What is multifactor authentication?
Multifactor authentication (MFA) is an IT security technology that requires multiple sources of unique information from independent categories of credentials to verify a user's identity for a login or other transaction. MFA combines two or more independent credentials -- what the user knows, such as a password; what the user has, such as a security token; and what the user is, by using biometric verification methods.

MFA aims to create a layered defense that makes it more difficult for an unauthorized person to access a target, such as a physical location, computing device, network or database. If one factor is compromised or broken, the attacker still has at least one or more barriers to breach before successfully breaking into the target.
In the past, MFA systems typically relied on two-factor authentication (2FA). Vendors increasingly use the label multifactor to describe any authentication scheme that requires two or more identity credentials to decrease the possibility of a cyberattack. Multifactor authentication is a core component of an identity and access management (IAM) framework.
Why multifactor authentication is a must
One of the most significant shortcomings of traditional user ID and password logins is that passwords can be easily compromised, potentially costing organizations millions of dollars. For example, techniques such as phishing, which trick users into revealing their account credentials in the guise of a security check or account update, remain a common attack method. Brute-force attacks are also a real threat, as bad actors can use automated tools to guess various combinations of usernames and passwords until they find the correct sequence.
Although locking an account after a certain number of incorrect login attempts can help protect an organization, hackers have numerous other methods for system access and carrying out cyberattacks. This is why a multifactor authentication process is so important, as it can help reduce security risks.
How MFA works
At the highest level, MFA requests additional credentials to validate a user's identity and allow access. For example, a user enters their username, password and other details uniquely generated in real time. The principal point here is that additional credentials are typically generated by the MFA platform and exchanged with devices deemed unique to or in the sole possession of the user.
Perhaps the most common type of MFA is the dynamic six-digit code that's sent to a device, such as a smartphone, associated with the user. The user receives the code and uses it to complete the access process. Since many smartphones include powerful integrated security features such as fingerprint or facial recognition, simply accessing the smartphone to receive the unique MFA code requires user authentication at the smart device as well. These factors combine to strengthen the confidence that access requests are coming from the intended user -- vastly improving application, data and account security.
In actual practice, MFA follows a well-established three-step process:
- Account creation. MFA starts when the user first creates an account with an employer or a third party, such as a banking institution. The traditional process of establishing a username and password remains virtually unchanged. When MFA is added or required, the user associates other elements to the account. Additional elements can include a hardware token or other physical device such as a smartphone. Virtual elements can readily include one or more verifiable email addresses -- often added for alerting and actions such as account recovery -- and an authenticator app such as Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator.
- Access request. Access starts with a traditional username and password request; this is what the user knows. In many cases, this initial access request conveys information about the user's general geographic location and the device being used, such as its unique media access control address. If the initial login shows inconsistencies with the credentials or device, the user might receive an alert by email or text message. If the initial login is acceptable, the remote site connects to other elements for authentication and generates an MFA challenge for the user. For example, the MFA platform will send a unique, time-limited code by email or text, or request a response from the user's authenticator app; this is what the user has. In most cases, additional security is applied to access the MFA challenge. For example, a user might need to access their smartphone to retrieve the MFA code; this can represent what the user is.
- Assess response. The user receives the MFA challenge and completes the authentication process by verifying the MFA query. For example, they enter the unique code or press a button on a hardware fob. Once this additional authentication is validated, the user will be granted normal access.
Some MFA implementations might only present an MFA challenge when requesting access for the first time on a new or previously unknown device, such as a different computer or tablet. Once accessed successfully, the MFA platform might forego further challenges when access requests arrive from a known device and rely on usernames and passwords only, or present MFA challenges to a known device only periodically.
The prevailing theory is that once a device is known through a successful MFA login, confidence in its validity is extremely high. This is an expression of the inheritance factor -- what something is -- and is a well-understood MFA authentication method. The exact application of MFA on known devices depends on how MFA technologies are implemented and configured.
