What is multi-user MIMO?
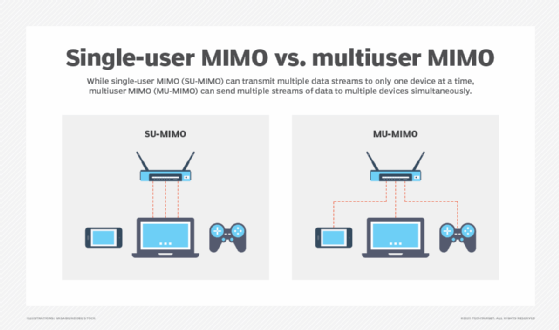
Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) is a wireless communication technology that uses multiple antennas to improve communication by creating multiple connections to the same device simultaneously. MIMO is an acronym that stands for multiple input, multiple output.
MU-MIMO is common in routers and works with mobile devices, such as smartphones and laptops. The technology supports environments where multiple users access the same wireless network at once.
Typically, when many users connect to the same router, congestion builds up. The router services the first device's requests, while the other devices wait. The waiting time for each device generally isn't long, but it builds up with enough devices. MU-MIMO helps relieve this potential congestion by creating multiple device connections, increasing network efficiency.
MU-MIMO takes advantage of multipath, which is when a radio signal reflects and bounces around surrounding objects so it's picked up by a receiver in a user's device at slightly different times and angles. MU-MIMO typically has multiple antennas at the signal's transmit end and one antenna at the receiving end.
MU-MIMO devices separate bandwidth into individual streams that share an equal connection. These streams typically divide as 2x2, 3x3, 4x4 or 8x8, which refers to the number of streams. The data streams directly to one device, meaning an MU-MIMO router only sends and receives data from one device at a time.
Network pros use algorithms to enable fair access to multiple devices to an access point (AP). Initially, only routers supported MU-MIMO, but as time went on, other endpoint devices caught up.
Types of MU-MIMO
Each type of MU-MIMO has its own use case. The following are some examples of MU-MIMO:
- MIMO multiple-access channels. Network pros use MIMO MAC in uplink scenarios. In MIMO MAC, the receiver performs most of the processing and requires large uplink capacity levels.
- MIMO broadcast channels. MIMO broadcast channels enable more throughput.
- Cross-layer MIMO. Cross-layer MIMO improves MIMO link performance by fixing problems when employing MIMO configurations.
- Dirty paper coding. Dirty paper coding is a technique that enables data to move through channels with interference more efficiently.
- Cooperative MIMO. Cooperative MIMO uses distributed antennas belonging to other users instead of a logical terminal.
Benefits of MU-MIMO
MU-MIMO benefits from its construction and operations in the following ways:
- Uses beamforming to direct signals toward a wireless device.
- Decreases the time each device waits for signals.
- Increases the user's router capacity and efficiency.
- Maintains performance, despite antenna correlation and channel rank loss.
- Centralizes processing with APs.
- Eliminates the need for multiple antennas on user devices.
- Improves performance on devices connected to an MU-MIMO network by reducing wait times.
- Improves video playback streams and eliminates some buffering or lower video quality.







