snooping
What is snooping?
Snooping, in a security context, is unauthorized access to another person's or company's data. The practice is similar to eavesdropping but is not necessarily limited to gaining access to data during its transmission.
Snooping is a broad term that can include casual observance of an email that appears on another person's computer screen or watching what someone else is typing. More sophisticated snooping uses software to remotely monitor activity on a computer or as communications data traverses a network.
An example of electronic snooping is a keylogger, a program that monitors and captures keystrokes, including passwords and login information, and can intercept email and other private communications and data transmissions. Keyloggers are commonly installed on endpoint devices, such as PCs and laptops, and operate without the user knowing. The keylogger creates a text file that captures every keyboard command issued. Later, hackers who installed the keylogger retrieve the keystroke file and analyze it to find information they can use for other malicious purposes, including accessing other protected resources, bribery or identity theft.
It should also be pointed out that corporations sometimes snoop on employees legitimately to monitor their use of business computers and track internet usage and productivity. The latest trend of employees working from home rather than in the office has further fostered the use of remote snooping tools.
Different types of electronic snooping methods and tools
Although snooping has a negative connotation in general, in computer technology, snooping can refer to any program or utility that performs a monitoring function. Thus, the types of snooping methods and tools can vary widely, including the following:
- keylogger
- man-in-the-middle network snooping
- packet capture or sniffer
- employee performance monitoring
- telephone wiretaps
- audio/video surveillance
What is the difference between snooping and spoofing?
The terms snooping and spoofing are often used interchangeably. However, this is incorrect. Snooping is a form of eavesdropping with the purpose of learning information that is not intended to be visible or shared. Spoofing, on the other hand, is a method used to make an electronic device or network look like it is a trusted source. A spoofed device is used to gain the trust of a remote device, user or service so that it can freely share information. While the two terms are used to refer to activities to gain unauthorized access to information, they use different tactics to accomplish that goal.
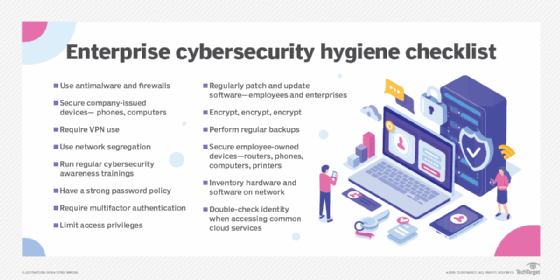
How to prevent electronic snooping attacks
There are several methods users can practice to help reduce the chance of electronic snooping. Some common examples are the following:
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Use secure Wi-Fi authentication techniques.
- Conduct rogue Wi-Fi access point searches.
- Keep antivirus software updated.
- Use strong passwords, and change them frequently.
- Use encryption when transmitting and storing sensitive data.
- Know your surroundings, and turn computer screens away from surveillance cameras.
- Deploy network monitoring and prevention tools, such as firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs) and anti-Address Resolution Protocol/domain name system spoofing services.
- Segment networks so that secure communications flow through specific portions of the network that can be better protected from spoofing attacks.
As more companies adopt a permanent remote work environment, they are transitioning from VPNs to zero-trust networks. Learn how this helps them better secure this evolving work environment.