What is cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks and data from digital threats. It involves strategies, tools and frameworks designed to safeguard sensitive information and ensure the integrity of digital operations.
An effective cybersecurity strategy can provide a strong security posture against malicious attacks designed to access, alter, delete, destroy or extort an organization's and user's systems and sensitive data. Cybersecurity is also instrumental in preventing attacks designed to gain unauthorized access to systems or devices and then disable, disrupt or steal from them.
An ideal cybersecurity approach has multiple layers of protection across any potential access point or attack surface. This includes a protective layer for data, software, hardware and connected networks. In addition, all employees within an organization who have access to any of these endpoints should be trained on the proper compliance and security processes. Organizations also unified threat management systems and other tools as another layer of protection against threats. These tools detect, isolate and remediate potential threats to business and notify users when additional action is needed.
Cyberattacks can disrupt or immobilize their victims, so creating a strong cybersecurity strategy for businesses is an integral part of any organization. Organizations should also have a disaster recovery plan in place so they can quickly recover in the event of a successful cyberattack.
Why is cybersecurity critical in the enterprise?
With the number of users, devices and programs in the modern enterprise increasing, along with vast amounts of sensitive and confidential data, cybersecurity has become more important than ever. However, the volume and sophistication of cyberattacks and attack techniques compound the problem even further.
According to a Gartner survey, 61% of CEOs are concerned about cybersecurity threats and 85% believe cybersecurity is critical for business growth. Without a proper cybersecurity strategy and a staff that is trained on security best practices, malicious actors can bring an organization's operations to a standstill.
The following are some key points highlighting the importance of cybersecurity:
- Protecting against cyberattacks. Cybersecurity plays a critical role in safeguarding businesses from the growing threat of cyberattacks and data breaches. By adopting comprehensive security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and multifactor authentication (MFA), organizations can defend their networks and systems against cyberattacks.
- Protecting data. Organizations handle vast amounts of confidential data, including personal information, financial records and proprietary business information. Cybersecurity helps protect this data from unauthorized access and theft, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure.
- Preventing financial losses. Cyberattacks can directly lead to financial losses through unauthorized transactions, ransomware demands or stolen funds from bank accounts. Strong cybersecurity measures help prevent these costly incidents, reducing the risk of fines, revenue loss and reputational damage.
- Ensuring business continuity. Cyberattacks can disrupt operations by shutting down systems, encrypting data and disabling critical infrastructure. For industries that rely heavily on online transactions and automation, such as e-commerce, manufacturing and healthcare, these disruptions can be devastating. Strong cybersecurity practices can ensure business continuity by minimizing downtime and reducing productivity losses.
- Safeguarding critical infrastructure. Infrastructure, such as energy, healthcare, transportation and government services, are prime targets for cyberattacks. A single successful attack on these systems can disrupt essential services and negatively affect public safety. Cybersecurity protects these vital operations.
- Improving recovery times. Effective cybersecurity measures help organizations quickly detect and respond to cyberincidents, reducing recovery time after a breach. With well-prepared incident response plans and backup systems in place, businesses can restore operations faster, while minimizing downtime and limiting damage.
- Maintaining trust and reputation. Preserving customer trust is essential for businesses. A single data breach can harm a company's reputation, resulting in lost customers and revenue. By adopting cybersecurity measures, organizations foster and sustain customer trust, making them feel safe when sharing their personal information.
- Complying with legal and regulatory requirements. Many industries face regulatory requirements for protecting sensitive information. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to fines, legal consequences and damage to an organization's brand or reputation. By adhering to cybersecurity best practices, organizations can meet regulatory obligations and operate within legal boundaries.
What are the elements of cybersecurity and how does it work?
Cybersecurity can be broken into several different security sectors, the coordination of which within the organization is crucial to the success of a cybersecurity program. These sectors include the following:
- Application security. These measures prevent data and code within an application from being misused or hijacked. Application security includes secure coding, regular updates and vulnerability assessments.
- Information security. Also referred to as data security, information security focuses on protecting the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data, ensuring that sensitive information isn't accessed, altered or lost.
- Network security. This approach protects the integrity and usability of networks and data. Network security uses firewalls, intrusion detection systems and secure communication protocols to do this.
- Disaster recovery. DR strategies and business continuity planning help recover data and maintain business operations in the event of a cyberattack or system failure.
