metropolitan area network (MAN)
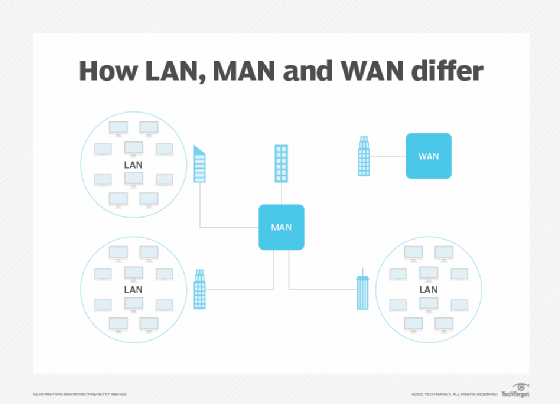
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a computer network that is larger than a single building local area network (LAN) but is located in a single geographic area that is smaller than a wide area network (WAN). Generally, it is several LANs interconnected by dedicated backbone connections. It may also refer to public use networking infrastructure in a municipality or region.
Metropolitan area networks for organizations
A metropolitan area network traditionally refers to a private data network used by a single organization in several buildings or by several organizations interconnected in the same geographic vicinity. It is larger than a LAN in a single building but not large enough to be considered a WAN. The size usually ranges from 5 kilometers to 50 km. If all the buildings are on a single piece of contiguous property, it may also be considered a campus network.
Generally, a MAN is small enough that dedicated point-to-point, or backbone, data connections are established between buildings or to a hosted colocation (colo) data center. These backbone connections can use a variety of link technologies, including Ethernet runs, leased Dark fiber or private fiber, point-to-point Wi-Fi, wireless LAN (WLAN), millimeter wave (MM wave) radio and microwave radio links or private 5G networks. Public internet routed links, such as through a virtual private network (VPN) or public cloud, would not be considered part of a MAN but may be included in a MAN diagram for simplicity. A well-designed system will have redundant links between locations.
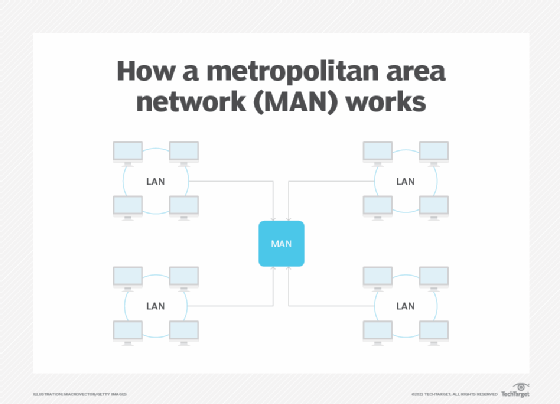
A MAN may use a local exchange carrier (LEC) to provide the connections between LANs and may connect to an internet exchange point for high-speed communication between the MAN and the public internet. It may also connect to other vendors at a peer exchange or to cloud vendors, such as with Amazon Web Services (AWS) Direct Connect.
Metropolitan area network advantages and disadvantages
The primary advantage of a MAN over a WAN is the high bandwidth enabled by the dedicated links of a metropolitan area network. This application of a MAN provides higher speed, from 1 gigabit per second to 100 Gbps, and lower latency than would be possible over a WAN. Since the organization maintains control of the connection, it can apply traffic shaping and increased security.
Disadvantages of a MAN over a WAN include potentially higher costs, greater complexity and additional logistics required to maintain the links. A well-designed MAN will also have redundant connections, requiring at least two connections per building.
Metropolitan area network extended use
Since a metropolitan area network only refers to relative size, it may also be used to describe a public or private network that attempts to provide connectivity that covers an entire metropolitan area. In this sense, a MAN can be closely related to smart city concepts in several different ways:
- A MAN may be a large number of privately owned or telecommunication provider interconnects between organizations.
- A MAN may be a public or free Wi-Fi system provided to residents of a city.
- A MAN may be a network used by a municipality or company to interconnect its public works systems and internet of things (IoT) devices.
As technology continues to advance and more devices become interconnected, the use of metropolitan area networks will continue to increase. Some also use MAN to refer to the high-speed internet connectivity across a city provided by 5G cellular technology, while a potential future use for a MAN would be a citywide network of autonomous vehicles sharing location, traffic and destination data.
Examples of a metropolitan area network
Cisco Systems owns several buildings located in three different areas of San Jose, Calif. The company connected these sites by trenching its own fiber and leasing dark fiber from another company to form a single metropolitan area network.
CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, owns several buildings on a single piece of land in Geneva and connects them together with optical fiber into a campus area network or MAN.
New York City provides free Wi-Fi access to all residents as a large single MAN. It also connects traffic lights and parking meters wirelessly as a metropolitan area network.

A telecommunications provider in London leases fiber connections. Many companies use these to interconnect, forming a large MAN.
National Smart Cities Mission is a program by the Indian government that seeks to simplify communication among the government, citizens and public resources. The mission, which initially included 100 cities and is set for completion in 2023, requires the use of a MAN.







