white hat hacker
What is a white hat hacker?
A white hat hacker -- or ethical hacker -- is an individual who uses hacking skills to identify security vulnerabilities in hardware, software or networks. However, unlike black hat hackers -- or malicious hackers -- white hat hackers respect the rule of law as it applies to hacking. Many white hat hackers are former black hat hackers. The terms come from old Western movies, where heroes often wore white hats and the bad guys wore black hats.
White hat hackers only seek vulnerabilities or exploits when they are legally permitted to do so. White hat hackers may do their research on open source software, as well as on software or systems they own or have been authorized to investigate, including products and services that operate bug bounty programs. These types of programs reward individuals with money for disclosing security flaws.
Unlike black or gray hat hackers, white hat hackers fully disclose all the vulnerabilities they find to the company or product owner who is responsible for fixing the flaws so the issues can be resolved before they are exploited by malicious hackers.
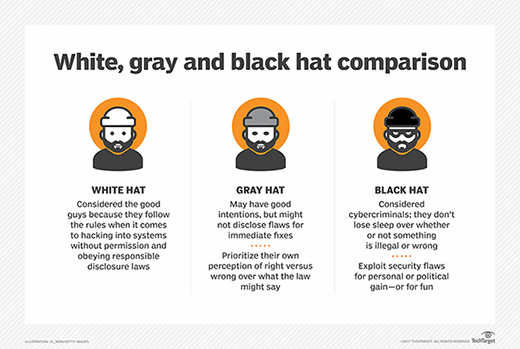
What is the difference between white, black and gray hat hackers?
Besides white hat, there are two other types of hackers: black hat and gray hat.
Where white hat hackers disclose all the vulnerabilities they find to the party responsible for the system -- usually, the company or vendor that makes the affected product -- a black hat hacker has no qualms about selling vulnerabilities and exploits to the highest bidder.
Gray hat hackers fall between white and black hats on the moral spectrum. Gray hats generally consider themselves good guys who are more flexible about the rules under which they operate. For example, a gray hat hacker may be more likely than a white hat hacker to access systems without getting permission or authorization from the owners but would be less likely than a black hat hacker to cause damage to those systems.
In late 2018, when cryptocurrency was just starting to gain mainstream momentum, a gray hat hacker in Russia automated the process of breaking into MikroTik manufactured routers across the internet and proceeded to patch a discovered exploit that enabled black hat hackers to turn the hardware into a crypto mining bot. While unauthorized access did occur, the gray hat did seemingly have good intentions when he broke into and patched more than 100,000 vulnerable devices.
White hat hacking tools and techniques
White hat hackers, especially those performing external penetration tests (pen tests), use the same hacking techniques and tools as black hat hackers. But white hat hackers do so with the intent of helping an organization improve its security posture. Common examples include the following:
- Pen testing. Ethical hackers use their skills to help identify potential entry points and system vulnerabilities and then try to penetrate the organization's network or exposed system.
- Email phishing. White hat hackers conduct legitimate anti-phishing campaigns to find and fix possible issues within an organization's network before an attack can occur. Email phishing tricks the recipient of the email into providing sensitive information or clicking on a malicious file or link.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attack. This type of attack temporarily disrupts or degrades the performance of a machine or network resource, making it unavailable to users. A white hat hacker can simulate this type of attack to help an organization develop its DoS response plan.
- Social engineering. White hat hackers use behavioral techniques to test the security level of a company's systems so it can prevent an attack. Social engineering attacks take advantage of human nature and trust in order to trick employees into breaking security protocols or giving away sensitive information.
- Security scanning. Ethical hackers use a variety of tools to automate the process of finding known vulnerabilities. These range from tools to detect web application vulnerabilities, such as Acunetix or Netsparker, to open source pen testing tools, including Metasploit Framework or Nikto.
How can I become a white hat hacker?
Some white hat hackers used to be black hat hackers who became more ethically attuned as they matured; others were caught and then decided to take the ethical hacker path to pursue their interests without the threat of prosecution.
Undergraduate and graduate degrees in computer science, information security or mathematics are good backgrounds for white hat hackers to have, though having a genuine interest in and passion for security is the biggest asset.
People who want to become white hat hackers may also find the following certifications helpful:
- Certified Ethical Hacker from EC-Council, which is a vendor-neutral credential that is recognized by the U.S. Department of Defense.
- Global Information Assurance Certification Security Essentials Certification, GIAC Penetration Tester, and GIAC Exploit Researcher and Advanced Penetration Tester.
A background or certification in computer forensics can also be useful for ethical hackers.
Famous white hat hackers
There are several well-known white hat hackers in the industry:
- Marc Maiffret. Known for exposing vulnerabilities in Microsoft products, such as the Code Red worm, Maiffret went on to co-found a software security company and eventually become the chief technology officer of security company BeyondTrust.
- Kevin Mitnick. Formerly known as the most wanted cybercriminal in America, Mitnick was arrested in 1995 and served five years in jail for his hacking. After that brush with the law, he became a white hat hacker and now runs a security consulting firm.
- Robert "RSnake" Hansen. This well-known white hat hacker co-coined the term clickjacking. He is the chairman and founder of OutsideIntel, a company that focuses on corporate discovery and business intelligence.
Other big names in white hat hacking include Jeff Moss, who founded the Black Hat and DEFCON security conferences; Dr. Charlie Miller, who hacked for the National Security Agency for five years; and Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak.
What legal issues are there with white hat hacking?
The differences between a white hat hacker and a black hat hacker come down to permission and intent. White hat hackers do not hack systems without written permission from the company to test its defenses, and they disclose vulnerabilities responsibly. However, the white hat hacker and the black hat hacker use similar tools and techniques. This can lead to complicated legal situations for ethical hackers.
For instance, in order to thoroughly test a company's security, an ethical hacker has to try to gain access to the company's systems not just directly, but also through its business partners. If the company that requested pen testing does not also get consent from its business partners, the white hat hacker could end up illegally penetrating the business partner's systems.
Additionally, if ethical hackers are able to access sensitive data, their duty is to report it to the company responsible for that data. This, however, does not necessarily mean the customer will be notified that its information was exposed. It also means the ethical hacker has personally viewed the data.
TechTarget is responding to readers' concerns as well as profound cultural changes. In some cases, we are defaulting to industry standards that may be seen as linguistically biased in instances where we have not found a replacement term. However, we are actively seeking out and giving preference to terms that properly convey meaning and intent without the potential to perpetuate negative stereotypes.