- Operational security. This aspect encompasses the processes and decisions for handling and protecting data assets. Operational security includes user permissions and access controls.
- Cloud security. These practices and policies are designed to protect data, applications and services hosted in cloud environments. Cloud security focuses on mitigating cyberthreats, ensuring confidentiality, integrity and availability.
- Critical infrastructure security. This involves protecting the essential systems and assets that are vital to a nation's security, economy, public health and safety, ensuring their resilience against disruptions or attacks.
- Physical security. Protecting an organization's physical assets -- such as servers, data centers and network equipment -- from unauthorized access, theft, damage or tampering. Physical security ensures the integrity and availability of digital systems and data.
- End-user education. Training and educating users about the importance of cybersecurity, teaching them to recognize threats such as phishing and to follow best practices for password management and safe browsing.
Maintaining cybersecurity in a constantly evolving threat landscape is a challenge for all organizations. Reactive approaches, in which resources are put toward protecting against the biggest known threats while lesser- threats go undefended, aren't sufficient.
To keep up with changing security risks, a more proactive and adaptive approach is necessary. Several key cybersecurity advisory organizations offer guidance. For example, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends adopting continuous monitoring and real-time assessments as part of a risk assessment framework to defend against known and unknown threats.
Enterprise cybersecurity frameworks
Enterprise cybersecurity frameworks provide structured approaches to managing cyber-risks, ensuring compliance and protecting critical assets. The following are some of the frameworks available:
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF 2.0)
NIST CSF 2.0 offers a flexible, risk-based approach to cybersecurity. It's comprised of five core functions:
- Identify.
- Protect.
- Detect.
- Respond.
- Recover.
NIST CSF 2.0 emphasizes governance, supply chain security and identity management, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes and industries. It provides a common language for cybersecurity discussions across organizational levels and is widely adopted in both public and private sectors.
ISO/IEC 27001
This international standard provides guidance on establishing, implementing and maintaining an information security management system. ISO/IEC 27001 is a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity and availability.
Organizations must systematically examine security risks, enforce controls and adopt an overarching management process for continuous improvement. Certification demonstrates compliance and commitment to information security.
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification 2.0
CMMC 2.0 is a U.S. Department of Defense framework that enhances the cybersecurity posture of federal contractors and the defense industrial base. Its tiered approach has three levels of certification, ranging from basic cybergenic to advanced security practices.
Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies
COBIT is a framework for developing, implementing, monitoring and improving IT governance and management practices. It encompasses the entire IT environment, providing structured guidance for developing effective cybersecurity governance models and management practices.
COBIT helps organizations optimize IT-related risk, improve resource use and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. It integrates with other frameworks such as the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, ISO 27000 and NIST.
Center for Internet Security Critical Security Controls
CIS controls are a prioritized set of 18 actionable cybersecurity best practices developed by a global community of experts. It's organized into three implementation groups of increasing sophistication, making it adaptable to organizations of varying security maturity levels.
CIS focuses on mitigating the most common attack vectors based on real-world threat data. The framework is continuously updated to address the evolving threat landscape. It offers organizations guidance on which security controls to use first for maximum defensive effectiveness.
In addition to enterprise-wide security frameworks, several industry-specific frameworks exist, such as the following:
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. PCI DSS is a mandatory security standard for organizations handling credit card data. The major credit card companies developed it to protect cardholder data.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act Security Rule. The HIPAA Security Rule establishes national standards to protect electronic personal health information.
- North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection. NERC CIP standards are mandatory cybersecurity regulations designed to protect North America's bulk electric system from cyber and physical attacks.
- Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council. The FFIEC standard provides a framework for financial institutions to evaluate their risk and cybersecurity preparedness.
What are the different types of cybersecurity risks and threats?
Cyberthreats take many forms. Types of cyberthreats include the following:
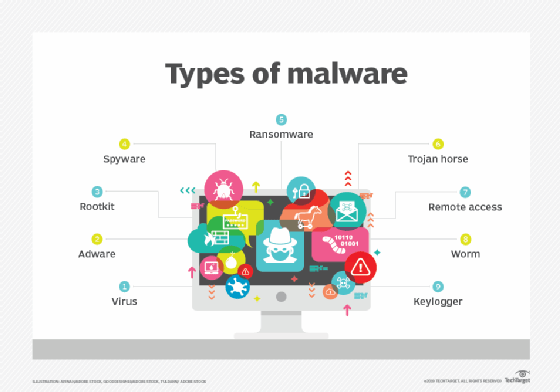
- Malware. This refers to a malicious software in which any file or program can be used to harm a user's computer. Different types of malware include worms, viruses, Trojans and spyware.