MFA authentication methods
An authentication factor is a category of credentials used for identity verification. For MFA, each additional factor is intended to increase the assurance that an entity involved in some communication or requesting access to a system is who -- or what -- it says it is. Using multiple forms of authentication can help make a hacker's job more difficult, which is why MFA techniques are used.
The three most common categories, or authentication factors, are often described as something you know, or the knowledge factor; something you have, or the possession factor; and something you are, or the inherence factor. MFA works by combining two or more factors from these categories.
Knowledge factor
Knowledge-based authentication typically requires the user to answer a personal security question. Knowledge factor technologies generally include passwords, four-digit personal identification numbers (PINs) and one-time passwords (OTPs). Typical user scenarios include the following:
- Swiping a debit card and entering a PIN at the grocery checkout.
- Downloading a virtual private network client with a valid digital certificate and logging into the virtual private network (VPN) before gaining access to a network.
- Providing answers to personal security questions -- such as mother's maiden name or previous address -- to gain system access.
Possession factor
To log in, users must have something specific in their possession, such as a badge, token, key fob or mobile phone subscriber identity module (SIM) card. A smartphone often provides the possession factor with an OTP app for mobile authentication.
Possession factor technologies include the following:
- Security tokens. These small hardware devices store a user's personal information and are used to authenticate that person's identity electronically. The device can be a smart card or an embedded chip in an object, such as a Universal Serial Bus (USB) drive or wireless tag.
- Software tokens. These software-based security applications generate a single-use login PIN. Software tokens are often used for mobile multifactor authentication, in which the device itself --such as a smartphone -- provides the possession factor authentication.
Typical possession factor user scenarios include the following:
- Mobile authentication. Users receive a code on their smartphone to gain or grant access. Other mobile authentication methods include text messages and phone calls sent to a user as out-of-band authentication, smartphone OTP apps, SIM cards and smart cards with stored authentication data.
- USB hardware token. This device generates an OTP that authenticates the user and allows them to log in to a VPN client.
Inherence factor
Any biological traits the user has that are confirmed for login. Inherence factor technologies include the following biometric verification methods:
- Retina or iris scan.
- Fingerprint scan.
- Voice authentication.
- Hand geometry.
- Digital signature scanners.
- Facial recognition.
- Earlobe geometry.
Authentication can also be inherited virtually when a successful login process is completed. For example, logging into a financial website using MFA can enable the user to opt out of further MFA logins on that device and browser because that point of access has already been validated. Such opt-outs can be permanent or allowed for limited periods such as 30-90 days, depending on specific IAM configurations and MFA requirements.
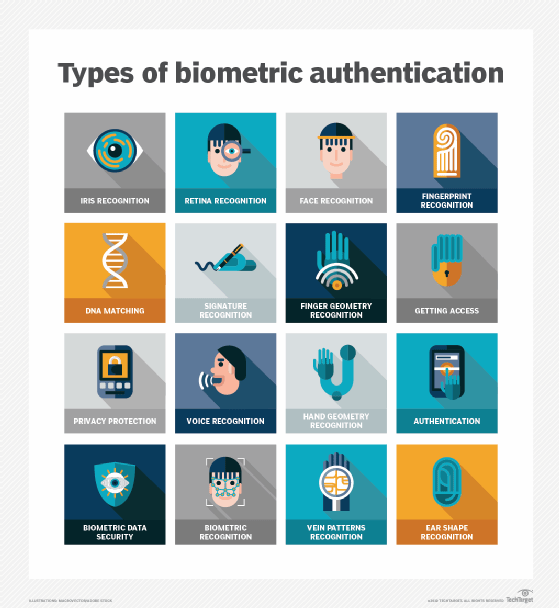
Biometric device components include a reader, a database and software to convert the scanned biometric data into a standardized digital format and compare the observed data's match points with stored data.
Typical inherence factor scenarios include the following:
- Using a fingerprint or facial recognition to access a smartphone.
- Providing a digital signature at a retail checkout.
- Identifying a criminal using earlobe geometry.
