Organize your team with an Agile scaling frameworks comparison
Large Scale Scrum (LeSS) is a lightweight framework to extend Scrum to more than one team.
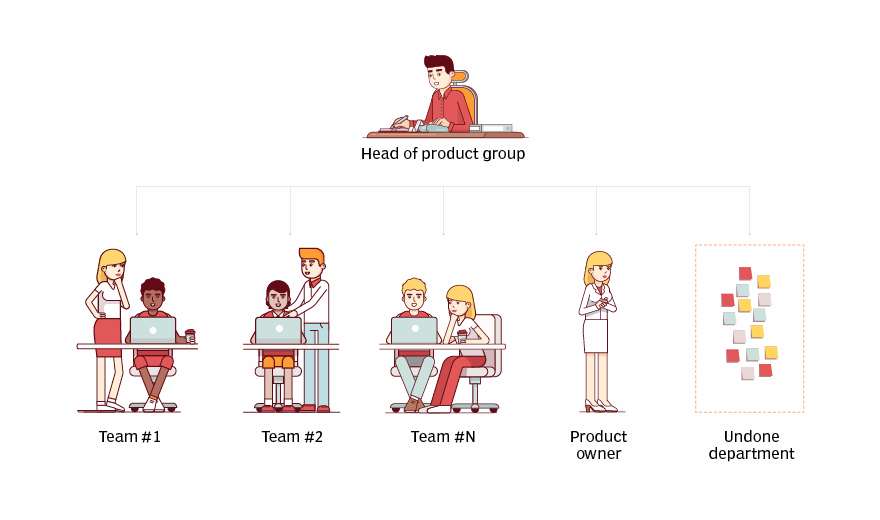
Basic LeSS, for two to eight teams, is like an extension of the Scrum of Scrums method to scale Agile, wherein a team forms with representatives from multiple Scrum teams to supervise integration and other collaboration requisites. Thus, they create a team of teams. LeSS Huge is a version of the LeSS framework meant for more than eight groups, and it gets into teams of teams of teams.
Rather than focus on Scrum rules, artifacts and roles, LeSS targets continuous improvement. A LeSS framework recommends cross-functional teams that work on features end-to-end, not on components. By comparison, Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) argues that this approach is not that simple, and there should be a mix of perhaps 75% feature teams and 25% component teams. LeSS recommends that many teams have one single backlog, with one product owner, with all the teams in the same coordinated sprint.
To adopt the LeSS framework, software development groups go through six phases:
- educate everyone;
- define product;
- define done;
- align the teams;
- have a single product owner; and
- keep the project managers away from the teams.
To accomplish that last mandate, the teams need to create visibility and consistency in the software development process. Project managers in a LeSS framework are tasked with teaching the team how to solve problems and improve. The product owner decides what the teams work on, and teams decide how to do the work.
Large Scale Scrum pros and cons
Most organizations adopt Scrum at the team level, then struggle to scale Agile beyond it. The LeSS framework, whether for Basic LeSS or LeSS Huge, is a lightweight way for teams of teams to self-organize and align. But the lightweight nature of this framework might not fit the needs of some organizations.
There is little prescriptive guidance on how to handle the coordination between teams. The LeSS framework also lacks advice on portfolio management, as well as on funding and budgeting. Also, the popularity of LeSS pales in comparison to SAFe, especially in the U.S., which can make implementation under the direction of a trained expert more difficult.