network hub
What is a network hub?
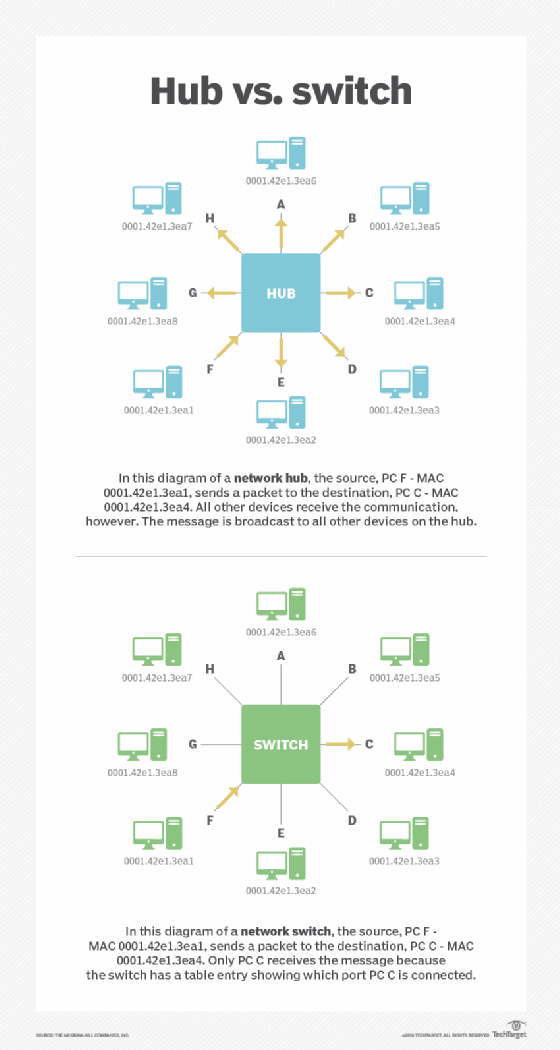
A network hub is a node that broadcasts data to every computer or Ethernet-based device connected to it. A hub is less sophisticated than a switch, the latter of which can isolate data transmissions to specific devices.
Network hubs are best suited for small, simple local area network environments. Hubs can't provide routing capabilities or other advanced network services. Because they operate by forwarding Ethernet frames across all ports indiscriminately, network hubs are sometimes referred to as dumb switches.
With limited capabilities and poor scalability, network hubs had primarily one competitive advantage over switches: lower prices. As switch prices fell in the early to mid-2000s, hubs began getting phased out of use. Network hubs are far less common today, but they have some niche uses and continue to offer a simple means of networking.
How network hubs work
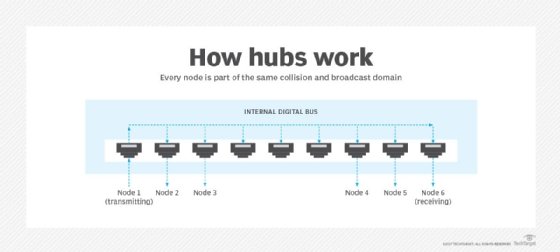
Network hubs are categorized as Layer 1 devices in the Open Systems Interconnection model. They connect multiple computers together and transmit data received at one port to all its other ports without restriction.
Hubs operate in a half-duplex model. The half-duplex model raises security and privacy concerns because it can't safeguard or quarantine traffic. It also presents a practical issue in terms of traffic management: Devices on a hub function as a network segment and share a collision domain.
When two devices connected to a network hub transmit data simultaneously, the packets collide, which causes network performance problems. Switches or routers can mitigate this issue, as each port represents a separate collision domain.
All devices connected to a network hub equally share all available bandwidth. This differs from a switch environment, where each port receives a dedicated amount of bandwidth.
Types of network hubs
Two types of network hubs are the following:
- Active hubs. Active hubs repeat and strengthen incoming transmissions. They are also sometimes known as repeaters.
- Passive hubs. Passive hubs serve as a point of connectivity without any additional capabilities.
A third designation, intelligent hubs, is synonymous with a switch.
An unrelated use of the word hub involves network topologies. In a star topology, sometimes called hub and spoke, each host connects to a central hub. The hosts, however, don't directly connect to each other. In this context, the hub is typically a switch.