storage as a service (STaaS)
What is storage as a service (STaaS)?
Storage as a service (STaaS) is a managed service in which the provider supplies the customer with access to a data storage platform.
The service can be delivered on premises from infrastructure that is dedicated to a single customer, or it can be delivered from the public cloud as a shared service that's purchased by subscription and is billed according to one or more usage metrics.
STaaS customers access individual storage services through standard system interface protocols or application program interfaces (APIs). Typical offerings include bare-metal storage capacity; raw storage volumes; network file systems; storage objects; and storage applications that support file sharing and backup lifecycle management.
Storage as a service was originally seen as a cost-effective way for small and mid-size businesses that lacked the technical personnel and capital budget to implement and maintain their own storage infrastructure. Today, companies of all sizes use storage as a service.
Uses of STaaS
Enterprises can use storage as a service for data transfers and redundant storage, as well as to restore any corrupted or lost data. CIOs might want to use STaaS for the ability to deploy resources in an instant or to replace some existing storage space -- leaving room for on-premises storage hardware. CIOs might also appreciate the ability to tailor storage capacity and performance per workload.
As an example, instead of maintaining a large tape library and arranging to store tapes off-site, a network administrator who uses STaaS for backups could specify what data on the network should be backed up and how often.
The company would sign a service-level agreement (SLA). The STaaS provider agrees to rent storage space on a cost-per-gigabyte-stored and cost-per-data-transfer basis. The company's data would then be automatically transferred at the specified time over the storage provider's proprietary wide area network (WAN) or the internet. If the company's data were to ever become corrupt or lost, the network administrator could contact the STaaS provider and request a copy of the data.
Storage as a service in cloud computing
Instead of storing data on premises, organizations that use STaaS typically utilize a public cloud for storage and backup needs. Public cloud storage might also use different storage methods for STaaS. These storage methods include backup and restore, disaster recovery, block storage, solid-state drive (SSD) storage, object storage and bulk data transfer.
Backup and restore refers to the backing up of data to the cloud, which provides protection in case of data loss. Disaster recovery might refer to protecting and replicating data from VMs.
Block storage enables customers to provision block storage volumes for lower-latency input/output (I/O). SSD storage is another storage type that is typically used for intensive read/write and I/O operations. Object storage systems are used in data analytics, disaster recovery and cloud applications and tend to have high latency. Bulk data transfers use disks and other hardware to transfer data.
Advantages of STaaS
Key advantages to STaaS in the enterprise include the following:
- Storage costs. Personnel, hardware and physical storage space expenses are reduced.
- Disaster recovery. Having multiple copies of data stored in different locations can better enable disaster recovery measures.
- Scalability. With most public cloud services, users only pay for the resources that they use.
- Syncing. Files can be automatically synced across multiple devices.
- Security. Security can be both an advantage and a disadvantage, as security methods may change per vendor. Data tends to be encrypted during transmission and while at rest.
Disadvantages of STaaS
Common disadvantages of STaaS include the following:
- Security. Users might end up transferring business-sensitive or mission-critical data to the cloud, which makes it important to choose a service provider that's reliable.
- Potential storage costs. If bandwidth limitations are exceeded, these could be expensive.
- Potential downtimes. Vendors might go through periods of downtime where the service is not available, which can be trouble for mission-critical data.
- Limited customization. Since the cloud infrastructure is owned and managed by the service provider, it is less customizable.
- Potential for vendor lock-in. It might be difficult to migrate from one service to another.
Popular storage-as-a-service vendors
Examples of STaaS vendors include Dell, HPE, IBM, NetApp and Pure Storage.
Other public cloud vendors with cloud storage services include the following:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- Microsoft Azure.
- Google Cloud.
- Oracle Cloud.
- Box.
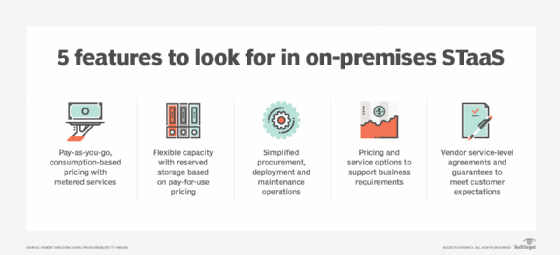
Before choosing a service method, an organization should consider the location of the data center, its security methods, cost, performance, availability, scalability and potential of vendor lock-in.
Editor's note: This article was revised in 2024 by TechTarget editors to improve the reader experience.







