Human error is the front-runner and large cause of data breaches and failed recovery after a breach. The chances of an IT team discovering a breach before it does harm are low, without the proper tools in place, meaning organizations have a responsibility to protect their business at every level of access.
Zero trust is gaining tremendous momentum as a best practice in cyber resiliency. In the U.S., the Office of Management and Budget recently released a federal zero trust strategy to push federal agencies’ networks and systems to a zero trust architecture.1
Overall, the market for zero trust security solutions is growing at a compound annual rate of 15.2%, which is being fueled, in part, by changes in the digital workplace and the growth of remote work, according to Grand View Research.2
On the surface, zero trust seems like a simple cybersecurity concept: Never trust, always verify. But deploying a zero trust architecture requires end-to-end visibility, automation, orchestration and other key elements.
In this article, we explore the basic pillars of a zero trust implementation and how solutions from Dell Technologies and VMware can simplify and accelerate the zero trust journey for IT decision-makers.
Why Zero Trust, and Why Now?
As defined by TechTarget, a zero trust architecture means that no user, even if allowed onto the network, should be trusted by default because that user could be compromised. Identity and device authentication are required throughout the network instead of just at the perimeter.
A zero trust model “provides strong protection against the types of attacks that plague businesses today, including theft of corporate assets and identities,” TechTarget says, adding that adopting a zero trust architecture enables organizations to:
- Protect company data
- Boost the ability to do compliance auditing
- Lower breach risk and detection time
- Improve visibility into network traffic
- Increase control in a cloud environment
Deploying Zero Trust
For most business and IT leaders, the question is not whether to move toward a zero trust architecture but how to do so cost efficiently and with minimal disruption to existing operations.
The first step is to understand the basic framework of a zero trust architecture. As shown in the figure below, a zero trust architecture is comprised of five pillars:
- Device trust
- User trust
- Transport/session trust
- Application trust
- Data trust
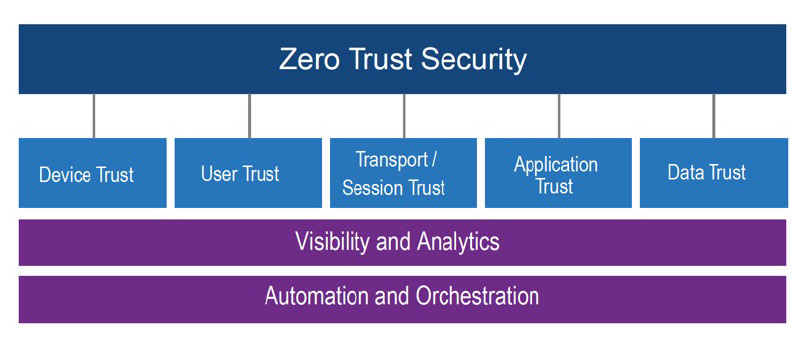
To deploy zero trust successfully, trust has to be established across each of these pillars, following the mantra that everything has to be verified—user, device, application, data and transport session—before it can gain access to the network, to other users, to applications, to data or to the cloud.
Once trust is established across all of the pillars, IT and security teams can expand visibility and apply analytics end to end to deliver enhanced security benefits and greater control over access, applications and sensitive data. In addition, because zero trust leverages high levels of automation and orchestration, the user experience is simpler and uncompromised.
User experience is an important factor because zero trust can and should be used to support remote work, work from home and the ongoing evolution of the digital workplace. Users can be onboarded faster, more securely and at greater scale. In addition, zero trust can be a critical element as organizations move toward an intrinsic security model.
Leveraging a Zero Trust Portfolio
One of the benefits of zero trust is that it can be rolled out strategically and in specific areas of the business without disrupting the entire organization. To accomplish this type of deployment, IT and cybersecurity teams are best served by leveraging a portfolio of solutions that addresses all five pillars of zero trust and delivers automation, orchestration, visibility and analytics across trusted infrastructure, to and from any device, any application and any cloud.
When it comes to a zero trust portfolio, Dell Technologies and VMware together offer the broadest set of solutions, enabling simple, cost-effective and comprehensive end-to-end zero trust deployments. Zero trust building blocks include:
- VMware Workspace ONE, which provides trust at the device, user, application and data layers.
- VMware Unified Access Gateway for devices and transport.
- VMware NSX-T Data Center for transport and data.
- Dell BIOS, SafeID for user and device identity.
- Dell PowerProtect Portfolio for applications and data.
- VMware Carbon Black for endpoint devices.
- VMware Horizon 7 for transport, applications and data for virtual desktops.
Taking the Next Step
Zero trust has become an imperative of the digital workplace. According to Enterprise Strategy Group:
In today’s dynamic environment, when users, applications and resources could be in corporate offices, at home, in public clouds or anywhere in between, zero trust has become not just an intriguing approach, but a required model to secure the modern enterprise.3
To implement zero trust, it is important to work with vendors you trust to deliver trusted solutions across all of the pillars of a zero trust architecture. To learn more about the Dell Technologies-VMware path to zero trust, take the Cyber Resiliency Assessment and see where your company is vulnerable and what you should be doing to take the next step.
1 “Office of Management and Budget Releases Draft Federal Strategy for Moving the U.S. Government Towards a Zero Trust Architecture,” White House press release, Sept. 07, 2021
2 “Zero Trust Security Market Size Worth $59.43 Billion by 2028, CAGR: 15.2%: Grand View Research,” Bloomberg, July 14, 2021
3 “ESG Research Report: The State of Zero-Trust Security Strategies,” Enterprise Strategy Group, April 13, 2021

