
Fotolia
Where is QLC NAND the most useful in the enterprise?
Quad-level NAND has its benefits, but is it right for enterprise-level companies? While it can be plagued by performance and durability issues, the technology still has its uses.
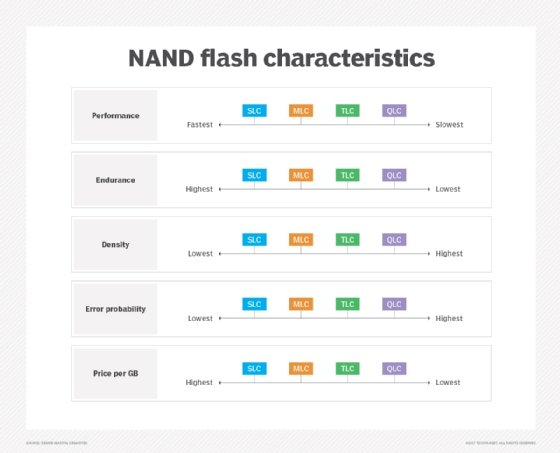
It's at least somewhat tempting to dismiss quad-level NAND as a poor choice for use in enterprise-class organizations. After all, the quad-level cells in storage devices are far less durable than single-level, multi- or two-level, and triple-level cells. Furthermore, QLC NAND generally doesn't perform quite as well as competing solid-state storage technologies. Even so, quad-level NAND does have its place.
Despite its flaws, QLC technology has found some fans among storage vendors. Micron is offering a QLC SSD -- the Micron 5210 ION SSD -- which is specifically designed for use in the data center. This drive is available in capacities ranging from 1,920 GB to 7,680 GB.
The Micron 5210 ION SSD suffers from poor durability, just like any other QLC NAND device. However, there are some compelling use cases for using QLC in the data center that are tied to quad-level NAND's two main benefits.
The two advantages of QLC NAND
One benefit of quad-level NAND storage is that it can be comparatively inexpensive. QLC drives can provide a 33% increase in storage capacity per cell over comparable triple-level cell (TLC) devices. This brings down the cost per gigabyte of storage, while also enabling larger overall storage capacities.
QLC NAND's other major strength is its speed. While a QLC drive probably isn't going to be as fast as a comparable TLC device on the market, it's still going to be far faster than spinning media. Micron estimated that its 5210 ION SSD can achieve 175 times faster random reads and 30 times faster random writes than the largest 10K hybrid HDDs available.
So, where does this technology work best? Quad-level NAND devices can provide relatively low-cost storage and a decent level of performance, but these drives cannot be used for write-intensive workloads. One potential use case for QLC NAND storage is machine learning or other types of data analytics. Analytical workloads commonly read vast quantities of data, without modifying the data in the process.
Another possible use is media streaming. The drive's capacity and speed make QLC storage devices well-suited to hosting video files.
QLC drives may also be a good fit for organizations that want to establish active archives in which the data remains online and accessible. Because archival data isn't typically modified, it poses little threat to QLC's limited durability.





