OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol)
What is OCSP?
OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol) is one of two common schemes used to maintain the security of a server and other network resources. An older method, which OCSP has superseded in some scenarios, is known as a certificate revocation list (CRL).
OCSP overcomes the chief limitation of CRL, which is that updates had to be frequently downloaded to keep the list current at the client end. For example, when a user attempts to access a server, OCSP sends a request for certificate status information. The server then sends back a response stating that it was "current," "expired" or "unknown."
The protocol specifies the syntax for communication between the server (containing the certificate status) and the client application (which is informed of that status). OCSP gives a user with an expired certificate a grace period so they can access servers for a limited time before renewing the certificate.
OCSP enables real-time status checks on security certificates and is fundamental to the extended validation of Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificates. For example, when a user makes an HTTPS connection with a web server, the browser typically performs an OCSP check with the certificate authority (CA) that issued the SSL certificate to ensure that it was not revoked. Sometimes, this process leads to short delays in the SSL handshake.
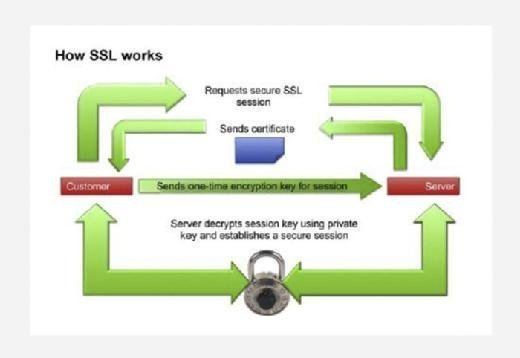
What is OCSP stapling?
OCSP stapling improves performance by directly positioning digitally signed and time-stamped OCSP certificates on the web server. This "stapled" response enables the web servers to include OCSP responses within the initial SSL handshake.
This approach negates the need for the user to initiate a separate external connection to the CA. The CA refreshes these stapled responses in predefined intervals.
Three key advantages of OCSP stapling are:
- By combining two requests, OCSP stapling improves SSL handshake connection speed. This approach also reduces the time to load encrypted web pages. (See the video below for more on cryptography).
- OCSP stapling ensures the privacy of end users as OCSP requests negate the need to connect with CRL. The certificate authority only sees OCSP requests from the websites and not visitors.
- Whenever devices connect to a hotspot or a portal for internet access, OCSP stapling provides the OCSP status from the hotspot or portal.
Two key disadvantages of OCSP stapling are:
- Only some browsers support OCSP stapling. In this scenario, if either the web server or the browser does not support OCSP stapling, the browser will not use it. Instead, the browser checks the OCSP validity status directly with the CA.
- OCSP also assumes that the requester has OCSP network access to connect with the appropriate OCSP responder. However, in some cases, requesters cannot connect because their local area network (LAN) does not allow direct access.
Such scenarios force internal servers to connect to the internet to use OCSP. However, this approach increases risk exposure and deperimeterization. In this case, OCSP stapling protocols can enable servers to cache OCSP responses, removing the requestor's need to interact with the OCSP responder directly.
What is OCSP certificate revocation?
Trust on the internet depends on digital certificates. For example, a web browser demands that all HTTPS websites validate their hostname and private key. However, threat actors who gain access to a private key can easily impersonate the website. This makes certificate revocation critical to mitigating risk. When this impersonation occurs, the website owner informs the issuer to revoke the untrusted certificate.
OCSP certificate management is necessary to create, store and revoke digital security certificates. This helps to ensure that the right users access only the resources allocated to them. However, OCSP certificate revocation does not mitigate man-in-the-middle attacks where threat actors compromise the HTTPS server's private key and impersonate that server.
Learn about application security threats and how to prevent them and how to assess secure web gateways to suit your network security needs. Explore the ultimate guide to cybersecurity planning for businesses.