- Ransomware. This is a type of malware that involves an attacker locking the victim's computer system files -- typically through encryption -- and demanding a payment to decrypt and unlock them.
- Social engineering. This is an attack that relies on human interaction. It tricks users into breaking security procedures to gain sensitive information that's typically protected.
- Phishing. This is a form of social engineering in which fraudulent email or text messages that resemble those from reputable or known sources are sent. These are often random attacks that intend to steal sensitive data, such as credit card or login information.
- Spear phishing. This is a type of phishing that has a specific target individual, organization or business.
- Insider threats. These are security breaches or losses caused by humans -- for example, employees, contractors or customers. Insider threats can be malicious or negligent in nature.
- Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Attackers use multiple systems to disrupt the traffic of a targeted system, such as a server, website or other network resource. By flooding the target with messages, connection requests or packets, DDoS attacks slow or crash the target system, preventing legitimate traffic from using it.
- Advanced persistent threat (APT). This is a prolonged targeted attack in which an attacker infiltrates a network and remains undetected for long periods of time. The goal of an APT is to steal data.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks. These are eavesdropping attacks that involve an attacker intercepting and relaying messages between two parties who believe they're communicating with each other. During an MitM attack, the attacker positions themselves between the two communicating parties. They can then read, insert and modify the messages, making both parties believe they're directly communicating with each other, rather than with an intermediary.
- SQL injection. This technique involves attackers adding a string of malicious SQL code to a database query to gain access to a web application database. A SQL injection provides access to sensitive data and lets attackers execute malicious SQL statements.
- Zero-day exploits. These attacks target vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to the vendor and for which no patch is available. Hackers take advantage of these unpatched vulnerabilities to infiltrate systems and cause damage.
- Internet of things vulnerabilities. The proliferation of IoT devices have introduced new entry points for cyberattacks. Many IoT devices have weak security, making them easy targets for cybercriminals looking to gain unauthorized access or disrupt services.
- Artificial intelligence-based attacks. Attackers use AI technology to automate and enhance attacks, making them more sophisticated, scalable and difficult to detect. These attacks include highly convincing phishing scams using deepfakes and AI-generated text, rapid exploitation of system vulnerabilities, and attacks that target AI models themselves, potentially compromising critical AI-driven systems.
Other common types of attacks include botnets, drive-by-download attacks, exploit kits, malvertising, vishing, credential stuffing attacks, cross-site scripting attacks, keyloggers and worms.
What are the top cybersecurity challenges?
Cybersecurity is continually challenged by hackers, data loss, privacy and changing cybersecurity strategies. And the number of cyberattacks isn't expected to decrease anytime soon. In 2024, the average cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million, which is a 10% increase over the previous year, according to IBM and the Ponemon Institute's "Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024."
Moreover, increased entry points for attacks from IoT technology and the growing attack surface increase the need to secure networks and devices. The following cybersecurity risk management challenges must be continuously addressed.
Evolving threats
One of the most problematic elements of cybersecurity is the evolving nature of security risks. As new technologies emerge -- and as technology is used in new or different ways -- new attack avenues are developed. Keeping up with these changes and advances in attacks, as well as updating practices to protect against them, is challenging. Issues include ensuring all elements of cybersecurity are continually updated to protect against potential vulnerabilities.
This can be especially difficult for small organizations that don't have adequate staff or in-house resources.
Data deluge
Organizations gather a lot of potential data on the people who use their services. With more data being collected comes the potential for a cybercriminal to steal personally identifiable information. For example, an organization that stores personally identifiable information, or PII, in the cloud could be subject to a ransomware attack.
Cybersecurity awareness training
Cybersecurity programs should also include end-user education. Employees can accidentally bring threats and vulnerabilities into the workplace on their laptops and mobile devices. Likewise, they can act imprudently; for example, they might click links or download attachments from phishing emails. Regular security awareness training can help employees do their part in keeping their company safe from cyberthreats.
Workforce shortage and skills gap
Another cybersecurity challenge is a shortage of qualified cybersecurity personnel. As the amount of data collected and used by businesses grows, the need for cybersecurity staff to analyze, manage and respond to incidents also increases.
