities of the DR team.
- Guidelines for when to use the plan.
- The DR policy statement.
- Plan goals and history.
- Information on geographical risks.
- Incident response and recovery steps.
- Authentication tools.
The DRP should also take staffing into account, ensuring that personnel able to execute the various steps of a DR plan are always available to enact critical recovery tasks. Like the BCP, it should be consistently reviewed, tested and updated.
Developing the BCP and DRP typically starts with the BIA and risk assessment, outlined above. Other steps in a planning checklist include risk mitigation and an emergency communications plan. The latter details the method, or methods, an organization will use to disseminate information on an emergency to employees, customers and third parties.
BCDR testing
Testing a business continuity and disaster recovery plan provides assurance that the recovery procedures put in place will work as expected to preserve business operations. The testing phase might also highlight areas for improvement, which the organization can address and incorporate into the next version of the plan.
Tests can range from simple to complex. A discussion-based tabletop exercise brings together participants to walk through the plan steps. This type of test helps employees with BCDR roles become more familiar with the response process, while letting administrators assess the effectiveness of the BCDR plan.
On the other end of the testing spectrum, a full-scale test simulation calls for participants to perform their BCDR functions rather than just discussing them. These drills might involve the use of backup systems and recovery sites.
Even in its simplest forms, testing requires time, funding, management support and employee participation. The testing process also includes pre-test planning, training test participants and reporting on the test.
The frequency of testing varies by organization. Larger enterprises should conduct tabletop exercises at least quarterly, while smaller organizations can test less often, Insight Enterprises' Thomann said. A full BCDR test, which is more time- and resource-intensive, can be conducted annually, he added.
Ton also recommended a quarterly testing schedule for disaster recovery, with a full DR test conducted twice a year and tabletop exercises in between those tests. Business continuity tests can be conducted annually on a separate basis, according to Ton. He said he's found it more effective to separate the tests because conducting the DR one on its own is less disruptive to the organization.
Periodic testing, plan maintenance and resilience are interrelated. An organization improves its resilience when it updates its BC and DR plans and then tests them continually.
BCDR cost management
Changes in the threat landscape or new business ventures might compel an organization to expand its BCDR coverage. That change in scope could call for spending on consulting services or backup and disaster recovery technologies. BCDR managers might need to seek new funding for the expanded BCDR plan and resilience technologies if the dollars aren't available in the current budget.
An investment proposal should be built on a business case that emphasizes the positive results the new BCDR capabilities will provide for the organization. The bid for funding should also determine whether the revised BCDR plan will affect other areas, such as cybersecurity.
Ton said organizations should strike a balance between the level of investment in BCDR approaches and the anticipated financial effects of a given disaster scenario. "You don't want to come up with a solution that costs 200 times more than the disaster would have," he said.
Asking business leaders from various corporate disciplines to estimate the expected costs associated with different types of events can help organizations establish a baseline from which they can make informed BCDR investment decisions.
Standards, templates, software and services for BCDR planning
Organizations embarking on a business continuity and disaster recovery planning process have numerous resources to draw upon. Those include standards, tools ranging from templates to software products, and advisory services.
"To build a plan, you have many templates that exist and many best practices and many consultants," ESG's Bertrand said. "There's no reason not to have a strong DR plan."
BCDR standards
Government and private sector standards bodies, including NIST and ISO, have published BCDR guidelines. The standards, which cover topics from crisis management to risk assessment, provide frameworks on which businesses can build their BCDR plans.
The following is a sampling of standards:
- ISO 22316:2017 Security and resilience -- Organizational resilience -- principles and attributes (to be replaced by ISO/AWI 22316, which is currently in development).
- ISO 22301:2019 Security and resilience -- Business continuity management systems -- Requirements.
- ISO 22313:2020 Security and resilience -- Business continuity management systems -- Guidance on the use of ISO 22301.
- ISO 22320:2018 Security and resilience -- Emergency management -- Guidelines for incident management.
- ISO/IEC 27031:2011 Information technology -- Security techniques -- Guidelines for information and communication technology readiness for business continuity (to be replaced by ISO/IEC FDIS 27031 once it's finalized.)
