blockchain storage
What is blockchain storage?
Blockchain storage is a way of saving data in a decentralized network, which utilizes the unused hard disk space of users across the world to store files. The decentralized infrastructure is an alternative to centralized cloud storage and can solve many problems found in a centralized system.
How blockchain storage works
Blockchain relies on distributed ledger technology (DLT). The DLT acts as a decentralized database of information about transactions between various parties. Operations fill the DLT in chronological order and are stored in the ledger as a series of blocks. An interconnected chain is formed between blocks with each one referring to the block before it, thus creating a blockchain.
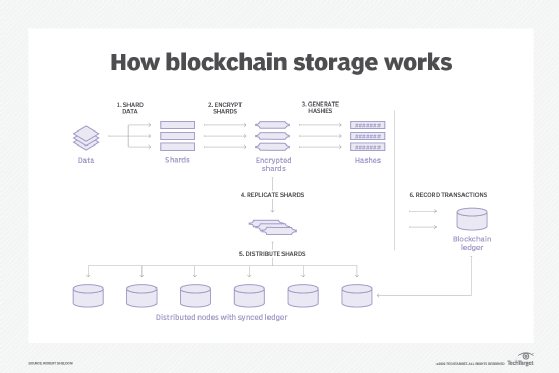
In blockchain storage, files are first broken apart in a process called sharding. Each shard is copied to prevent loss of data should an error occur during transmission. The files are also encrypted with a private key that makes it impossible for it to be viewed by other nodes in the network. The replicated shards are distributed among decentralized nodes all over the world. The interactions are recorded in the blockchain ledger, allowing the system to confirm and synchronize the transactions across the nodes in the blockchain. Blockchain storage is designed to save these interactions forever and the data can never be changed.
Blockchain storage vs. cloud storage
Blockchain storage is a potentially cheaper, more secure and more reliable alternative to centralized cloud storage.
Providers of centralized cloud storage prevent data loss by making copies of the data and storing it in different data centers. The large amount of data that is duplicated in this process can create excessive amounts of surplus information. Also, cloud storage requires enterprise-grade hardware for its data centers. These factors can make centralized data storage significantly more expensive than blockchain storage.
By taking advantage of the empty space on users' devices across the world, blockchain storage can cut up to 90% of the cost of centralized cloud storage, proponents claim. Individuals and businesses can profit by renting out the unused space on their hard disks for others to use.
Advantages of blockchain storage
In addition to the advantages explained above, having data stored across dozens of individual nodes also gives blockchain storage security benefits. Encrypting the files and distributing them across the decentralized network makes it harder for hackers to access the data. There is no central entity controlling access to files or possessing the keys needed to decrypt the files. The private keys are controlled entirely by the user, making it theoretically impossible for a third party to access the files. Sharding also promotes security and privacy.
Blockchain storage could also allow faster and more customizable storage systems because users are able to manipulate settings, such as the speed of retrieval and redundancy.
Expand your knowledge of blockchain technology
Top 9 blockchain platforms to consider in 2021
Blockchain terminology: A glossary for beginners
Current blockchain storage projects
BitTorrent, Filecoin, Sia and Storj are among the decentralized storage networks using blockchain.
BitTorrent's decentralized storage network is based on its file-sharing protocol (BTFS) and Tron's decentralized blockchain platform. The network lets storage "renters" pay "hosts" for their excess capacity.
The Filecoin distributed cloud storage network uses blockchain and the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) to let users purchase storage from providers on the network. IPFS is a peer-to-peer (P2P) hypermedia distribution system designed to provide a decentralized method for storing and sharing files. Nodes within the IPFS network form a distributed file system that can be accessed in many ways, including the Linux-based FUSE interface and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol). Local files can be added to the IPFS network and made available to the world.
Sia is a decentralized storage marketplace built on open source software developed by the SIA Foundation. The platform lets renters enter contracts with hosts that offer their excess storage.
Storj, based on the Ethereum blockchain platform, aims to provide private, secure and efficient P2P-based cloud storage. The Storj platform uses sharding and end-to-end encryption (E2EE) to store and protect data.
BitTorrent, Filecoin, Sia and Storj provide their own cryptocurrencies (BTT, Siacoin, STORJ token and FIL) in an attempt to create a market for buying and selling decentralized storage and encouraging its use. The major obstacle that organizations launching blockchain storage projects will face is scalability.