According to an estimate from the "2024 ISC2 Cybersecurity Workforce Study," the global cybersecurity workforce gap, which is the number of security professionals organizations need compared to the number of active pros, has grown to nearly 4.8 million, representing a 19% increase from 2023.

Supply chain attacks and third-party risks
Organizations can do their best to maintain security, but if the partners, suppliers and third-party vendors that access their networks don't act securely, all that effort is for naught. Software- and hardware-based supply chain attacks are becoming increasingly difficult security challenges.
Organizations must address third-party risk in the supply chain and reduce software supply issues, for example, by using software bills of materials.
Cloud security misconfigurations
The widespread adoption of cloud services introduces new security challenges, particularly related to misconfigurations. Improperly configured cloud settings can lead to data breaches and unauthorized access. Organizations must implement comprehensive cloud security strategies, including regular audits, automated compliance checks and strong access controls to mitigate these risks.
Hybrid work environments
The shift to hybrid and remote work has blurred traditional corporate network boundaries, expanding the attack surface. With employees now working from diverse, often less secure locations, endpoints such as laptops and mobile devices operate outside managed office networks.
As a result, organizations must secure not just their internal infrastructure and cloud environments, but also an array of remote devices and variable network conditions. This demands a comprehensive, adaptive security strategy that goes beyond on-premises defenses to protect the entire distributed workforce and their access to cloud-based applications and data.
Cybersecurity metrics and KPIs for CISOs
For chief information security officers, selecting the right cybersecurity metrics and key performance indicators is crucial for demonstrating the effectiveness of security initiatives, securing budget approvals and aligning with organizational goals. The following is a list of some essential cybersecurity KPIs and metrics that CISOs should monitor:
Detection and response metrics
These metrics focus on the efficiency and effectiveness of responding to and managing security incidents and demonstrate the organization's resilience. Common metrics in this category include the following:
- Mean time to detect. MTTD is the average time it takes to identify a security incident from its onset. A lower MTTD indicates strong detection capabilities.
- Mean time to respond. MTTR is the average time taken to begin addressing a detected security incident. It shows how fast a security team can react.
- Mean time to contain. MTTC is the average time it takes to stop the spread and limit the impact of a security incident. This is critical for minimizing damage.
- Mean time to recover. This is the average time taken to restore systems and operations to normal after an incident. This highlights business continuity and disaster recovery effectiveness.
These metrics focus on proactive measures to identify and address weaknesses before they can be exploited. Common metrics in this category include the following:
- Number of open vulnerabilities. This is the total count of identified vulnerabilities that have not yet been remediated.
- High-risk vulnerabilities remediated on time. This is the percentage of high-priority vulnerabilities patched or addressed within defined service-level agreements.
- Vulnerability recurrence rate. This is the frequency with which previously remediated vulnerabilities reappear. This indicates issues with root cause analysis or sustainable options.
- Patch management compliance. This is the percentage of systems that are up to date with security patches and updates.
Incident and cost metrics
Understanding the financial effects of cybersecurity incidents is essential for CISOs to justify security investments and communicate risks effectively to stakeholders. These metrics encompass both direct and indirect costs associated with security breaches. Common metrics in this category include the following:
- Number of security incidents. This metric counts the total number of security events over a specified period. An increase might indicate emerging threats or gaps in defenses.
- Cost per Incident. This calculates the average financial toll of each security incident, including remediation and reputational damage.
- Breach costs. This metric assesses the total expenses incurred from a data breach, encompassing legal fees, system repairs and customer notification costs.
Human factor and awareness metrics
These metrics assess the role of human firewall and the effectiveness of security oversight and awareness programs. Common metrics in this category include the following:
- Phishing attack success rate. This is the calculation of the percentage of employees who fall for simulated phishing attempts. A lower rate indicates effective training. In early 2025, over a million phishing attacks were observed by the Anti-Phishing Working Group, indicating a significant increase in phishing threats.
- Employee security awareness assessment scores. These are the results from quizzes or assessments testing employees' understanding of security best practices.
- Reporting of suspicious activity. This is the number of employees who report potential security threats or suspicious emails. This indicates a strong security culture.
User and compliance metrics
Metrics that track user activity and compliance include the following:
- Security awareness training completion rate. This metric measures the percentage of employees who have completed cybersecurity training. Higher completion rates are associated with reduced human error incidents.