User location is often suggested as a fourth factor for authentication. Again, the ubiquity of smartphones can help ease the authentication burden: Users typically carry their phones, and all basic smartphones have Global Positioning System tracking, providing credible confirmation of the login location.
Time-based authentication is also used to prove a person's identity by detecting presence at a specific time and granting access to a particular system or location. For example, bank customers can't physically use their automated teller machine (ATM) card in the U.S. and Russia 15 minutes later. These types of logical locks can help prevent many cases of online bank fraud.
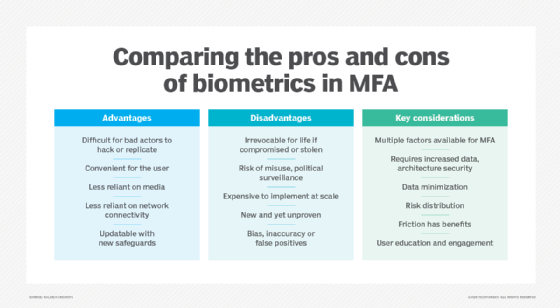
What are the pros and cons of MFA?
Multifactor authentication (MFA) was introduced to harden security access to systems and applications through hardware and software. The goal was to authenticate users' identities and assure the integrity of their digital transactions. The downside to MFA is that users often forget the answers to the personal questions that verify their identity, and some users share personal ID tokens and passwords.
Other benefits and disadvantages of MFA include the following:
Pros
- Adds layers of security at the hardware, software and personal ID levels.
- Sends to phones OTPs that are randomly generated in real time and difficult for hackers to break.
- Helps reduce security breaches by up to 99.9% over passwords alone.
- Provides easy setup for users.
- Enables businesses to restrict access for time of day or location.
- Offers a scalable cost, as there are expensive and highly sophisticated MFA tools but also more affordable ones for small businesses.
- Improves security measures and response for companies, as they can set up a multifactor authentication system to actively generate an alert whenever questionable login attempts are detected.
- Provides adaptive authentication, which helps employees work remotely.
- Helps meet Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act and other compliance requirements, which require only authorized and restricted access to sensitive information, such as personal medical records.
Cons
- Requires access to a phone or email to get text message codes.
- Hardware tokens such as fobs can get lost or stolen.
- Phones can get lost or stolen.
- Resistance due to complexity or login friction might prompt users to log in less or demonstrate lower productivity.
- The biometric data calculated by MFA algorithms for personal IDs, such as thumbprints, aren't always accurate and can create false positives or negatives.
- MFA verification can fail if there's a network or internet outage.
- MFA techniques must constantly be upgraded to protect against cybercriminals who work incessantly to break them.
Multifactor authentication vs. two-factor authentication
When authentication strategies were first introduced, the intent was to enforce security and keep it as simple as possible. Users were asked to supply only two security keys to inform a system that they were authentic and authorized users. Common forms of 2FA were user ID and password or ATM bank card and PIN.
Unfortunately, hackers quickly discovered ways to buy or break passwords or skim debit cards at ATMs. This prompted companies and cybersecurity vendors to look for more hardened forms of user authentication that used additional security factors for verification.
While MFA requires at least two authentication factors, if not more, 2FA only requires two. Therefore, 2FA is a subset of MFA -- all 2FA is MFA, but not vice versa.
What is adaptive multifactor authentication?
Adaptive MFA is a security approach that chooses which authentication factors to apply to a user's login attempt based on business rules and contextual information. It's also referred to as adaptive MFA or risk-based authentication.
Traditional MFA uses set credentials and a second factor. Still, adaptive MFA is a bit more advanced. It automatically adapts authentication by considering several variables, such as user location, device being used, number of failed login attempts, user behavior and environment. This strategy makes it harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access because authentication is coordinated with the degree of risk.
For example, if a user attempts to access a corporate local area network from a known device, simple 2FA might be deemed sufficient. However, suppose the user possesses extended access privileges -- regardless of location -- because of their position in the company. In that case, if the login attempt is coming from a wide area network or an unknown device, or if there was an initial mistake in the username or password entry, the MFA system can adapt to pose additional challenges to validate the access attempt.
