ISO 27002 (International Organization for Standardization 27002)
What is ISO 27002?
The ISO 27002 standard is a collection of information security management guidelines that are intended to help an organization implement, maintain and improve its information security management system (ISMS). The standard is published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
ISO 27002 is designed to work with ISO 27001, which provides the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and improving an ISMS. ISO 27002 provides guidelines, general principles and control mechanisms for implementing, maintaining and improving information security management in an organization.
Any information technology (IT) group using ISO 27001 to build or enhance an ISMS will want to also follow ISO 27002 guidance. All types and sizes of organizations can benefit from basing their ISMS on the two standards. They can help establish an effective IT security risk assessment and risk management process and an ISMS implementation that adapts to the organization's size and specific needs.
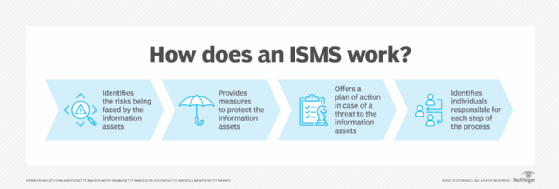
How ISO 27001 and 27002 work together
ISO 27001 and 27002 are intended to be used together and complement one another. ISO 27001 is an acknowledged compliance and audit standard. ISO 27002 supplements ISO 27001, providing information that helps organizations prepare for potential ISO 27001 compliance audits and assessments.
ISO 27002 is used as a reference for implementing the controls required by ISO 27001. ISO 27001 doesn't provide detailed guidelines on how to implement the controls but relies on the information provided by ISO 27002 as a source of information security best practices. ISO 27002 provides guidance on the selection, implementation and management of controls required to achieve the objectives of ISO 27001.
Together, the two standards provide a comprehensive starting point for an organization to establish risk-awareness and identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. Using them to implement an ISMS can help organizations improve their security risk management capabilities, cybersecurity and resilience. It also establishes a security management process that's globally recognized and accepted.
Benefits of ISO 27002
The benefits of using ISO 27002 along with ISO 27001 include the following:
- Reducing vulnerability to cyber attacks.
- Adapting to evolving security risks.
- Developing a centrally managed framework for security management.
- Increasing security awareness among employees.
- Ensuring critical information is protected from cyber attacks.
History of ISO 27002
ISO 27002 was originally named ISO/IEC 17799 when it was first released in 2000. It was updated in 2005 as ISO 17799, when it was accompanied by the newly published ISO 27001.
The two standards are updated regularly to incorporate references to other ISO/IEC-issued security standards in new versions of the ISO/IEC 27000 series. Each update adds information security guidance and best practices that emerged since previous versions were published. They include the selection, implementation and management of information security controls based on an organization's unique information security risk environment. Controls focus on areas such as information security policies, human resources security, asset management, access control, cryptography, communications security, information systems acquisition, development and maintenance, supplier relationships, information security incident management and business continuity management.
The 2022 version was released in December 2022, and builds on previous editions of the standards, specifically the 2013 version. ISO/IEC 27002:2022 decreased the number of controls addressed to 93 from 114 in the ISO/IEC 27002:2013.
What's included in 2022 version of ISO 27002
Controls in the 2022 version of the ISO 27002 standard are organized into four categories:
- Controls that affect people.
- Controls that affect physical objects, such as computing devices and buildings.
- Controls that affect technology.
- Controls that are linked with activities associated with organizations.
Controls in each category have five attributes assigned to them that fine-tune how the controls are applied to specific requirements. Attributes provide maximum flexibility when users apply them to specific information security activities. They include the following:
- Control type. These attributes specify the circumstances under which a control is to be used to prevent an attack, identify the nature of an attack or correct things once an issue occurs.
- Information security properties. These attributes are designed to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information.
- Cybersecurity concepts. These attributes address actions an information security system must perform when responding to a cyber attack, such as identify, protect, detect, respond and recover from an event.
- Operational capabilities. These are attributes that reflect the processes security practitioners use. Examples include governance, asset management, physical security, identity and access management, continuity, legal and compliance, and security information and event management.
- Security domains. These controls focus on information security domains, including governance and ecosystem, protection, defense and resilience.
Each control is structured according to the following configuration:
- Control title. Name of the control.
- Attribute table. Values of each attribute as applicable to the specific control.
- Control. Definition of the control.
- Purpose. Rationale for using the specific control.
- Guidance. Implementation steps for the control.
- Other information. Details of the control and references to other documents.
The following table lists the four categories of controls, with examples of in each category.
| Control category | Control name |
| Organizational | Information security policies |
| Management responsibilities | |
| Access control | |
| Identity management | |
| Information security during a disruption | |
| People | Employee screening |
| Information security awareness, education and training | |
| Confidentiality of nondisclosure agreements | |
| Remote working | |
| Event reporting | |
| Physical | Physical security perimeters |
| Working in secure areas | |
| Clear desk and clear display screen | |
| Storage media | |
| Equipment maintenance | |
| Technological | Information access restrictions |
| Protection against malware | |
| Configuration management | |
| Network security | |
| Change management |
Source: ISO 27002:2022
Additional ISO 27000 series standards
The ISO 27000 family of standards includes dozens of information security standards. These are the eight standards following ISO 27002:
- ISO/IEC 27003. How to plan and implement an ISMS.
- ISO/IEC 27004. How to monitor and measure security and ISMS performance.
- ISO/IEC 27005. How to implement information security risk management processes.
- ISO/IEC 27006. Guidance for organizations providing audits and certification of an ISMS.
- ISO/IEC 27007. How to conduct an ISMS audit.
- ISO/IEC 27008. How to review the implementation and operation of security controls.
- ISO/IEC 27009. How to tailor the requirements of ISO 27001 to specific sectors, such as markets and technologies.
- ISO/IEC 27010. Implementation guidance on information security management techniques as applied to multiple information-sharing groups in the same or different sectors.
Learn what you need to know about 10 common information security threats.