- MFA coverage. This tracks the percentage of user accounts secured with MFA. Aiming for 95% coverage enhances account protection.
- Compliance rate. This evaluates adherence to regulatory standards such as ISO 27001 or PCI-DSS. Maintaining high compliance is essential for avoiding penalties.
Operational efficiency metrics
The following are metrics focused on operational efficiency:
- False positive rate. The FPR metric monitors the percentage of security alerts that are false alarms. A lower FPR indicates more accurate threat detection systems.
- Patch velocity. This metric measures the number of patches applied over a specific period. Higher patch velocity indicates a responsive and proactive patch management process.
- Security testing coverage. This metric assesses the percentage of systems and applications that undergo regular security testing. Comprehensive testing helps identify vulnerabilities before exploitation.
Cybersecurity best practices
To minimize the chance of a cyberattack, it's important to implement and follow a set of best practices that includes the following:
- Keep software up to date. Employees should keep all software, including antivirus software, up to date. This ensures attackers can't take advantage of known vulnerabilities that software companies have already patched.
- Change default usernames and passwords. Malicious actors can easily guess default usernames and passwords on factory preset devices to gain access to a network. To reduce this risk, it's essential to change all default usernames and passwords immediately upon setup.
- Use strong passwords. Employees should select passwords that use a combination of letters, numbers and symbols. Those types of passwords are difficult to hack using a brute-force attack or guessing. Employees should also change their passwords often.
- Use multifactor authentication. MFA requires at least two identity components to gain access. This approach minimizes the chances of a malicious actor gaining access to a device or system.
- Train employees on proper security awareness. Companies should provide security awareness training to help employees understand how seemingly harmless actions can leave systems vulnerable to attack. This should also include training on how to spot suspicious emails to avoid phishing attacks.
- Implement an identity and access management system. IAM defines the roles and access privileges for each user in an organization, as well as the conditions under which they can access certain data.
- Implement an attack surface management system. This process encompasses the continuous discovery, inventory, classification and monitoring of an organization's IT infrastructure. It ensures security covers all potentially exposed IT assets accessible from within an organization.
- Use a firewall. Firewalls restrict unnecessary outbound traffic, which helps prevent access to potentially malicious content.
- Implement a DR process. In the event of a successful cyberattack, a disaster recovery plan helps an organization maintain operations and restore mission-critical data.
- Adopt a zero-trust architecture. Companies should adopt a zero-trust model where trust is never assumed, and verification is continuous. This approach is essential as organizations increasingly rely on cloud services and remote work.
- Incorporate secure-by-design principles. It's important to integrate security into the software development lifecycle from the outset. This proactive approach helps in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities early, fostering a culture of security across the organization.
How is automation used in cybersecurity?
Automation has become an integral component to keeping companies protected from the increasing number and sophistication of cyberthreats. Using AI and machine learning in areas with high-volume data streams can help improve cybersecurity in the following three main categories:
- Threat detection. AI platforms can analyze data and recognize known threats, as well as predict novel threats that use newly discovered attack techniques that bypass traditional security.
- Threat response. AI platforms create and automatically enact security protections. For example, upon detecting a security threat, automated systems can trigger predefined responses, such as isolating compromised endpoints, blocking malicious Internet Protocol addresses or executing scripts to neutralize malware. This minimizes the time between detection and remediation.
- Human augmentation. Security professionals are often overloaded with alerts and repetitive tasks. AI can help eliminate alert fatigue by automatically triaging low-risk alarms and automating big data analysis and other repetitive tasks. This frees IT professionals for more sophisticated tasks.
Other benefits of automation in cybersecurity include attack classification, malware classification, traffic analysis and compliance analysis.
Cybersecurity vendors and tools
Vendors in the cybersecurity field offer a variety of security products and services that fall into the following categories:
- Antimalware and antivirus.
- Cloud access security broker.
- Cloud workload protection platform.
- Data loss prevention.
- Encryption.
- Endpoint detection and response.
- Endpoint protection.
- Firewalls.
- IAM.
- Intrusion prevention systems and detection systems.
- Security information and event management.
- Virtual private networks.
- Vulnerability scanners.
According to Informa TechTarget's research, common cybersecurity vendors include the following:
- Acronis. Provides data protection options, including backup, DR and secure file sharing.
- Check Point Software. Provides unified threat management through advanced firewalls, intrusion prevention systems and secure access options.