MFA products that use adaptive authentication can provide organizations with a more secure login experience. These tools use artificial intelligence to monitor user activity over time to identify patterns, establish user behaviors and detect abnormal behavior. They can adjust authentication requirements based on factors such as user location and recent login activity.
Best practices for implementing MFA
Although MFA implementation practices can vary by industry and specific business needs, the following best practices can potentially enhance the success and effectiveness of MFA technology:
- Apply MFA across the business. An organization might be tempted to implement MFA for certain departments or personnel with sensitive access, but hackers are always looking for soft targets. When a business decides to implement MFA, it should apply to all personnel regardless of their role.
- Use adaptive MFA technologies. Select and implement adaptive or context-based MFA controls using factors such as device, location, time and behavior. This can ease access for trusted devices while adding security to the business. Given the rate at which attacks occur, it's an easy addition to MFA deployment.
- Allow multiple MFA methods. Different users can have different needs and preferences, and MFA should allow varied authentication methods. For example, allowing an OTP code by SMS text and email can accommodate both in-office and remote users.
- Train users. User resistance and implementation friction can be reduced when users are informed about MFA, clear on its benefits and trained in its proper use. Ensure that users know any backup or fallback authentication methods and that those backup methods work properly. This is often part of broader security training for the workforce.
- Combine MFA and least-privilege strategies. MFA is often used with other security strategies. Common access control strategies such as least-privilege and zero-trust can help to ensure that access granted through MFA is limited to only the assets needed for the user to act and attempting to access additional resources can trigger an alert.
- Combine MFA and single sign-on. SSO allows a properly authenticated user to seamlessly access all the applications they should have without signing on to each app. Adding SSO to MFA can reduce friction and boost user satisfaction and productivity.
- Adhere to established standards. An MFA system should adhere to standards such as Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service and Open Authentication. This helps to ensure that MFA platforms function properly and are interoperable with other security elements of the IT infrastructure.
- Review and update regularly. MFA implementation and configurations should be reviewed and reevaluated periodically, along with the organization's entire security posture. Consider the emergence of patches and updates, new regulatory demands and advances in MFA and other infrastructure technologies. Changing needs can drive the implementation of new MFA options and platforms, such as moving from MFA to adaptive MFA.
Addressing the challenges of multifactor authentication
Users might be reluctant to adopt MFA since it presents certain usability challenges, such as remembering several passwords to log in. Along with user resistance, there could be other obstacles with MFA, including integration problems. Consequently, the goal of MFA is to simplify authentication for users.
The following four approaches are being used to simplify MFA:
- Adaptive authentication. As described above, this approach applies knowledge, business rules or policies to user-based factors, such as device or location. For example, a corporate VPN knows it's OK for a user to sign on from home because it sees the user's location and can determine the risk of misuse or compromise. However, an employee who accesses the VPN from a coffee shop will trigger the system and be required to enter MFA credentials.
- SSO. This one-stop authentication method lets users maintain one account that automatically logs them into multiple applications or websites with a single ID and password. SSO establishes the user's identity and then shares this information with each application or system that requires it.
- Push authentication. This is an automated mobile device authentication technique where the security system automatically issues a third, single-use identification passcode or push notification to the user's mobile device. For example, users who want to access a secured system enter their user ID and password. A security system automatically issues a third, single-use identification code to their mobile device. Users enter that code into the system to gain access. Push authentication simplifies MFA by providing users with a third code, eliminating the need to remember it.
- Passwordless authentication. Passwordless authentication forgoes conventional passwords in favor of additional authentication factors such as hardware tokens or biometrics, including fingerprints and facial recognition. Remembering passwords is hard, so this makes it easier for users to authenticate and improves an organization's security posture, as most phishing attacks target password vulnerabilities for unauthorized access.
Cybersecurity is necessary for all organizations, but some businesses don't think it applies to them. Learn about several persistent security myths and how they can leave organizations vulnerable to cyberattacks.