- ISO 31000:2018 Risk management -- Guidelines.
- IEC 31010:2019 Risk management -- Risk assessment techniques.
- ISO/TS 22317:2021 Security and resilience -- Business continuity management systems -- Guidelines for business impact analysis.
- FINRA Rule 4370. Business Continuity Plans and Emergency Contact Information.
- National Fire Protection Association 1660 -- Standard for Emergency, Continuity and Crisis Management: Preparedness, Response and Recovery.
- NIST Special Publication 800-34 Rev. 1: Contingency Planning Guide for Federal Information Systems.
- American National Standards Institute/ASIS ORM.1.201 Security and Resilience in Organizations and Their Supply Chains.
Business continuity and disaster recovery plan templates
Templates provide preset forms that organizations can fill out to create BCDR planning documents. Some templates cover the BCDR plan as a whole or address particular aspects of BCDR planning.
This general BCP template, for example, includes provisions for natural disasters, fires, network service provider outages and floods or other water damage. A planning template can also assist SMBs, which could simplify the process, depending on an organization's size and complexity.
A BCDR plan might call for a service-level agreement (SLA), which sets standards for the quality of an organization's BCDR recovery program. It can also help ensure services obtained through third parties, such as DR hot sites, perform at acceptable levels. This template addresses SLAs for BCDR programs.
As noted above, conducting a BIA can help organizations with business continuity planning. This BIA report template provides a mechanism for documenting parent processes, subprocesses and the financial and operational effects in the event of an interruption.
Organizations can also benefit from scheduling BCDR activities for the ongoing care and maintenance of their business continuity strategy. Activities range from scheduling a BIA to reviewing a technology disaster recovery plan.
BCDR software
Specialized BCDR software provides another tool for organizations ready to build a plan. BCDR products, sometimes referred to as business continuity software or business continuity management software, aim to help organizations build business continuity and disaster recovery plans. They typically cover several planning activities, such as BIA and risk assessment, and offer incident response capabilities.
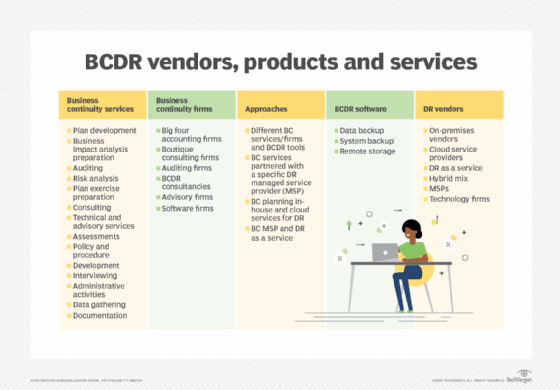
There also are other approaches to BC and DR technologies, including business continuity services mixed with disaster recovery software.
G2, which publishes peer reviews on its online software marketplace, listed 83 offerings in the business continuity management category as of February 2024. TechTarget entered a strategic content sharing partnership with G2 in February 2024.
BCDR planning services
Another option is to outsource the organization's BCDR needs to a third-party firm that can provide risk analysis, plan development and maintenance, and training. It's incumbent upon the business to analyze its needs before selecting a BCDR firm, defining what it wants to outsource, what services it expects of the vendor, the risks of an outsourcing agreement and how much it plans to spend.
Potential sources of business continuity services include auditing firms, accounting firms and consultancies. Auditing firms determine the extent to which a business adheres to business continuity standards, while accounting firms take on tasks such as conducting a BIA. Consulting firms, meanwhile, can advise businesses on establishing business continuity procedures.
In addition, managed services providers (MSPs) often serve as virtual CIOs for their SMB customers. In that role, MSPs can help with BCDR planning. For example, they can use their knowledge of a customer's IT assets to develop a plan for dealing with technology outages.