- Cisco. Offers a comprehensive suite of security tools, including next-gen firewalls, secure access and threat intelligence platforms.
- Code42 Software. Specializes in data loss prevention with real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities.
- CrowdStrike. Delivers endpoint protection and threat intelligence, using AI and machine learning through its Falcon platform.
- Fortinet. Offers high-performance network security products, including firewalls and SD-WAN security.
- IBM. Provides a range of cybersecurity services, such as identity and access management, threat intelligence and incident response.
- Imperva. Specializes in data and application security, offering options including DDoS protection and web application firewalls.
- KnowBe4. Focuses on security awareness training and simulated phishing attacks to educate employees.
- McAfee. Offers comprehensive endpoint protection, cloud security and threat intelligence options.
- Microsoft. Provides integrated security products across its cloud and on-premises environments, including identity protection and threat detection.
- Palo Alto Networks. Delivers next-gen firewalls and advanced threat prevention capabilities for enterprise environments.
- Rapid7. Specializes in vulnerability management, application security and incident detection and response.
- Sophos. Offers endpoint protection, firewall, and encryption options with a focus on simplicity and automation.
- Splunk. Offers a platform for searching, monitoring and analyzing machine-generated big data via a web-style interface.
- Symantec by Broadcom. Provides endpoint security, cloud security and advanced threat protection options.
- Trend Micro. Offers products for endpoint, server and cloud security, focusing on threat intelligence and advanced malware protection.
- Trustwave. Provides managed security services, including threat detection, compliance and vulnerability management.
- Watchguard. Offers network security products, including firewalls, secure Wi-Fi, and multi-factor authentication.
- Zscaler. Specializes in secure internet access and private application access through its cloud-native platform.
What are the career opportunities in cybersecurity?
As the cyberthreat landscape continues to grow and new threats emerge, organizations need individuals with cybersecurity awareness and hardware and software skills. IT professionals and other computer specialists are needed in the following security roles:
- Chief information security officer. A CISO is the person who implements the security program across the organization and oversees the IT security department's operations.
- Chief security officer. A CSO is the executive responsible for the physical and cybersecurity of a company.
- AI security architects. AI security architects design and implement security frameworks that protect AI systems and the data they process. This role combines cybersecurity expertise with deep knowledge of AI and machine learning technologies.
- Network security architects. Their responsibilities include defining network policies and procedures and configuring network security tools such as antivirus and firewall configurations. Network security architects strengthen network security while maintaining network availability and performance.
- Security architects. Security and cybersecurity architects are responsible for planning, analyzing, designing, testing, maintaining and supporting an enterprise's critical infrastructure.
- Security engineers. These IT professionals protect company assets from threats with a focus on quality control within the IT infrastructure.
- Computer forensics analysts. These analysts investigate computers and digital devices involved in cybercrimes to prevent a cyberattack from happening again. A computer forensics investigation uncovers how a threat actor gained access to a network, identifying security gaps. This position is also in charge of preparing evidence for legal purposes.
- Incident response analysts. These professionals investigate and respond to security incidents, minimizing the effects of data breaches. They also collect digital evidence for potential legal proceedings.
- Security analysts. These IT professionals plan security measures and controls, protect digital files, and conduct internal and external security audits.
- Security software developers. These IT pros develop software and ensure it's secured to help prevent potential attacks.
- Threat hunters. IT professionals who aim to uncover vulnerabilities and attacks. Threat hunters help mitigate vulnerabilities before they compromise a business.
- Penetration testers. These are ethical hackers who test system, network and application, security to find vulnerabilities that malicious actors could exploit.
Other cybersecurity careers include security consultants, data protection officers, cloud security architects, security operations managers and analysts, security investigators, cryptographers and security administrators.
