Why zero trust requires microsegmentation
Microsegmentation is a key security technique that enables organizations to achieve a zero-trust model and helps ensure the security of workloads regardless of where they are located.
As organizations become increasingly dispersed by using cloud services and having remote employees, it has become increasingly critical to ensure data remains protected regardless of where it goes and to ensure only the proper users have the proper access to the data they need.
Zero-trust microsegmentation aims to help in this situation. Let's take a look at what zero trust is, what microsegmentation is, and how the two work together to create microperimeters to protect data.
What is zero trust?
Zero trust is a network security methodology in which all users, devices, endpoints, systems and workloads are considered untrusted until verified, and are then continuously reverified over time.
Zero trust is accomplished by applying zero-trust principles to the seven core pillars of zero trust via a variety of technologies. The pillars of zero trust are workforce security, device security, workload security, network security, data security, visibility and analytics, and automation and orchestration.
The zero-trust framework has become increasingly popular as enterprises move away from traditional perimeter-based, castle-and-moat network security models to perimeterless environments that better accommodate remote workers and cloud services.
What is microsegmentation?
Microsegmentation is the process of dividing networks into smaller zones down to a workload level. It is a way to granularly control lateral workload communications for distributed services inside and between data centers and clouds.
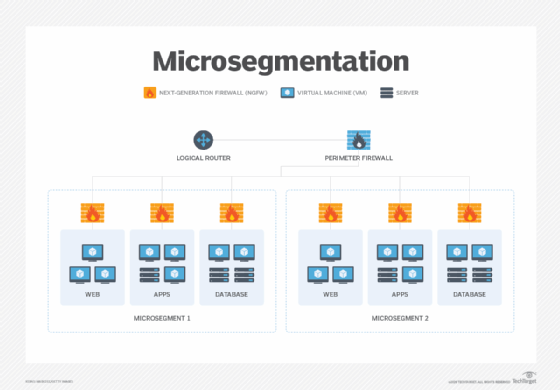
Microsegmentation is accomplished by using various distributed network security tools, such as L4-7 firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, sandboxing and network detection and response, down to the hypervisor/OS level. The distributed tools can then have access policies applied to them to restrict east-west data flow, as well as to closely inspect the flow of the communications that are granted. This is unlike network segmentation, which is designed to control north-south data.
Other benefits of microsegmentation include the following:
- Because segments can be managed and maintained on a smaller scale, it can be easier to maintain security posture.
- Issues can be quickly isolated and remediated.
- The attack surface is reduced.
- Automation can ease access and security policy enforcement.
How zero trust and microsegmentation work together
Microsegmentation is synonymous with zero-trust segmentation and workload segmentation. Zero trust and segmentation do not compete, rather they should be used in tandem.
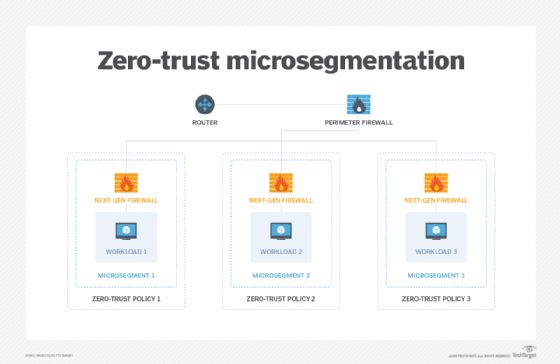
Combining zero-trust security and microsegmentation solves three major challenges facing today's enterprise environments.
- applying authentication and access control down to the workload level;
- controlling lateral movement within networks; and
- securing workloads in dynamic environments.
Applying authentication and access control down to the workload level
In a zero-trust framework, controls must be in place to grant permissions for which applications, files and services users and devices can access. With microsegmentation, highly granular microsegments -- down to the workload -- can be created, then have zero-trust policies applied to them.
Controlling lateral movement within networks
When the concept first emerged, and until recently, much of the original focus of a zero-trust framework was on user and device authentication, and access control. Lately, the zero-trust concept has gained traction due to its ability, when combined with microsegmentation, to prevent lateral attacks.
As mentioned, microsegmentation can ensure an attacker is contained to a microsegment in the event of a breach. The attacker cannot evade the microsegment that was infiltrated to access other parts of the network. With zero trust enabled, another layer of protection is added, as the attacker cannot bypass principle of least privilege access.
Securing workloads in dynamic environments
The increased adoption of cloud computing and virtualization has furthered the need for zero trust.
While internal workloads can be monitored with traditional tools, monitoring workloads and securing them as they cross the boundaries of clouds and virtualized environments is challenging. For example, dynamic assets such as virtual instances (running on virtualization infrastructure technology) and containers are difficult to position behind fixed network enforcement points.
Microsegmentation can create segments down to the workload level, and zero trust enables the application of granular access policies on each workload. Because zero-trust policies are applied directly to them, workloads are thus protected regardless of where they run -- on premises, in the cloud, across multi-cloud environments, or in trusted or untrusted networks.
Zero-trust microsegmentation only allows traffic to flow between approved systems and connections regardless of what environment they are in. Virtual systems can use a hypervisor backplane that all communications and behaviors are linked to, facilitating zero trust in a more scalable way. Automation can also help ease the burden of applying policies to individual microsegments, which can be a complex and overwhelming task for security teams.
In sum, microsegmentation is the architectural design that helps enable zero trust. Zero trust is the model and set of principles that can apply fine-grained access control.
Dave Shackleford contributed to this article.






