
Tom Wang - stock.adobe.com
5G network slicing security benefits IoT, mobile
The fifth generation of mobile cellular technology offers a unique benefit its predecessors don't: network slicing. Learn more about these virtual slices and their security benefits.
For all the reported security risks being attributed to 5G, the fifth generation of mobile cellular technology brings major security and privacy benefits.
From checks to prevent stolen devices from using network services -- thereby discouraging device theft -- to antitracking and antispoofing features that make it harder to track and manipulate individual device connections, 5G is set to improve mobile security, especially in an IoT-enabled world. Resilience, communication security, identity management, privacy and security assurance have all been built into the core network architecture of 5G.
There is one technique, however, key to enabling 5G to deliver a trustworthy communications platform: 5G network slicing. And the good news is it can be put to use now.
5G network segmentation = slicing
Network segmentation, splitting a computer network into subnetworks, has long been a standard security best practice. The most common form of network segmentation is a firewall deployed to separate an internal network from the internet.
In the world of 5G, network segmentation is called network slicing. It is a specific form of virtualization that enables multiple logical networks to run on top of a shared physical network infrastructure, providing an end-to-end virtual network encompassing not just networking, but also compute and storage functions. This type of network segmentation is more important than ever due to the inherent vulnerability of many IoT devices and the increase in the attack surface they produce.
By creating separate slices that prioritize different aspects of 5G technology, a 5G operator can create customized offerings to accommodate different quality service requirements -- such as connectivity, speed, capacity and security -- all tailored to meet the needs of a particular client or application. For example, in a smart metering deployment, remote operation of machinery or telesurgery, connectivity is critical. However, each scenario has vastly different capacity, power consumption, throughput and security demands. These slices can be customized with different security controls and policies, such as firewall configurations, authentication schemes, access policies and packet inspection, for the specific application. This capability delivers far greater security, particularly to IoT devices, as many cannot handle the existing one-size-fits-all security mechanisms that are available. Additionally, because each network slice is an isolated end-to-end network, it not only improves efficiency, flexibility and security, but also provides isolation between the slices, both in terms of traffic and resources.
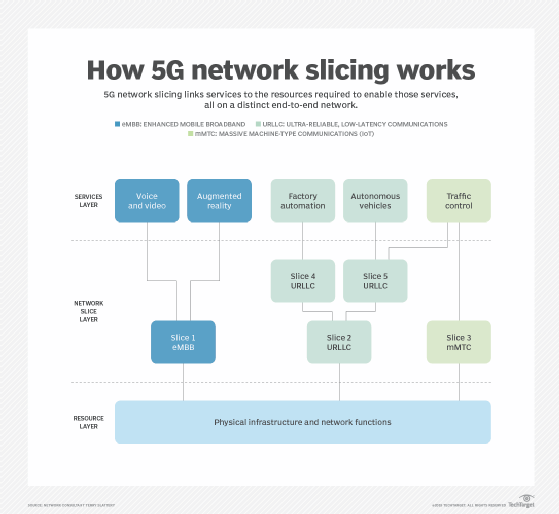
Additional 5G network slicing security benefits
Isolating resources and control, in addition to user traffic, is important to protect critical systems from denial-of-service attacks and fault occurrences as only the target slice is affected. In addition, a slice optimized for performance and scalability, for example, could be later optimized for security should the need arise.
With 5G network slicing, locating devices with similar behavior and characteristics on the same slice makes it easier to baseline typical behavior and detect anomalies or unexpected changes in traffic patterns. A device whose traffic falls outside regular traffic patterns can trigger a warning or be moved to a quarantine slice, either for deeper analysis or to enable it to continue to operate but under tighter restrictions.
5G is soon to become an essential component of our connected society, performing tasks we cannot yet imagine and handling highly sensitive applications, some with life-or-death implications, making security more important than ever. It will require mobile operators to implement all the recommended protocols, which has not always happened in the past, even when a standard states it is mandatory.
Because 5G will be so critical in our lives, it may need government regulation and oversight that enforce how the 5G standard is implemented to ensure we all benefit from the security it can provide, particularly as the cost of risk mitigation now will be a lot cheaper than trying to do it further down the road.
Note that, while 5G introduces several security enhancements, due to the need for interoperability with 3G and 4G, it will be several more years before we can benefit from pure 5G security. However, network slicing is a security control that can be deployed and taken advantage of now.