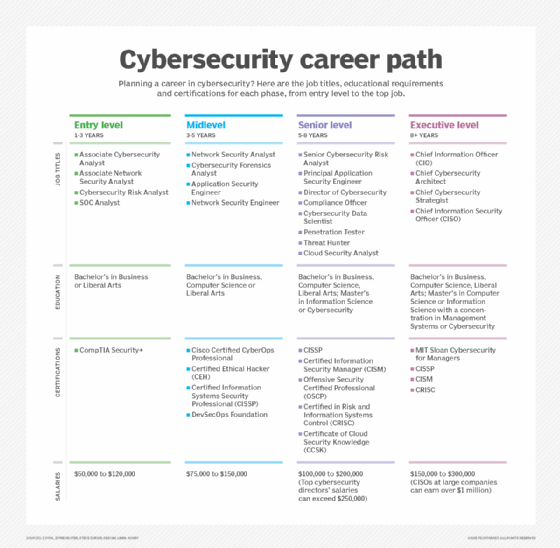
Entry-level cybersecurity positions typically require one to three years of experience and a bachelor's degree in business or liberal arts, as well as certifications, such as CompTIA Security+. Jobs in this area include associate cybersecurity analysts and network security analyst positions, as well as cybersecurity risk and SOC analysts.
Mid-level positions typically require three to five years of experience. These positions typically include security engineers, security analysts and forensics analysts.
Senior-level positions typically require five to eight years of experience. They typically include positions such as senior cybersecurity risk analyst, principal application security engineer, penetration tester, threat hunter and cloud security analyst.
Higher-level positions generally require more than eight years of experience and typically encompass C-level positions.
Advancements in cybersecurity technology
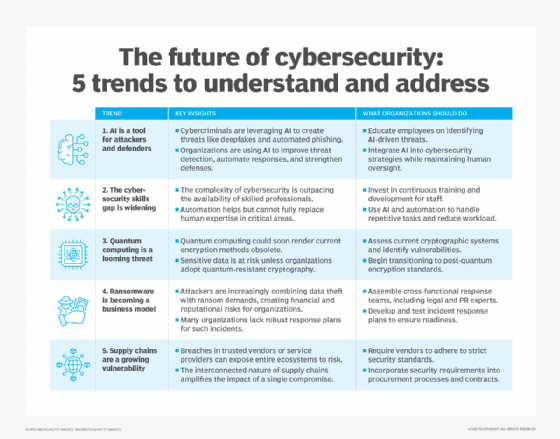
As newer technologies evolve, they can be applied to cybersecurity to advance security practices. Some recent technology trends in cybersecurity include the following:
- Security automation through AI. While AI and machine learning can aid attackers, they can also be used to automate cybersecurity tasks. AI is useful for analyzing large data volumes to identify patterns and for making predictions on potential threats. AI tools can also suggest possible fixes for vulnerabilities and identify patterns of unusual behavior.
- Zero-trust architecture. Zero-trust principles assume that no users or devices should be considered trustworthy without verification. Implementing a zero-trust approach can reduce both the frequency and severity of cybersecurity incidents, along with other zero-trust benefits.
- Behavioral biometrics. This cybersecurity method uses machine learning to analyze user behavior. It can detect patterns in the way users interact with their devices to identify potential threats, such as if someone else has access to their account.
- Improvements in response capabilities. Organizations must be continually prepared to respond to large-scale ransomware attacks, so they can properly respond to a threat without paying any ransom and without losing any critical data.
- Quantum computing. While this technology is still in its infancy and still has a long way to go before it sees use, quantum computing will have a large impact on cybersecurity practices -- introducing new concepts such as quantum cryptography.
- Deception technology. This approach involves creating traps and lures within networks to detect and analyze unauthorized activity. Deception technology provides early warning of potential cyberattacks and alerts organizations of unauthorized activity, enhancing internal threat detection capabilities.
- Machine identity management. The proliferation of generative AI (GenAI), cloud, automation and DevOps has caused an uncontrolled surge in machine identities and credentials. If these machine identities aren't properly managed, secured and monitored, they can create a significant vulnerability. For example, an attacker exploiting just one unmanaged machine identity could gain unauthorized access, move laterally through a network and cause extensive damage. As a result, machine identity management has become a critical priority that organizations can no longer afford to ignore.
- Continuous exposure management. Customer exposure management provides continuous, real-time monitoring and assessment of an organization's security vulnerabilities and exposures. It focuses on identifying and mitigating risks by analyzing attack paths and providing recommendations. This ensures organizations maintain a resilient cybersecurity posture.
As technologies such as AI, zero trust, behavioral analytics and quantum computing mature, cybersecurity practitioners must adopt a mindset of continuous learning and agility. Embracing these innovations will be essential for staying ahead of increasingly sophisticated threats and maintaining a strong and adaptive security posture.
Cybersecurity has many facets that require a keen and consistent eye for successful use. Improve your cybersecurity implementation with these cybersecurity best practices and tips.







