
kras99 - stock.adobe.com
How Wireshark OUI lookup boosts network security
Learn why using Wireshark OUI lookup for tracking devices by their network interface's organizationally unique identifier is such an important tool for security pros.
Wireshark OUI lookup is one of the most important features of the leading open source network protocol analyzer -- and one of the least understood.
The key to network protocol analysis is to identify network endpoint devices and match them up with other network endpoints. This gives network defenders a tool for keeping track of potentially harmful network activity between endpoints. That goes for all the networks involved:
- Networks of processes running on a single system are identified by the ports they are listening to for requests.
- Physical networks are linked through a system's network interface card (NIC) to communicate on their local networks and are identified on those physical networks by their media access control (MAC) addresses.
- The IP addresses assigned to systems for interoperability around the world are used to identify networked devices in the global internet.
When sniffing physical networks, one of the key pieces of information that can be accessed is the MAC address of the connected devices. Every NIC can be uniquely identified by its MAC address, with the first half of the physical address identifying the device vendor and the second half of the MAC address uniquely identifying the device itself. The first half of the MAC address is the organizationally unique identifier (OUI) that is registered to the NIC vendor.
Wireshark, the leading open source network protocol analyzer, captures network traffic and enables network engineers to match network protocol data units -- packets, segments, datagrams, etc. -- up and down the protocol stack. This means Wireshark analysis reveals the ports network traffic is being sent to, the IP addresses the traffic is traversing and the identity of the NIC through which data is being physically transmitted.
The Wireshark OUI lookup tool provides an important service for protocol analysis of local network interfaces, but to understand what it is and how it works, it's important to understand how MAC addresses are created and assigned.
What is an organizationally unique identifier?
Most modern NICs are identified by MAC addresses made up of six octets (48 bits). These are usually represented as 12 hexadecimal digits in six pairs, separated by colons or hyphens, for example:
00:00:5E:AB:CD:EF
00-00-5E-12-34-56
The first three octets -- highlighted in yellow above -- are the OUI assigned by the IEEE registration authority to the NIC vendor. The OUI database was used originally to associate Ethernet cards with their manufacturers, but the OUI has been expanded to cover all types of NICs, including Wi-Fi and other non-Ethernet devices.
With more than 16 million distinctive OUI addresses, each OUI can have no more than that many unique MAC addresses: 24 bits enable unique addresses for no more than 224, or 16,777,216, addresses. Given the scale and number of networked devices, this means vendors that manufacture tens or hundreds of millions of NICs need to use more than one OUI address.
OUI databases include the following information about each OUI:
- the OUI address;
- the vendor name; and
- an optional extended vendor name and/or notes associated with the address.
While many MAC address lookup tools rely solely on a single source -- usually, the IEEE list of OUI assignments -- the Wireshark manufacturer database draws its data from the IEEE list, as well as from other sources that document MAC addresses, like the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority listings for reserved addresses. The Wireshark OUI database was originally drawn from Michael Patton's Ethernet Codes master page and has been merged with that source since 2016.
The Wireshark manuf software library is used to load all the Ethernet vendor codes and well-known MAC addresses into working memory so the OUI lookup tool can be used anywhere.
MAC address lookup by itself is useful for enumerating devices on a physical network and keeping track of device movements from one physical network to another.
How does Wireshark OUI lookup work?
When using Wireshark to capture and analyze network traffic, OUI lookup is integrated into the analyzer interface, as shown in Figure 1 of Wireshark running on a Linux system. The OUI data is integrated into the display, along with all the other protocol data, and is highlighted in Figure 1.
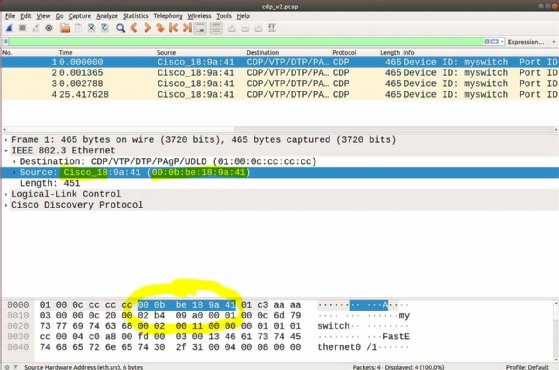
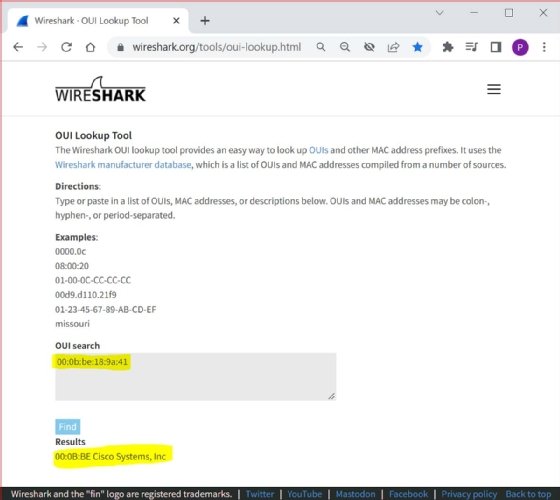
The Wireshark OUI service can also be accessed interactively through the Wireshark website at this URL:
https://www.wireshark.org/tools/oui-lookup.html
Security and network engineers can use this public-facing tool to flag questionable or suspicious devices or to search for specific vendors.
OUI lookup can also return information about Individual Address Block (IAB) data. IAB was replaced in 2014 with the MAC Address Block Small (MA-S) registry that fulfills the same function under IEEE. Both IAB and MA-S are used by organizations that need far fewer than 16 million MAC addresses. Unlike ordinary MAC addresses, addresses assigned under IAB/MA-S are provided with a 36-bit vendor ID. This leaves just 12 bits -- 212, or 4,096, unique addresses -- for addressing individual NICs using MA-S.
Why use Wireshark OUI lookup
Since Wireshark OUI lookup returns results from multiple data sources, the Wireshark manufacturer database can help network and security engineers identify vulnerabilities based on specific hardware or vendors. Other top reasons to use Wireshark OUI lookup include the following:
- Users can search for NICs of connected network devices that were manufactured by specific vendors. This helps identify Wi-Fi endpoints, as well as flag IoT devices, such as hidden wireless cameras.
- Security professionals use OUI lookup to help craft seemingly valid link layer addresses for penetration testing engagements. OUI lookup can help differentiate crafted link layer addresses from valid ones.
- OUI lookup aids in network device enumeration, which is important for many reasons, including better IT support, as well as tracking potential vulnerabilities.
- Users can identify specialized network devices, such as routers or Wi-Fi access points, by retrieving OUI vendor information.
- OUI lookup can be used to identify otherwise hidden devices, such as wireless cameras or other surveillance devices that have been improperly or unknowingly installed at a location.
Wireshark users can access OUI lookup information gathered during packet captures and use OUI addresses to filter traffic to and from specific addresses. Likewise, using the Wireshark OUI lookup webpage enables security professionals to access the database from a smartphone browser.






