Fibre Channel (FC) port types
What are Fibre Channel (FC) port types?
A Fibre Channel port is a hardware pathway into and out of a node that performs data communications over an FC link. (An FC link is sometimes called an FC channel.) In today's FC environments, three of the most common port types are the N-port, F-port and E-port.
| Port |
Full name |
Port function |
| N-port |
Node port |
Node port that connects to an F-port on an FC switch or to an N-port on another node |
| F-port |
Fabric port |
Switch port that connects to an N-port on an FC node |
| E-port |
Expansion port |
Switch port that connects to another FC switch to create an interswitch link (ISL) |
Either a server or a storage system can use an N-port to connect to an FC switch. An FC switch, in turn, can use an F-port to connect to either type of node. An FC switch can also use an E-port to connect to another switch or an FL-port to connect to an arbitrated loop. These are by no means the only types of switches available, but they represent some of the most common.
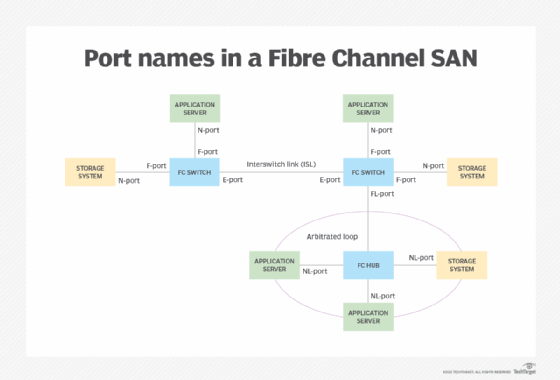
An arbitrated loop is an FC topology that uses arbitration to establish a point-to-point circuit for connecting devices in a one-way ring. An arbitrated loop prevents multiple ports from sending frames at the same time. A node in an arbitrated loop uses an NL-port to connect the next node in the loop, often via an FC hub. An FC switch can connect to the arbitrated loop through an FL-port. An arbitrated loop might also include other port types.
| Port |
Full name |
Port function |
| L-port |
Loop port |
FC port that contains the functionality necessary to support an arbitrated loop |
| NL-port |
Node loop port |
Type of L-port on a node in an arbitrated loop that connects to an NL-port on another node in the loop, often via an FC hub; an NL-port can also connect to an FL-port on an FC switch, either directly or through a hub |
| FL-port |
Fabric loop port |
Type of L-port on an FC switch that connects to an arbitrated loop, either through an FC hub or directly to an NL-port |
| GL-port |
Generic loop port |
Switch port that can operate as an F-port, E-port or FL-port |
| Nx-port |
Multipurpose node port |
Node port that can operate as an N-port or NL-port |
| Fx-port |
Multipurpose fabric port |
Switch port that can operate as an F-port or FL-port |
In addition to the more common port types, an FC network might incorporate other port types as well, such as the B-port, G-port, EX-port or TE-port. In some cases, a port might be specific to a vendor or to one of that vendor's product lines. For example, the TE-port is specific to the Cisco MDS 9000 family of switches.
| Port |
Full name |
Port function |
| B-port |
Bridge port |
Port on a bridge device that connects to an E-port on an FC switch |
| G-port |
Generic port |
General-purpose FC port that can operate as an F-port or E-port |
| EX-port |
External E-port |
FC port that connects an FC router and FC switch; on the switch side, it looks like a normal E-port, but on the router side, it is an EX-port |
| TE-port |
Trunking E-port |
Trunking port that expands E-port functionality to support virtual storage area network (SAN) trunking, the FC trace feature and transport quality of service parameters |
See also: SAN switch, Fibre Channel over Ethernet, Fibre Channel director, Fibre Channel adapter, Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop, non-volatile memory express over Fibre Channel and World Wide Name.