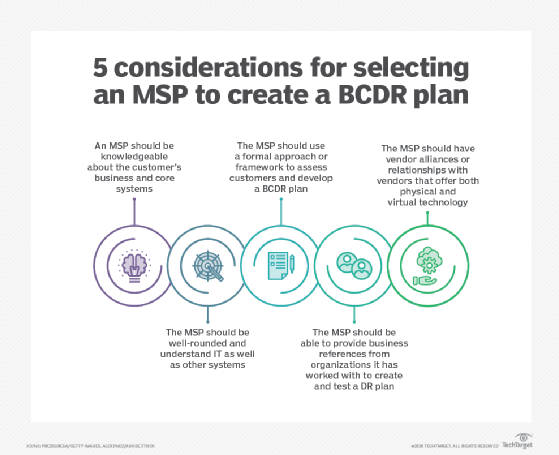
Supporting technologies and strategies
The technology options for executing the DR portion of a BCDR plan have expanded in recent years due to the accelerated adoption of cloud computing. Traditionally, organizations built or hired out an off-site facility to handle their DR needs. Such DR sites require a duplication of in-house production systems, potentially putting them beyond the financial reach of an SMB. However, cloud-based offerings such as cloud DR and disaster recovery as a service have made DR more accessible for smaller organizations.
Other resilience offerings include emergency notification systems, cybersecurity systems and incident response systems, which might be included in business continuity management products.
Keeping the plan updated to avoid BCDR pitfalls
Change is perhaps a BCDR plan's key nemesis. As the pace of technology change accelerates, organizations are left updating IT equipment -- from storage and servers to networks and their associated devices. Some IT assets are moving to the cloud. A 5-year-old BCDR plan is unlikely to reflect -- and prove adequate to protect -- the current IT estate.
An organization's change management process can help address this issue. Change management oversees adjustments to systems, networks, infrastructure and documents. It addresses similar situations as BCDR planning and testing, so an organization might decide to include business continuity and disaster recovery in the change management process.
That process contains six major activities:
- Identify a potential change.
- Analyze the change request.
- Evaluate the change.
- Plan the change.
- Implement the change.
- Review and close out the change process.
An organization, of course, is also subject to change. Organizations make acquisitions, divest non-core operations and create new lines of business, for example. An effective BCDR plan must be periodically updated to account for those developments. Regularly scheduled BCDR testing can expose gaps in the plan where it has failed to account for technology or business changes.
Perceptual gaps can also undercut BCDR plans. ESG's Bertrand said many organizations adopting SaaS offerings have a false sense of security regarding data protection.
ESG's "Data Protection for SaaS" report, published in February 2023, found that about 33% of surveyed IT leaders whose organizations use SaaS rely on the vendor to protect the application data residing on their SaaS tools. SaaS vendors, however, are not responsible for customers' data, Bertrand noted.
Pitfalls abound, but an organization can use a BCDR checklist -- or a series of checklists -- covering plans, policies and recovery strategies to root out potential problems and flag BCDR weak points. BCDR teams should also stay abreast of the changing threat landscape to make sure their plans reflect emerging threats. Business continuity risks that organizations should monitor range from evolving cybersecurity attacks to active shooter incidents.
The future of BCDR
BCDR planning and execution will continue to evolve with the changing nature of threats. Below are a few developments to consider:
- The confluence of cybersecurity and BCDR. The role of cyberattacks, such as ransomware, in disrupting business operations appears set to continue. Cybersecurity and business continuity have been traditionally separate functions in an organization, but will become increasingly interlocked in data protection and recovery strategies.
- AI's growing influence on BCDR. AI will likely become a bigger factor in some BCDR elements. In risk management, for instance, AI use cases include threat intelligence analysis, security information and event management, fraud detection, workplace risk reduction and data classification.
- More planning for environmental hazards. Air quality issues have emerged in recent years amid wildfires in the western U.S. and Canada. In June 2023, Google advised East Coast employees to work from home when smoke from Canadian wildfires created hazardous air quality levels. Organizations might look more closely at such environmental factors as they update BCDR plans.
- Sustainability and BCDR pull closer together. Corporate sustainability initiatives focus on efficient power usage and equipment recycling among other environmental-focused practices. BCDR planners can also address environmental issues as they devise ways to boost the sustainability of technology and systems.
Editor's Note: This article was republished on March 1, 2024, to reflect market changes.
John Moore is a writer for TechTarget Editorial covering the CIO role, economic trends and the IT services industry.






