What are port numbers and how do they work?
A port number is a way to identify a specific process to which an internet or other network message is to be forwarded when it arrives at a server. All network-connected devices have standardized ports with assigned numbers. These numbers are reserved for certain protocols and their associated functions. HTTP messages, for example, go to port 80 -- one of the most commonly used ports.
Developers of the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, or ARPANET, an informal cooperation of system administrators and software authors, proposed the concept of port numbers. Once known as socket numbers, the early incarnation of port numbers was similar to the Internet Protocol (IP) address class used today.
What is the difference between an IP address and a port number?
An IP address identifies a machine in an IP network and is used to determine the destination of a data packet. Port numbers identify a particular application or service on a system. As an analogy, if each computer were a building and the internet were a city, then the IP address would be the building's street address, and the port number would be the apartment number.
An IP address is a logical address used to identify a device on the network. Any device connected to the internet or network is assigned a unique IP address for identification. This identifying information enables devices to communicate over the internet.
Port numbers are part of the addressing information that helps identify senders and receivers of information and a particular application on the devices. Port numbers consist of 16-bit numbers, from 1 to 65,535.
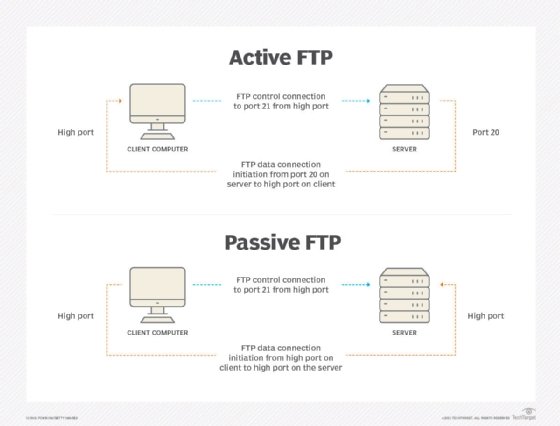
For example, a user request for a file transfer from a client, or localhost, to a remote server on the internet uses File Transfer Protocol (FTP) for the transaction. Both devices must be configured to transfer files using FTP. To transfer the file, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) software layer in localhost identifies the port number of 21, which by convention associates with an FTP request, in the 16-bit port number integer that is appended to the request. At the server, the TCP layer will read port 21 and forward the request to the server's FTP program.
What are the different types of port numbers and their uses?
While there are 65,535 port numbers, not all are used every day. Restricted port numbers or well-known port numbers are reserved by prominent companies or uses, and range from 0 to 1023. Apple QuickTime, Structured Query Language services and Gopher document exchange services use some of these restricted ports.
Vendors and others that want to register a specific port number can choose from 1024 to 49151. Software companies typically register these port numbers for their specific protocol. Dynamic, ephemeral or private ports ranging from 49152 to 65535 are available for any program to use.
In other scenarios, a port number can be assigned temporarily -- for the duration of the request and its completion -- from a range of assigned port numbers. This is called a temporary port number.
Some commonly used ports and their associated networking protocols include the following:
- Ports 20 and 21. FTP and Secure FTP are used to transfer files between a client and a server.
- Port 22. Secure Shell is one of several tunneling protocols used to build secure network connections.
- Port 25. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is commonly used for email.
- Port 53. Domain Name System (DNS) is a critical process that matches human-readable domain names to machine-readable IP addresses on the internet. It helps users load websites and applications without having to type in a long list of IP addresses.
- Port 80. HTTP is the protocol that enables the World Wide Web.
- Port 123. Network Time Protocol helps computer clocks sync with each other. It's a vital process in encryption.
- Port 179. Border Gateway Protocol helps establish efficient routes between the large networks or autonomous systems that make up the internet. These large networks use BGP to broadcast which IP addresses they control.
- Port 443. HTTPS is like HTTP, but enhanced with security features. All HTTPS web traffic goes straight to port 443. Any network service that uses HTTPS for encryption, such as DNS over HTTPS, also connects directly to this port.
- Port 500. Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol, or ISAKMP, helps set up IPsec to help ensure data transmissions are secure.
- Port 3389. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) enables users to connect to their desktop computers from another device remotely.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, or IANA, allocates and maintains all the port numbers listed above.
What are open ports and port scanning?
An open port is a port number that is active and ready to receive requests. When a program wants to receive communication over a network, it registers with the system network process to open a port number. When the system receives any network traffic for that port number, the system will forward it to the program to handle.
Port scanning is the process of checking every port number of an IP address or range to see if it responds. These are often targeted at single ports on a large number of IP addresses or at a single IP address over every port. Port scanning is a common way for attackers to identify potential targets to try to exploit.
How do firewalls protect ports?
A firewall sits between two networks and decides what traffic can go between them. Firewalls can be hardware devices that physically connect the two networks, or they can be software that runs on a computer. Most firewalls primarily use IP address and port number information to allow or disallow traffic.
Firewall rules enable administrators to make resources available while stopping attackers from accessing the wrong things. Imagine you had a Windows server offering up a webpage to the internet. The firewall would be set to allow all connections to port 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) from any IP address inbound while blocking all other ports. If someone needed to establish a remote desktop connection into the server, the firewall would block access. So, the administrator would have to add a rule that opens port 3389 (RDP) for access from only one particular IP address.
Some common questions asked about port numbers
Below are some common questions and the relevant answers about port numbers.
What is the port number for localhost?
Localhost is the default name used to establish a connection with a computer. The IP address is usually 127.0.0.1. This is done by using a loopback address network. Port 80 is the common standard port for HTTP.
What is port number 8080 used for?
Port 8080 is usually used for web servers. When a port number is added to the end of the domain name, it drives traffic to the web server. However, users cannot reserve port 8080 for secondary web servers.
What is port number 3360 used for?
TCP/IP networks use port 3360. The connection-oriented protocol TCP demands handshaking to set up end-to-end communications. Upon establishing the connection, user data is transferred bidirectionally over the connection.
What is my IP address and port number?
The easiest way to find a router's public IP address is to search "what is my IP?" on a search engine like Google. Identifying a port number will depend on the operating system. The port number will change depending on what programs are running.
For Windows:
- Go to the command prompt.
- Type ipconfig.
- Type netstat to populate a list of all the port numbers that the computer is currently connected to or from.
For macOS:
- Go to System Preferences.
- Select Network > Advanced.
- Click on the Port Scan tab and enter the user's IP address.
What is a proxy server address and port number?
Essentially, a proxy server is a computer that sits between a client device and the remote server. It acts as an intermediary to handle communication requests over the internet.
Using a proxy, when the local computer sends a web request, it will automatically go through the proxy server. The proxy server uses its own IP address for the web request and not the user's IP address. Proxy servers offer privacy benefits, such as the ability to change the client IP address to mask the user's location.
The proxy server address includes an IP address with the port number attached to the end of the address. The port number 8080 is usually used for web servers, proxy and caching.
What is the port number for Gmail?
Gmail uses both Internet Message Access Protocol and SMTP. The IMAP port is 993, and the SMTP port is 25.
Learn about common network protocols and their functions. Also, without proper protections, keeping port 139 open can present a major security risk. See how to protect port 139 from Server Message Block attacks.





