What is SAP Sales and Distribution (SAP SD)?
SAP Sales and Distribution (SAP SD) is an SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) core functional module that helps organizations store and manage customer- and product-related data. Organizations use this data to manage all ordering, shipping, billing and invoicing of their goods and services.
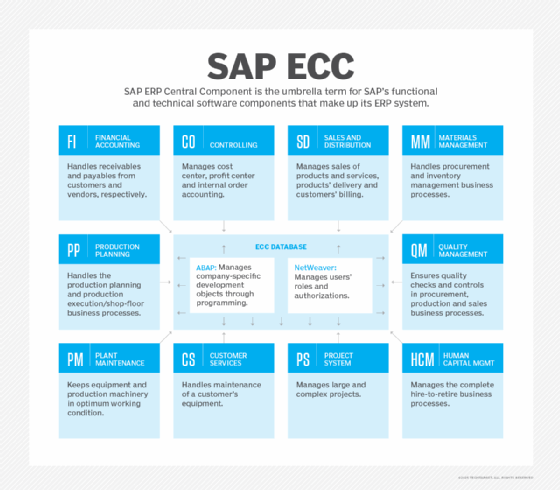
SAP SD supports the management of many sales- and distribution-related processes and activities, including the following:
- Material sorting.
- Credit and risk management.
- Sales orders.
- Back-order processing.
- Billing.
- Payment card processing.
- Shipping and transportation.
- Customer service processing.
SAP SD's modules and capabilities facilitate seamless integration of different business departments likes sales and finance, ensuring a smooth flow of information and better coordination. This can have a positive impact on the organization's sales and revenues.
SAP SD also includes numerous information and analysis tools that can yield better visibility into the current business situation and guide next steps to resolve supply chain management issues, including how to optimize sales, distribution, inventory levels, billing and customer satisfaction.
Key modules in SAP SD
Several SAP SD modules are configured to handle specific sales and distribution lifecycle functions. The main modules are as follows:
- SD-BF. Basic functions and master data in SD processing represent the company structure in the system and address pricing, availability check, material determination, text processing, tax determination and account determination.
- SD-BF-AS. This module addresses material sorting and accommodates printing material items in a document in the user-defined sequence and displaying customer-specific material items on a print form.
- SD-SLS. The sales module executes transactions based on four kinds of sales documents:
-
- Customer inquiries and quotations.
- Sales orders.
- Outline agreements.
- Complaints.
- SD-BF-PR. The pricing and conditions module helps organizations calculate prices for external use and costs for internal use. They can also configure the user interface of pricing data for certain business documents, including SD documents, materials management (MM) documents and global trade management documents.
- SD-BF-CM. The credit and risk management module supports specifying credit limits for customers to minimize the company's credit risk and improve credit-related decision-making.
- SD-BIL-IV. The payment card processing module lets companies handle payment cards in different business environments and functions in sales, point of sale, financial accounting and e-commerce.
- SD-BF-OC. This module is used for output determination. Sales transactions can be managed by linking sales activity output directly to the transaction as soon as a sales order is created.
- SD-EDI. With this module, users can receive inbound messages like sales orders and send outbound messages like order confirmation through Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). They can convert the information into intermediate documents and store IDocs in the system for easy retrieval.
- SD-SLS-OA. This customer service processing module accommodates planning and managing different customer service scenarios, including warranties, service notifications, repair orders and service orders.
- SD-BIL. The billing module is used to create invoices, issue credit or debit memos, cancel billing transactions, issue rebates and transfer billing data to Financial Accounting.
- LE-SHP. Improve and automate the shipping process with this module, which is used for analyzing business agreements with customers, recording material requests and including shipping conditions in sales orders.
Benefits of SAP SD
SAP SD automates many manual and labor-intensive sales and distribution activities such as creating sales orders, invoicing and delivery. Automation reduces errors and streamlines many parts of sales and distribution operations.
The automations, data processing and data analysis capabilities of SAP SD also enable faster order processing and more timely deliveries. This boosts cash flow, revenues and profitability.
SAP SD also integrates master data about customers, products, services and business partners. Better outcomes accrue from giving sales and other teams more comprehensive, timely information. With it, they can optimize transactions and customer interactions.
SAP SD also reduces an organization's credit risk. Teams can take a customer's financial pulse and identify early warning signs that doing business with a particular customer is risky. A company can use this information to make better credit-related decisions.
SAP provides FT, an application that can be integrated with SAP SD to simplify foreign trade and customs activities, including orders, delivery, goods issue and billing documentation. Users can manage import and export processes, identify licensing requirements for current regulations, create and submit declarations, send or receive data via EDI systems, and change data (if needed) in foreign trade documents before issuing the final goods.
The importance of master data is SAP SD
As with all the modules in SAP ECC, everything in SAP SD revolves around master data stored in the system. Storing the master data is required for SAP SD transactions and processing and it must be stored in a specific structure to allow various departments to access it. To facilitate sales processing, data about the company's products, services and business partners must be available in SAP SD.
In SAP SD, all business transactions are stored as documents with a specific structure based on certain criteria. This ensures all important information is stored systematically.
Integration with other SAP modules
SAP SD can deliver a streamlined order-to-cash cycle because it integrates with these other SAP modules:
- MM for materials management.
- PP for production planning.
- FICO for finance and controlling.
SD handles all the details in the sales and distribution part of the cycle. In a typical cycle, SD generates a sales quote, the customer places a sales order, the goods are picked from a warehouse or production facility and shipped to the customer, an invoice is sent with the order, and accounts receivable settles the payment with the customer. Each step generates transactions in the SD module, which then generate further transactions in the other ECC modules. For example, when a sales order is generated in SD, it establishes a link for a product availability check to MM, a credit check to FICO or a tax calculation to FICO.
SAP SD also integrates with SAP JAM, a secure enterprise social collaboration tool intended to help drive business process actions and decisions. Because of the integration, many data objects from SAP SD can be viewed in SAP JAM, including sales orders, invoices, quotations, and information related to customers and outbound delivery.
See how to think long term about SAP ECC customizations and check out steps for creating an analytics strategy on SAP ECC. Explore ERP use cases to consider before buying an ERP system and learn why ERP data quality is important. Read about critical ERP trends for today and beyond.






