What are managed network services?
Managed network services are networking applications, functions and services that a managed service provider (MSP) remotely operates, monitors and maintains for an enterprise.
Managed network services range from basic network access and transport services to newer software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) connections and virtual network services. A variety of managed services are available, such as the following.
- Local area network (LAN) and WAN optimization.
- Unified messaging.
- Network administration, monitoring, management, security and troubleshooting.
- Network maintenance and installation, such as cable management.
- Managed security firewalls.
- Virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Identity and access control.
The role of MSPs
MSPs primarily host managed enterprise network services in their data centers and facilities, where they host virtual network functions. MSPs range from small, niche service providers to large, traditional national and global telecommunications providers.
MSPs offer managed network services with service-level agreements (SLAs) for customers. SLAs are contractual arrangements that explain the performance and quality metrics the managed service provides. SLA factors include the following:
- Quality of service.
- Reliability.
- Availability.
- Scope of services.
- Customer responsibilities.
Benefits of managed network services
Small and medium-sized businesses often contract with MSPs because they have limited in-house IT capabilities and staff. Managed network services offer organizations IT and networking expertise without hiring more staff. As a result, a company's existing IT staff can focus on other tasks. This increases operational efficiency because MSPs can monitor services and troubleshoot when necessary.
Managed network services are also a viable option for companies interested in trying out new technologies but question the associated risks and complexity. MSPs can handle enterprise networking issues such as the following:
- Integration.
- Troubleshooting.
- Technical support.
- Policy setting.
Because MSPs take a proactive network management approach, they can ensure IT problems don't disrupt business operations. MSPs also offer cost savings for larger organizations, such as government agencies. They contract with MSPs when they face budget pressure and hiring limitations to supplement in-house IT staff.
Challenges of managed network services
Many businesses consider it risky to outsource network and service management to an MSP. It's important for customers to clearly define their expectations and requirements in SLAs to mitigate risk. Companies should monitor MSP performance and make sure it's consistent with the terms of their contract.
Customer support also presents a challenge with managed network services. Depending on MSP response times, enterprises might face longer wait times for technical issues.
Managed network services pricing models
Enterprises usually sign an annual or multi-year contract with an MSP for managed network services. Pricing models for managed network services can be complex, with tiered or a-la-carte options. Pricing formulas are based on the type of service, speed, interfaces, geographies, number of sites and level of managed support offered.
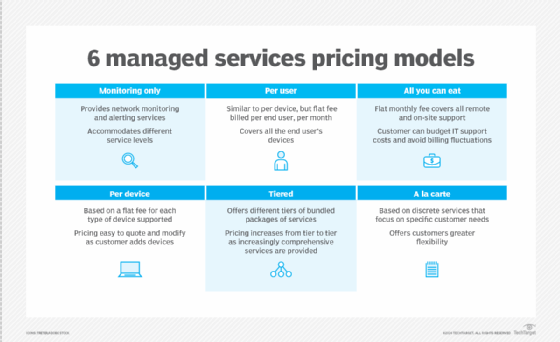
Common pricing models for managed network services include the following:
- Monitoring only.
- Per device.
- Per user.
- A la carte.
- Tiered.
- All-you-can-eat.
Once customers have established the specifics of a service, they can budget fixed monthly expenses. Managed services enable enterprises to move these costs out of their Capex budgets -- used to maintain and buy new equipment -- and into their Opex budgets.
Managed network services provide MSPs with a predictable monthly revenue stream from customers. A fixed recurring revenue has attracted many traditional service providers to add managed services to their operations.
History of managed network services
Network providers have offered managed services for decades. Centrex, a managed private branch exchange service, is an early example of a managed service developed in the 1960s. Centrex provided remote enterprise telephony services using communications equipment and software owned by the telephone company located on switches in its central offices, not on the customers' premises.
Managed services continued to change as networks evolved. When the Bell System monopoly broke up in 1984, seven individual Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs) emerged to offer local telephone services. Some business customers wanted the ability to contract with one provider rather than negotiate services with individual RBOCs, leading to more growth in managed connectivity services.
The Telecommunications Act of 1996 led to the rise of competitive local exchange carriers that offered communications services in addition to the RBOCs. Customers then had a wider range of providers to choose from. The primary MSP handled its customers' connections with other service providers to simplify the management of multiple different service provider connections.
In the 1990s, application service providers (ASPs) emerged to offer remote application hosting services. ASPs paved the way for service providers to offer remote IT infrastructure support. These companies are also called MSPs or IT service providers, although their service model differs from managed network services.
The 2010s and 2020s saw the emergence of software-based networking technologies. These include SD-WAN, cloud computing, IoT capabilities and artificial intelligence, or AI. As a result of the demand for these capabilities, MSPs began to offer services to manage newer cross-provider virtual network services.
An evolution of managed network services is network as a service (NaaS). With NaaS, service providers offer network services -- including hardware, software, management and licensing -- on a subscription basis. Common examples of NaaS include SD-WAN and secure access service edge.







