
Intro: How to use BlackArch Linux for pen testing
BlackArch Linux offers a lot of pen testing and security benefits, but it requires knowledgeable and independent professionals who can put the distribution to work.
BlackArch Linux is an Arch Linux-based penetration testing, ethical hacking and security auditing distribution. While many Linux users have heard of the Kali Linux security distribution, fewer are familiar with BlackArch.
Before digging into how to use BlackArch, let's compare it to two other well-known pen testing platforms: Kali Linux and ParrotOS.
Kali Linux vs. ParrotOS vs. BlackArch Linux
Kali Linux, based on Debian Linux, includes about 600 utilities. Kali offers a reasonably user-friendly GUI, a solid support community and good documentation.
ParrotOS is available in several editions, with Parrot Security and Parrot Home versions the most popular. The Parrot Security edition is most similar to BlackArch. It contains both pen testing and security analysis tools.
BlackArch Linux derives from Arch Linux, so its backers assume you know what you're doing or have the luxury of learning as you go. Arch Linux is community-driven and not derived from Red Hat or Debian, as most distributions are. It's typically not a great choice for Linux beginners and is less user-friendly than Kali or Parrot. As a result, BlackArch expects you to be even more independent and knowledgeable. On the other hand, it offers more built-in tools than Kali and a more aggressive rolling release schedule. The installation and daily use of BlackArch are typically from the command line, although the installer offers several GUI options.
BlackArch use cases
So, who uses BlackArch Linux, and why?
Like Kali Linux, BlackArch is geared toward security professionals and Linux administrators -- folks who want to find and identify vulnerabilities to mitigate them. BlackArch helps do the following:
- Conduct pen testing.
- Perform security research.
- Identify OS, application and network vulnerabilities.
- Audit passwords.
Cybersecurity professionals use BlackArch for pen testing, security auditing, ethical hacking and vulnerability scanning. Sys admins benefit from checking the security posture of their systems to identify and fix security problems before they are exploited. Less-experienced IT and security staffers use BlackArch as a learning platform to become more familiar with Linux and security analysis utilities.
BlackArch includes tools for nearly every scenario, including the following:
- SQL injection utilities.
- Intelligence gathering and footprinting.
- Web application testing.
- Network scanning.
- Packet interception and analysis.
How to install BlackArch
The BlackArch site offers the following installation images:
- Full ISO contains all applications and several window managers to choose from.
- Slim ISO contains only selected tools and the Xfce desktop environment.
- Netinstall ISO contains only a few tools.
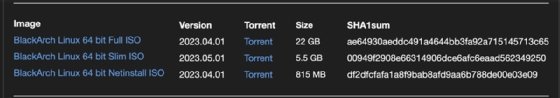
The download page contains a warning about not installing the Full ISO due to update and compatibility issues. Start with the Slim ISO, and add any tools you need that aren't already included. Many mirrors offer the ISOs.
The installation steps are extensive but cover the same general tasks all Linux installers rely on -- find details in the installation documentation. Specify install types, network settings, partitions, etc. Verify you have internet connectivity before beginning the installation. BlackArch runs on VMs or bare-metal devices.
Here is a brief overview of the installation steps:
- Download the ISO, burn it to a DVD or USB stick, and then boot to it.
- Log in to the live session that hosts the installer using these credentials:
-
- Full ISO: username root and password blackarch.
- Slim ISO: username liveuser and password blackarch.
- Run the installation script from the root user's home directory. The command is blackarch-install.
- Choose installation sources, such as repos or the Live ISO.
- Specify the system hostname and IP addressing -- manual or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol-assigned.
- Configure boot, root and swap partitions, select file systems and then configure Linux Unified Key Setup disk encryption if desired.
- Create a non-root user account for standard tasks.
- Install a GUI (optional).
- Reboot.
Remember, BlackArch Linux is a more advanced distribution. The installation process is entirely text-based; it has no graphical mouse-driven interface. It assumes you know what to do at each step. As a result, there's little guidance.
BlackArch documentation and community
Begin by checking out the BlackArch website. Download the official documentation to explore the distro more deeply. A quick-start guide is also available.
The BlackArch community posts updates and other information across a variety of sites, among them GitHub, YouTube and X, formerly Twitter. This community offers comprehensive support and quickly warns BlackArch users about application problems, driver issues or other potential pitfalls.
Applications included with BlackArch, including Nmap and Wireshark, have their own support pages and documentation.
BlackArch pacman package manager
Because Arch Linux doesn't originate from the Red Hat or Debian branches of the Linux family, it uses its own package manager, pacman. Like other package managers, it can install dependencies and package groups.
| Command | Description |
| pacman -S {package} | Install only the specified package. |
| pacman -Syu | Update all packages on the system (could be time-consuming). |
| pacman -R {package} | Remove only the specified package. |
| pacman -Si {package} | Display information about the specified package. |
The pacman package manager is comprehensive and offers options to maintain the applications on your system. Check the Arch documentation to effectively manage packages on your BlackArch installation.
The full version contains more than 2,900 tools.
Gauging use of BlackArch
BlackArch Linux might be your next security research platform, but it probably won't be your daily driver OS. Like Kali and Parrot, it's focused on security analysis tools, but it comes with a much steeper learning curve -- the site even warns visitors that BlackArch isn't appropriate for newer Linux users. The installation process alone reflects its complexity, although the pacman package manager is straightforward.
There's little in the way of formal training for BlackArch Linux and no specific certification path. Users have access to the official documentation and community, plus the application websites and general security practices, to guide them through using the OS.
If you're looking for a more flexible and customizable Linux distribution without the preinstalled security tools, consider BlackArch Linux. It offers power users and administrators many options not easily found on the more user-friendly Fedora and Ubuntu types of distributions.
If it sounds like you're a good match for BlackArch, download and install it to a VM or bare-metal hardware today, and then start analyzing your systems to mitigate threats.
Damon Garn owns Cogspinner Coaction and provides freelance IT writing and editing services. He has written multiple CompTIA study guides, including the Linux+, Cloud Essentials+ and Server+ guides, and contributes extensively to TechTarget Editorial and CompTIA Blogs.






